* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download QL - uOttawa
Neuroblastoma wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
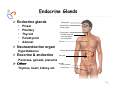
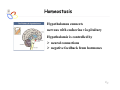
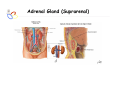
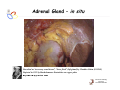
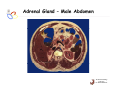
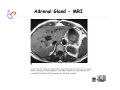
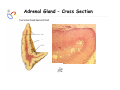
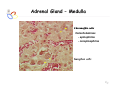
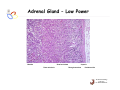
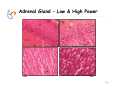
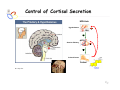
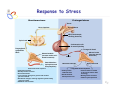
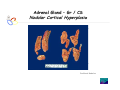
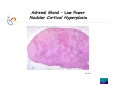
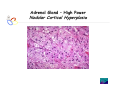
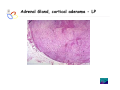
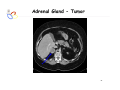
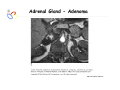
Endocrine Diseases Th P The Pathological th l i l Basis B i of f Disease Di - Graduate Course CMM5001 Qiao Li, Li MD, MD PhD Faculty of Medicine University of Ottawa Qi Li@ [email protected] QL Outline Endocrine System Adrenal Gland • • • • • Anatomy & Histology Steroid Hormones Addison’s Disease Cushingg Syndrome y Clinical Case Presentation QL Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands • • • • • Pineal Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands (on dorsal aspect of thyroid gland) Thymus Neuroendocrine organ Hypothalamus Exocrine & endocrine Adrenal glands Pancreas Pancreas, gonads, placenta Other Thymus, heart, kidney etc. Gonads • Ovary (female) • Testis (male) QL Endocrine Function Controls & Integrates Growth G th and d development d l t Maintenance of electrolyte, water & nutrient balance of blood Regulation of cellular metabolism & energy balance Mobilization of body defenses Reproduction QL Homeostasis Hypothalamus connects nervous with i h endocrine d i via i pituitary i i Hypothalamic is controlled by neural connections negative feedback from hormones QL The Summary Hypothalamic Hormone Anterior Pituitary Hormone Target Organ Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH) Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Thyroid Gland Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH) Adrenocorticoidtropic Hormone (ACTH) Adrenal Glands Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone o o e (G (GnRH)) Folicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Lutenizing ute g Hormone o o e (LH) ( ) Ovaries O a es / Testes estes Prolactin-Inhibiting Hormone (PIH, Dopamine) Prolactin (PRL) Breast Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH) GHIH (Somatostatin) Growth Hormone (GH, Somatotropin) Liver Hypothalamus Hypothalamic neurons synthesize GHRH, GHIH, TRH, CRH, GnRH, PIH Anterior lobe of pituitary Superior hypophyseal artery Hypophyseal portal system • Primary capillary plexus • Hypophyseal portal veins • Secondary capillary plexus GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, PRL Anterior lobe of pituitary QL Homeostatic Imbalance Increases risk of disease Causes changes associated with aging control systems less efficient most disease seen as a disturbance of homeostasis (homeostatic imbalance) aging associated with progressive decrease in our ability to maintain homeostasis (greater risk for illness) QL Adrenal Gland • • • • • Anatomy & Histology Steroid Hormones Addison’s Disease Cushing Syndrome Clinical Case Presentations QL Characteristics Origin all ll glands l d arise i from f the th epithelium ith li (all ( ll three th germ layers) l ) Microscopic Structure cords, d clumps, l h ll follicles hollow f lli l & abundant b d t capillaries ill i Merocrine Secretion QL Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal) Adrenal Gland – in situ Described as “accessory renal tissue”, “loose flesh” (left gland) by Claudius Galen (130-201) Depicted in 1552 by Bartholomeaus Eustachius on copper plate R Reproduced d d by b prints i in i 1563 The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education Adrenal Gland – Male Abdomen The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education Adrenal Gland - CT Adrenal Gland - MRI Adrenal Gland – Gross The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education Adrenal Gland – Cut Surface The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education Adrenal Gland – Cut Surface Adrenal Gland – Cross Section Adrenal Gland – Medulla Chromaffin cells Catecholamines - epinephrine - norepinephrine i hi Ganglion cells QL Adrenal Gland • • • • • Anatomy & Histology Steroid Hormones Addison’s Disease Cushing Syndrome Clinical Case Presentations QL Adrenal Gland – Low Power Medulla Zona fasciculata Zona reticularis Capsule Zona glomerulosa Periadrenal fat The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education Adrenal Gland – Low & High Power HP sinusoid HP-zf HP-zr QL Adrenal Cortex Steroids Zone Class Representative glomerulosa mineralocorticoids aldosterone fasiculata glucocorticoids reticularis sex steroids cortisol salt and water homeostasis carbohydrate metabolism androgens & estrogen O O Physiologic Effects CH2OH CH O O minimal effects CH2OH O O O QL Adrenal Steroidogenesis Glucocorticoids & the Receptor Cortisol (hydrocortisone) the majority of glucocorticoid activity in most mammals 90% off circulating i l ti cortisol ti l binds bi d to t cortisol ti l binding bi di globulin (CBG), for transportation, also limiting the rate of metabolic clearance & the concentration fluctuation Enter E t cells ll by b passive i diffusion diff i Histone acetylation p300/CBP TAFII250 TBP RNA Pol II QL Control of Cortisol Secretion HPA Axis y Hypothalamus CRH ACTH Anterior Pituitary Adrenal Cortex Cortisol Dr. Gary Farr QL Research Milestones * 1552: Bartholomaeus Eustachius - Depicted adrenal glands on copper plate * 1656: Thomas Wharton - Adrenals took something from the nerves and secreted it into the circulation * 1936: Edward Kendall and Tadeus Reichstein - Isolation and synthesis of cortisone * 1949: Edward Kendall and Philip Hench - Effects of cortisone and ACTH on rheumatoid arthritis * 1950: Nobel Prize to Kendall, Reichstein & Hench "for their discoveries relating to the hormones of the adrenal cortex, their structure and biological effects" QL Response to Stress Short-term stress Prolonged stress Stress Nerve impulses p Hypothalamus yp CRH (corticotropinreleasing hormone) Spinal cord Corticotropic cells of anterior pituitary Preganglionic sympathetic fib fibers To target in blood Adrenal medulla (secretes amino acid– based hormones) Catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) Short-term stress response • Heart rate increases • Blood pressure increases • Bronchioles dilate • Liver converts glycogen to glucose and releases glucose to blood • Blood flow changes, reducing digestive system activity and urine output • Metabolic rate increases Adrenal cortex (secretes steroid hormones) ACTH Mineralocorticoids Glucocorticoids Long-term stress response • Kidneys retain sodium & water • Blood volume & blood pressure rise • Proteins & fats converted to glucose or broken down for energy • Blood gl glucose cose increases • Immune syste supressed QL Adrenal Cortex Disorders CRH ACTH Cortisol CRH ACTH Cortisol QL Adrenal Gland • • • • • Anatomy & Histology Steroid Hormones Addison’s Disease Cushing Syndrome Clinical Case Presentations QL Addison’s Disease * General languor and debility * Remarkable feebleness of the heart's action *P Peculiar li change h in i the th color l off the th skin ki Chronic adrenocortical insufficiency progressive destruction of 90%of cortex extreme weakness and fatigue unintentional weight loss loss of appetite darkening of the skin low blood pressure, dizziness or fainting craving for salt nausea, diarrhea, vomiting irritability, depression Thomas Addison 1855 QL Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency * Primary chronic Hypocortisolism - Autoimmune adrenalitis - Infections (TB, AIDS) - Metastatic neoplasms - Genetic disorder 60 60--70% TB 90% CRH ACTH (Addison (Addison’s s disease) * Primary acute Hypocortisolism - Stress crisis (chronic AI) - Rapid Steroids withdraw - adrenal hemorrhage Cortisol QL Secondary Adrenocortical Insufficiency • Secondary Hypocortisolism CRH - Hypothalamic pituitary disease - Hypothalamic yp p pituitary y suppression pp ACTH Cortisol QL Managements CRH Glucocorticoid replacement Mineralocorticoid replacement ACTH Prevent adrenal crisis Medic Alert bracelet Cortisol QL Prognosis For people with Addison’s Disease * prior i to t 1930, 1930 90% di died d within ithi 5 years * from 1930, much better prognosis * since 1950, normal life span QL Adrenal Atrophy The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education Adrenal Gland • • • • • Anatomy & Histology Steroid Hormones Addison’s Disease Cushing Syndrome Clinical Case Presentations QL Causes of Cushing Syndrome Cushing’s Disease • Excessive Endogenous Cortisol - ACTH dependent: * Pituitary adenoma (70 (70--80%) * Small cell carcinoma - ACTH independent * Cortical tumor • Administration of Glucocorticoids - The most common cause CRH ACTH Cortisol Cushing’s Disease QL Ectopic ACTH Secretion • Excessive Endogenous Cortisol - ACTH dependent: * Pituitary adenoma * Small cell carcinoma (10%) - ACTH independent * Cortical tumor • Administration of Glucocorticoids - The most common cause CRH ACTH Cortisol QL Adrenal Defects • Excessive Endogenous Cortisol - ACTH dependent: * Pituitary adenoma * Small cell carcinoma - ACTH independent * Cortical tumor (10 (10--20%) • Administration of Glucocorticoids - The most common cause CRH ACTH Cortisol QL Exogenous CS • Excessive Endogenous Cortisol - ACTH dependent: * Pituitary adenoma * Small cell carcinoma - ACTH independent * Cortical tumor • Administration of Glucocorticoids - The most common cause CRH ACTH Cortisol QL Cushing Syndrome • Excessive Endogenous Cortisol - ACTH dependent: * Pituitary adenoma (Cushing’s Disease) * Small cell carcinoma - ACTH independent * Cortical tumor • Administration of Glucocorticoids - The most common cause CRH ACTH Cortisol H Harvey C Cushing hi 1912 QL Adrenal Gland – Gr / CS N d l C Nodular Cortical ti l H Hyperplasia l i Confluent Nodules Adrenal Gland – Low Power N d l C Nodular Cortical ti l H Hyperplasia l i Nodule Adrenal Gland – High Power N d l C Nodular Cortical ti l H Hyperplasia l i Adrenal Gland, cortical adenoma i C in Cushing hi Syndrome S d – Gr G / CS Adrenal Gland, cortical adenoma - LP Adrenal Gland - Tumor CT Adrenal Gland - Mass MRI : in-phase sequence Adrenal Gland - Adenoma MRI : out-of-phase sequence Clinical Manifestations • Moodiness, depression • Moon face • Facial plethora • Osteoprosis • Truncal obesity (buffalo hump) • Skin striae (abdomen) • Menstrual abnormalities • Weakness and fatigability • Hirsutism Hi i • Hypertension • Glucose intolerance / diabetes 7575-80% 85% 75% 75% 85--90% 85 50% 70% 85% 75% % 75% 70 / 20% Screening Tests 24--hour urine free cortisol level 24 am & pm cortisol level * circadian rhythm rhythm, a hall mark QL DST (Dex Suppression Test) Low--dose Dex suppression Low CRH * identify Cushing Syndrome g -dose Dex suppression High High- ACTH * identify Cushing’s Disease Cortisol QL Low Dose DST Low--dose DST Low Day 1: 1 mg of Dex at 11 pm Day 2: blood cortisol at 8 am 0.5 mg of Dex every 6 hrs for 48 hrs 24--hr urinary cortisol for 3 days 24 CRH ACTH * identify Cushing Syndrome High--dose DST High Day 1: a baseline cortisol at am 8 mg off Dex D att 11 pm Day 2: blood cortisol at 8 am 2 mg of Dex every 6 hrs for 48 hrs. 24--hr urinary cortisol for 3 days 24 Cortisol * identify Cushing's Disease QL High Dose DST Low--dose DST Low Day 1: 1 mg of Dex at 11 pm Day 2: blood cortisol at 8 am 0.5 mg of Dex every 6 hrs for 48 hrs 24--hr urinary cortisol for 3 days 24 CRH ACTH * identify Cushing Syndrome High--dose DST High Day 1: a baseline cortisol at am 8 mg off Dex D att 11 pm Day 2: blood cortisol at 8 am 2 mg of Dex every 6 hrs for 48 hrs. 24--hr urinary cortisol for 3 days 24 Cortisol * identify Cushing's Disease QL Determining the Etiology • Is ACTH dependent? • If ACTH dependent CRH * pituitary or ectopic • Source of overproduction ACTH * MRI pituitary * CT adrenals, chest, abdomen Cortisol QL Adrenal Gland - Comparison The Internet Pathology Laboratory for Medical Education Managements Surgical Treatment CRH l laparoscopic i adrenalectomy d l t Medical Treatment ACTH adrenal d l enzyme blockers bl k Cortisol QL Resources • Pathologic Basis of Disease R bbi & Cotran Robbins C t 7th Edition Editi • Basic Pathology Robins R b 7th Edition Ed • Handbook of Clinical Pathology 2nd Edition QL