* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is heat transfer?
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
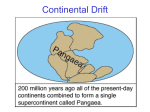
Chapter 1 Study Guide Atmosphere Geosphere Hydrosphere Biosphere Parts of Earth’s System The relatively thing later of gases that form Earth’s outermost layer The densest parts of Earth that include the crust, mantle, and core The portion of Earth that consists of water in any of its forms, including oceans, glaciers, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and water vapor The parts of Earth that contain living things _____________________________________________________________________________________ Sources of Energy for Earth’s Systems: Heat from the sun Heat from the Earth _____________________________________________________________________________________ Term Definition Examples Constructive force A natural process that builds up Earth’s surface Volcanoes, earthquakes Destructive Force Any natural force that tears down or wears away Earth’s surface, such as through weathering and erosion Ice, rain, wind, changing temperatures Chapter 1 Study Guide How do geologists study the Earth? Direct Evidence Rock Samples Indirect Evidence Seismic Waves Geologists get rock by drilling into Earth or from volcanic eruptions. The rocks tell scientists about the structure and conditions inside Earth. Seismic waves are produced by earthquakes. Geologists can study the way the waves travel through Earth. The path of the waves changes when they hit different materials. What are the layers of Earth? Pressure increases as depth increases, Crust- outermost layer of solid rock Oceanic Crust- thinner crustmostly composed of basalt rock (Think: “salt” water) Continential Crust- thicker crust- mostly composed of granite rock Mantle-layer of hot rock Lithosphere-uppermost layer of the mantle with the crustrigid and rocky Asthenosphere- middle layer of the mantle- softer, but still solid Mesosphere- deepest layer of the mantle-hot, but more rigid because of heavy pressure Core-innermost part of Earth-mostly made of iron and nickel Outer Core-hot, molten liquid Inner Core-extremely hot, but solid due to intense pressure Scientists think the convection currents inside the liquid outer core create the Earth’s magnetic field! Chapter 1 Study Guide What is heat transfer? Heat transfer is the movement of energy (heat) from a warmer object to a cooler object. What are the three types of heat transfer? Radiation, Convection, Conduction What is radiation? Energy moves through empty space, such as in rays from the sun. The heat from the sun travels through the air to reach the Earth. What is conduction? Heat transfers between materials that are touching (direct contact). When you walk on the hot sand, the heat transfers directly to your feet through touch. What is convection? What is a convection current? Heat transfers through the movement of a liquid, such as when boiling soup. Convection current is the movement of a fluid caused by differences in temperature (heating and cooling). Heat from the core and mantle cause a convection current in Earth. What is density? Density is a measure of how much mass there is in a given volume of a substance.