* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and Momentum Methods
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Statistical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Lagrangian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Hamiltonian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
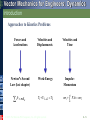
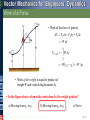
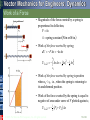
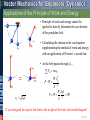
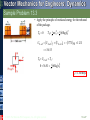
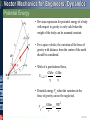
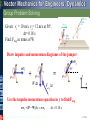
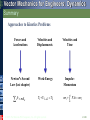
Tenth Edition CHAPTER 13 VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: DYNAMICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Phillip J. Cornwell Lecture Notes: Brian P. Self California Polytechnic State University Kinetics of Particles: Energy and Momentum Methods © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Contents Introduction Work of a Force Principle of Work & Energy Applications of the Principle of Work & Energy Power and Efficiency Sample Problem 13.1 Sample Problem 13.2 Sample Problem 13.3 Sample Problem 13.4 Sample Problem 13.5 Potential Energy Conservative Forces Conservation of Energy Motion Under a Conservative Central Force Sample Problem 13.6 Sample Problem 13.7 Sample Problem 13.9 Principle of Impulse and Momentum Impulsive Motion Sample Problem 13.10 Sample Problem 13.11 Sample Problem 13.12 Impact Direct Central Impact Oblique Central Impact Problems Involving Energy and Momentum Sample Problem 13.14 Sample Problem 13.15 Sample Problems 13.16 Sample Problem 13.17 13 - 2 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Energy and Momentum Methods The pogo stick allows the boy to change between kinetic energy, potential energy from gravity, and potential energy in the spring. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Accidents are often analyzed by using momentum methods. 2-3 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Introduction • Previously, problems dealing with the motion of particles were solved through the fundamental equation of motion, F ma. • The current chapter introduces two additional methods of analysis. • Method of work and energy: directly relates force, mass, velocity and displacement. • Method of impulse and momentum: directly relates force, mass, velocity, and time. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 4 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Introduction Approaches to Kinetics Problems Forces and Accelerations Velocities and Displacements Velocities and Time Newton’s Second Law (last chapter) Work-Energy ImpulseMomentum F ma G T1 U12 T2 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. t2 mv1 F dt mv2 t1 2-5 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force • Differential vector dr is the particle displacement. • Work of the force is dU F dr F ds cos Fx dx Fy dy Fz dz • Work is a scalar quantity, i.e., it has magnitude and sign but not direction. • Dimensions of work are length force. Units are 1 J joule 1 N 1 m © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 1ft lb 1.356 J 13 - 6 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force • Work of a force during a finite displacement, A2 U12 F dr A1 s2 s2 s1 s1 F cos ds Ft ds A2 Fx dx Fy dy Fz dz A1 • Work is represented by the area under the curve of Ft plotted against s. • Ft is the force in the direction of the displacement ds © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 7 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force What is the work of a constant force in rectilinear motion? a) b) c) d) © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. U12 F x U12 F cos x U12 F sin x U12 0 13 - 8 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force • Work of the force of gravity, dU Fx dx Fy dy Fz dz W dy y2 U12 W dy y1 W y 2 y1 W y • Work of the weight is equal to product of weight W and vertical displacement y. • In the figure above, when is the work done by the weight positive? a) Moving from y1 to y2 b) Moving from y2 to y1 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. c) Never 13 - 9 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force • Magnitude of the force exerted by a spring is proportional to deflection, F kx k spring constant N/m or lb/in. • Work of the force exerted by spring, dU F dx kx dx x2 U12 kx dx 12 kx12 12 kx22 x1 • Work of the force exerted by spring is positive when x2 < x1, i.e., when the spring is returning to its undeformed position. • Work of the force exerted by the spring is equal to negative of area under curve of F plotted against x, U12 12 F1 F2 x © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 10 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force As the block moves from A0 to A1, is the work positive or negative? Positive Negative As the block moves from A2 to Ao, is the work positive or negative? Positive © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Negative Displacement is in the opposite direction of the force Displacement is in the same direction of the force 13 - 11 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force Work of a gravitational force (assume particle M occupies fixed position O while particle m follows path shown), Mm dU Fdr G 2 dr r r2 Mm Mm Mm U12 G 2 dr G G r2 r1 r r1 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 12 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Does the normal force do work as the block slides from B to A? YES NO Does the weight do work as the block slides from B to A? YES NO © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Positive or Negative work? 2 - 13 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Work of a Force Forces which do not do work (ds = 0 or cos 0: • Reaction at frictionless pin supporting rotating body, • Reaction at frictionless surface when body in contact moves along surface, • Reaction at a roller moving along its track, and • Weight of a body when its center of gravity moves horizontally. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 14 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Particle Kinetic Energy: Principle of Work & Energy • Consider a particle of mass m acted upon by force F dv Ft mat m dt dv ds dv m mv ds dt ds F t ds mv dv • Integrating from A1 to A2 , s2 v2 s1 v1 Ft ds m v dv 12 mv2 12 mv1 2 2 U12 T2 T1 T 12 mv 2 kinetic energy • The work of the force F is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the particle. • Units of work and kinetic energy are the same: 2 m m 2 T 12 mv kg kg 2 m N m J s s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 15 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Applications of the Principle of Work and Energy • Force P acts normal to path and does no work. T1 U12 T2 • The bob is released from rest at position A1. Determine the velocity of the pendulum bob at A2 using work & kinetic energy. 0 Wl 1W 2 v2 2 g v2 2 gl • Velocity is found without determining expression for acceleration and integrating. • All quantities are scalars and can be added directly. • Forces which do no work are eliminated from the problem. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 16 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Applications of the Principle of Work and Energy • Principle of work and energy cannot be applied to directly determine the acceleration of the pendulum bob. • Calculating the tension in the cord requires supplementing the method of work and energy with an application of Newton’s second law. • As the bob passes through A2 , Fn m an v22 l W 2 gl P W 3W g l W P W g v2 2 gl If you designed the rope to hold twice the weight of the bob, what would happen? © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 17 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Power and Efficiency • Power rate at which work is done. dU F dr dt dt F v • Dimensions of power are work/time or force*velocity. Units for power are J m ft lb 1 W (watt) 1 1 N or 1 hp 550 746 W s s s • efficiency output work input work power output power input © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 18 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.1 SOLUTION: • Evaluate the change in kinetic energy. • Determine the distance required for the work to equal the kinetic energy change. An automobile of mass 1000 kg is driven down a 5o incline at a speed of 72 km/h when the brakes are applied causing a constant total breaking force of 5000 N. Determine the distance traveled by the automobile as it comes to a stop. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 19 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.1 SOLUTION: • Evaluate the change in kinetic energy. æ km öæ 1000 m öæ h ö v1 = ç 72 ÷ç ÷ç ÷ = 20 m s è h øè 1 km øè 3600 s ø T1 = 12 mv12 = 12 (1000 kg) ( 20 m/s) = 200000 J 2 v2 0 T2 0 • Determine the distance required for the work to equal the kinetic energy change. U1® 2 = (- 5000 N ) x + (1000 kg )(9.81 m/s2 )(sin 5°) x = - (4145N ) x T1 + U1® 2 = T2 200000 J - (4145N ) x = 0 x = 48.3 m © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 20 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.2 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of work and energy separately to blocks A and B. • When the two relations are combined, the work of the cable forces cancel. Solve for the velocity. Two blocks are joined by an inextensible cable as shown. If the system is released from rest, determine the velocity of block A after it has moved 2 m. Assume that the coefficient of friction between block A and the plane is mk = 0.25 and that the pulley is weightless and frictionless. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 21 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.2 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of work and energy separately to blocks A and B. W A 200 kg 9.81m s 2 1962 N FA m k N A m k W A 0.251962 N 490 N T1 U12 T2 : 0 FC 2 m FA 2 m 12 m A v 2 FC 2 m 490 N 2 m 12 200 kg v 2 WB 300 kg 9.81m s 2 2940 N T1 U12 T2 : 0 Fc 2 m WB 2 m 12 m B v 2 Fc 2 m 2940 N 2 m 12 300 kg v 2 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 22 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.2 • When the two relations are combined, the work of the cable forces cancel. Solve for the velocity. FC 2 m 490 N 2 m 12 200 kg v 2 Fc 2 m 2940 N 2 m 12 300 kg v 2 2940 N 2 m 490 N 2 m 12 200 kg 300 kg v 2 4900 J 12 500 kg v 2 v 4.43 m s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 23 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics 13.2 – Alternate Solution, Group Problem Solving Could you apply work-energy to the combined system of blocks? 2 1 Given: v1= 0, distance = 2 m, mk = 0.25 2m 1 What is T1 of the system? 2m 2 T1 0 What is the total work done between points 1 and 2? U12 0.25 200 9.81 2m 300 9.81 2m 4900 J What is T2 of the system? Note that vA = vB T2 12 mAv2 12 mBv2 12 200kg v2 12 300kg v2 Solve for v 4900 J 12 500kg v2 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. v 4.43 m s 2 - 24 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.3 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of work and energy between the initial position and the point at which the spring is fully compressed and the velocity is zero. The only unknown in the relation is the friction coefficient. A spring is used to stop a 60 kg package which is sliding on a horizontal surface. The spring has a constant k = 20 kN/m and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the relation is the velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown and the maximum deflection of the spring velocity at the final position. is 40 mm. Determine (a) the coefficient of kinetic friction between the package and surface and (b) the velocity of the package as it passes again through the position shown. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 25 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.3 SOLUTION: • Apply principle of work and energy between initial position and the point at which spring is fully compressed. T1 12 mv12 12 60 kg 2.5 m s 2 187.5 J U12 f m kW x T2 0 m k 60 kg 9.81m s 2 0.640 m 377 J m k Pmin kx0 20 kN m 0.120 m 2400 N Pmax k x0 x 20 kN m 0.160 m 3200 N U12 e 12 Pmin Pmax x 12 2400 N 3200 N 0.040 m 112.0 J U12 U12 f U12 e 377 J m k 112 J T1 U12 T2 : 187.5 J - 377 J m k 112 J 0 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. mk 0.20 13 - 26 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.3 • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. T 3 12 mv32 12 60kg v32 T2 0 U 23 U 23 f U 23 e 377 J m k 112 J 36.5 J T2 U 23 T3 : 0 36.5 J 12 60 kg v32 v3 1.103 m s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 27 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.4 SOLUTION: • Apply principle of work and energy to determine velocity at point 2. • Apply Newton’s second law to find normal force by the track at point 2. A 1000 kg car starts from rest at point 1 and moves without friction down the track shown. Determine: a) the force exerted by the track on the car at point 2, and • Apply principle of work and energy to determine velocity at point 3. • Apply Newton’s second law to find minimum radius of curvature at point 3 such that a positive normal force is exerted by the track. b) the minimum safe value of the radius of curvature at point 3. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 28 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.4 SOLUTION: • Apply principle of work and energy to determine velocity at point 2. T2 = 21 mv22 T1 = 0 U1® 2 = +W (12 m ) T1 + U1® 2 = T2 : 1 0 + W (12 m ) = m v22 2 ( v22 = 2 (12 m ) g = 2 (12 m ) 9.8m s2 ) v2 = 15.34 m/s • Apply Newton’s second law to find normal force by the track at point 2. Fn m an : v22 24 g - W + N = m an = m =m r2 6 N = 5W 5(1000 kg)(9.81 m/s2 ) N = 49.05kN © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 29 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.4 • Apply principle of work and energy to determine velocity at point 3. 1 0 + mg (7.5m ) = m v32 2 T1 + U1® 3 = T3 ( v32 = 15g = (15m ) 9.81 m/s2 ) v3 = 12.13m s • Apply Newton’s second law to find minimum radius of curvature at point 3 such that a positive normal force is exerted by the track. Fn m an : mg = m an v32 =m r3 v32 15g r3= = g g © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. r 3 = 15m 13 - 30 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.5 SOLUTION: Force exerted by the motor cable has same direction as the dumbwaiter velocity. Power delivered by motor is equal to FvD, vD = 2.5 m/s. The dumbwaiter D and its load have a combined mass of 300 kg, while the counterweight C has a mass of 400 kg. • In the first case, bodies are in uniform motion. Determine force exerted by motor cable from conditions for static equilibrium. Determine the power delivered by the electric motor M when the dumbwaiter (a) is moving up at a constant speed of 2.5 m/s and (b) has an instantaneous velocity of 2.5 m/s and an acceleration of 1 m/s2, both directed upwards. • In the second case, both bodies are accelerating. Apply Newton’s second law to each body to determine the required motor cable force. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 31 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.5 • In the first case, bodies are in uniform motion. Determine force exerted by motor cable from conditions for static equilibrium. Free-body C: Fy 0 : 2T - 400g = 0 T = 200 g =1962 N Free-body D: Fy 0 : F + T - 300 g = 0 F = 300 g - T = 300 g - 200 g = 981 N Power = FvD = (981 N)(2.5m/s) = 2452 W Power = 2.45 kW © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 32 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.5 • In the second case, both bodies are accelerating. Apply Newton’s second law to each body to determine the required motor cable force. aD = 1m s2 - aC = - 21 aD = 0.5m s2 ¯ Free-body C: Fy mC aC : 400 g - 2T = 400(0.5) T = 1862N Free-body D: Fy m D a D : F + T - 300 g = 300 (1) F + 186.2 - 300(9.81) = 300 F = 1381 N Power = FvD = (1381 N)(2.5m/s) = 3452W Power = 3.45kW © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 33 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving SOLUTION: The problem deals with a change in position and different velocities, so use work-energy. • Draw FBD of the box to help us determine the forces that do work. Packages are thrown down an incline at A with a velocity of 1 m/s. The packages slide along the surface ABC to a conveyor belt which moves with a velocity of 2 m/s. Knowing that mk= 0.25 between the packages and the surface ABC, determine the distance d if the packages are to arrive at C with a velocity of 2 m/s. • Determine the work done between points A and C as a function of d. • Find the kinetic energy at points A and C. • Use the work-energy relationship and solve for d. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 34 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving SOLUTION: Given: vA= 1 m/s, vC= 2 m/s, mk= 0.25 Find: distance d Will use: Draw the FBD of the block at points A and C TA +U A®B +U B®C = TC Determine work done A → B N AB mg cos30 FAB mk N AB 0.25 mg cos 30 U A B mg d sin 30 FAB d mg d (sin 30 mk cos 30) Determine work done B → C N BC mg xBC 7 m FBC mk mg U B C mk mg xBC © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 35 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving Determine kinetic energy at A and at C TA 1 2 mv A 2 and v A 1 m/s TC Substitute values into 1 2 mvC 2 and vC 2 m/s TA U A B U B C TC 1 2 1 2 mv A mg d (sin 30 mk cos30) mk mg xBC mv0 2 2 Divide by m and solve for d vC2 /2 g mk xBC v A2 /2 g d (sin 30 mk cos 30) d 6.71 m (2) 2/(2)(9.81) (0.25)(7) (1) 2/(2)(9.81) sin 30 0.25cos 30 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 36 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics mk= 0.25 If you wanted to bring the package to a complete stop at the bottom of the ramp, would it work to place a spring as shown? No, because the potential energy of the spring would turn into kinetic energy and push the block back up the ramp Would the package ever come to a stop? Yes, eventually enough energy would be dissipated through the friction between the package and ramp. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 37 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics The potential energy stored at the top of the roller coaster is transferred to kinetic energy as the cars descend. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. The elastic potential energy stored in the trampoline is transferred to kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy as the girl flies upwards. 2 - 38 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Potential Energy If the work of a force only depends on differences in position, we can express this work as potential energy. Can the work done by the following forces be expressed as potential energy? Weight Yes No Friction Yes No Normal force Yes No Spring force Yes No © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 39 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Potential Energy • Work of the force of gravity W, U12 W y1 W y2 • Work is independent of path followed; depends only on the initial and final values of Wy. V g Wy potential energy of the body with respect to force of gravity. U12 V g Vg 1 2 • Choice of datum from which the elevation y is measured is arbitrary. • Units of work and potential energy are the same: Vg Wy N m J © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 40 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Potential Energy • Previous expression for potential energy of a body with respect to gravity is only valid when the weight of the body can be assumed constant. • For a space vehicle, the variation of the force of gravity with distance from the center of the earth should be considered. • Work of a gravitational force, GMm GMm U12 r2 r1 • Potential energy Vg when the variation in the force of gravity can not be neglected, GMm WR 2 Vg r r © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 41 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Potential Energy • Work of the force exerted by a spring depends only on the initial and final deflections of the spring, U12 12 kx12 12 kx22 • The potential energy of the body with respect to the elastic force, Ve 12 kx 2 U1 2 Ve 1 Ve 2 • Note that the preceding expression for Ve is valid only if the deflection of the spring is measured from its undeformed position. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 42 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Conservative Forces • Concept of potential energy can be applied if the work of the force is independent of the path followed by its point of application. U12 V x1, y1, z1 V x2 , y2 , z2 Such forces are described as conservative forces. • For any conservative force applied on a closed path, F dr 0 • Elementary work corresponding to displacement between two neighboring points, dU V x, y, z V x dx, y dy, z dz dV x, y, z V V V Fx dx Fy dy Fz dz dx dy dz y z x V V V F gradV x y z © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 43 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Conservation of Energy • Work of a conservative force, U12 V1 V2 • Concept of work and energy, U12 T2 T1 • Follows that T1 V1 T2 V2 E T V constant T1 0 V1 W T1 V1 W T2 12 mv22 T2 V2 W 1W 2 g W V2 0 2g • When a particle moves under the action of conservative forces, the total mechanical energy is constant. • Friction forces are not conservative. Total mechanical energy of a system involving friction decreases. • Mechanical energy is dissipated by friction into thermal energy. Total energy is constant. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 44 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Motion Under a Conservative Central Force • When a particle moves under a conservative central force, both the principle of conservation of angular momentum r0 mv0 sin 0 rmv sin and the principle of conservation of energy T0 V0 T V 1 mv 2 0 2 GMm 1 2 GMm 2 mv r0 r may be applied. • Given r, the equations may be solved for v and j. • At minimum and maximum r, j 90o. Given the launch conditions, the equations may be solved for rmin, rmax, vmin, and vmax. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 45 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.6 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of conservation of energy between positions 1 and 2. • The elastic and gravitational potential energies at 1 and 2 are evaluated from the given information. The initial kinetic energy is zero. A 10 kg collar slides without friction along a vertical rod as shown. The spring attached to the collar has an undeflected length of 100 mm and a constant of 600 N/m. • Solve for the kinetic energy and velocity at 2. If the collar is released from rest at position 1, determine its velocity after it has moved 150 mm to position 2. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 46 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.6 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of conservation of energy between positions 1 and 2. 2 Position 1: Ve = 21 kx12 = 21 (600N/m )(0.2m - 0.1m ) =3J V1 = Ve + Vg = 3J + 0 = 3J Position 2: T1 = 0 2 Ve = 21 kx22 = 21 (600 N/m )(0.25 m - 0.1 m ) = 6.75J ) ( Vg = Wy = (10 kg ) 9.81 m/s2 = (- 0.15 m) = - 14.715 J V2 = Ve + Vg = 6.75 - 14.715 = - 7.965 J 1 T2 = 21 mv22 = (10) v22 = 5 v22 2 ( ) Conservation of Energy: T1 + V1 = T2 + V2 0 + 3 J = 5 v22 - 7.965 J © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. v2 = 1.481m/s ¯ 13 - 47 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.7 SOLUTION: • Since the pellet must remain in contact with the loop, the force exerted on the pellet must be greater than or equal to zero. Setting the force exerted by the loop to zero, solve for the minimum velocity at D. The 250 g pellet is pushed against the spring and released from rest at A. Neglecting friction, determine the smallest deflection of the spring for which the pellet will travel around the loop and remain in contact with the loop at all times. • Apply the principle of conservation of energy between points A and D. Solve for the spring deflection required to produce the required velocity and kinetic energy at D. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 48 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.7 SOLUTION: • Setting the force exerted by the loop to zero, solve for the minimum velocity at D. Fn man : W = man mg = m vD2 r ( ) vD2 = rg = (0.5 m ) 9.81m s2 = 4.905m 2 s2 • Apply the principle of conservation of energy between points A and D. V1 = Ve + Vg = 21 kx 2 + 0 = 21 (600 N/m ) x 2 = 300 x 2 T1 = 0 ) ( V2 = Ve + Vg = 0 + Wy = (0.25kg) 9.81m/s2 (1 m) = 2.45J 1 (0.25 kg) 4.905m2 s2 = 0.613J 2 T1 + V1 = T2 + V2 x = 0.101 m = 10/mm 0 + 300 x 2 = 2.45J + 0.613J T2 = 21 mvD2 = © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. ( ) 13 - 49 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.9 SOLUTION: • For motion under a conservative central force, the principles of conservation of energy and conservation of angular momentum may be applied simultaneously. A satellite is launched in a direction parallel to the surface of the earth with a velocity of 36900 km/h from an altitude of 500 km. • Apply the principles to the points of minimum and maximum altitude to determine the maximum altitude. • Apply the principles to the orbit insertion point and the point of minimum altitude to determine maximum allowable orbit Determine (a) the maximum altitude insertion angle error. reached by the satellite, and (b) the maximum allowable error in the direction of launching if the satellite is to come no closer than 200 km to the surface of the earth © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 50 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.9 • Apply the principles of conservation of energy and conservation of angular momentum to the points of minimum and maximum altitude to determine the maximum altitude. Conservation of energy: TA VA TA VA 1 mv 2 0 2 GMm 1 2 GMm 2 mv1 r0 r1 Conservation of angular momentum: r r0mv0 r1mv1 v1 v0 0 r1 Combining, 2 r0 2GM 1 v 2 1 r0 GM 1 r0 1 2 0 2 r0 r1 r1 r0v02 r1 r0 6370 km 500 km 6870 km v0 36900 km h 10.25 106 m s 2 GM gR 2 9.81m s 2 6.37 106 m 398 1012 m3 s 2 r1 60.4 106 m 60400 km © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 51 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.9 • Apply the principles to the orbit insertion point and the point of minimum altitude to determine maximum allowable orbit insertion angle error. Conservation of energy: GMm 1 mv 2 GMm 1 mv 2 T0 V0 TA VA 0 max 2 2 r0 rmin Conservation of angular momentum: r r0mv0 sin 0 rmin mvmax vmax v0 sin 0 0 rmin Combining and solving for sin j0, sin 0 0.9801 j 0 90 11.5 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. allowable error 11.5 13 - 52 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving SOLUTION: • This is two part problem – you will need to find the velocity of the car using work-energy, and then use Newton’s second law to find the normal force. A section of track for a roller coaster consists of two circular arcs AB and CD joined by a straight portion BC. The radius of CD is 80 m. The car and its occupants, of total mass 300 kg, reach Point A with practically no velocity and then drop freely along the track. Determine the normal force exerted by the track on the car at point D. Neglect air resistance and rolling resistance. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. • Draw a diagram with the car at points A and D, and define your datum. Use conservation of energy to solve for vD • Draw FBD and KD of the car at point D, and determine the normal force using Newton’s second law. 2 - 53 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving SOLUTION: Given: vA= 0 m/s, rCD= 800 m, W=300 kg Find: ND Define your datum, sketch the situation at points of interest Datum Use conservation of energy to find vD Find TA Find VA Find TD Find VD TA VA TD VD v A 0 TA 0 VA mgy A (300 kg)(9.81 m/s2 )(30 m 20 m) =147150 J TD 1 2 1 mvD (300)vD2 150 vD2 2 2 Solve for vD 150vD2 147150 vD2 981 vD 13.321 m/s yD 0 VD 0 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 54 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving Draw FBD and KD at point D en et man W mat ND Use Newton’s second law in the normal direction F man 2 vD N D mg m R 2 v N D m g D R n © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 981 N D 300 9.81 80 N D 6620 N 2 - 55 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving What happens to the normal force at D if…. …we include friction? a) ND gets larger b) ND gets smaller c) ND stays the same …we move point A higher? a) ND gets larger …the radius is smaller? a) ND gets larger b) ND gets smaller b) ND gets smaller c) ND stays the same c) ND stays the same © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 56 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Impulsive Motion The thrust of a rocket acts over a specific time period to give the rocket linear momentum. The impulse applied to the railcar by the wall brings its momentum to zero. Crash tests are often performed to help improve safety in different vehicles. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 57 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Principle of Impulse and Momentum • From Newton’s second law, d F mv mv linear momentum dt Fdt d mv t2 F dt m v m v 2 1 t1 • Dimensions of the impulse of a force are force*time. • Units for the impulse of a force are N s kg m s s kg m s 2 t2 Fdt Imp12 impulse of the force F t1 mv1 Imp12 mv2 • The final momentum of the particle can be obtained by adding vectorially its initial momentum and the impulse of the force during the time interval. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 58 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Impulsive Motion • Force acting on a particle during a very short time interval that is large enough to cause a significant change in momentum is called an impulsive force. • When impulsive forces act on a particle, mv1 F t mv2 • When a baseball is struck by a bat, contact occurs over a short time interval but force is large enough to change sense of ball motion. • Nonimpulsive forces are forces for which Ft is small and therefore, may be neglected – an example of this is the weight of the baseball. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 59 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.10 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of impulse and momentum. The impulse is equal to the product of the constant forces and the time interval. An automobile of mass 1800 kg is driven down a 5o incline at a speed of 100 km/h when the brakes are applied, causing a constant total braking force of 7000 N. Determine the time required for the automobile to come to a stop. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 60 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.10 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of impulse and momentum. mv1 Imp12 mv2 Taking components parallel to the incline, mv1 + ( mgsin 5°) t - Ft = 0 æ km öæ 1000 m öæ 1h ö 100 km/h = ç100 ÷ç ÷ = 27.78 m/s ÷ç è h øè 1 km øè 3600 s ø (1800 kg) ( 2778 m/s) + (1800 kg) ( 9.81 m/s2 ) (sin 5 )t - (7000 N)t = 0 t = 9.16s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 61 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.11 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of impulse and momentum in terms of horizontal and vertical component equations. A 120-g baseball is pitched with a velocity of 24 m/s. After the ball is hit by the bat, it has a velocity of 36 m/s in the direction shown. If the bat and ball are in contact for 0.015 s, determine the average impulsive force exerted on the ball during the impact. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 62 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.11 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of impulse and momentum in terms of horizontal and vertical component equations. mv1 Imp12 mv2 x component equation: - mv1 + Fx Dt = mv2 cos40° - (0.12 kg)(24 m/s) + Fx (0.015 s) = (0.12 kg)(36 m/s) cos 40 Fx = +412.6 N y component equation: y 0 + Fy Dt = mv2 sin 40° x Fy (0.015) = (0.12 kg)(36 m/s) sm40 Fy = +185.1N F = (413 N) i + (185.1 N) j , F = 452N © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 63 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.12 SOLUTION: A 10 kg package drops from a chute into a 24 kg cart with a velocity of 3 m/s. Knowing that the cart is initially at rest and can roll freely, determine (a) the final velocity of the cart, (b) the impulse exerted by the cart on the package, and (c) the fraction of the initial energy lost in the impact. • Apply the principle of impulse and momentum to the package-cart system to determine the final velocity. • Apply the same principle to the package alone to determine the impulse exerted on it from the change in its momentum. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 64 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.12 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of impulse and momentum to the package-cart system to determine the final velocity. y x m pv1 Imp12 m p mc v2 x components: m pv1 cos 30 0 m p mc v2 10 kg 3 m/s cos 30 10 kg 25 kg v2 v2 0.742 m/s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 65 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.12 • Apply the same principle to the package alone to determine the impulse exerted on it from the change in its momentum. y x m pv1 Imp12 m pv2 x components: m p v1 cos 30 Fx t m p v2 10 kg 3 m/s cos 30 Fx t 10 kg v2 y components: Fx t 18.56 N s m p v1 sin 30 Fy t 0 10 kg 3 m/s sin 30 Fy t 0 Imp12 Ft 18.56 N s i 15 N s j © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Fy t 15 N s Ft 23.9 N s 13 - 66 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.12 To determine the fraction of energy lost, T1 12 m p v12 T2 1 2 1 2 10 kg 3m s 45 J mp mc v22 2 1 2 10 kg 25 kg 0.742 m s 9.63 J 2 T1 T2 45 J 9.63 J 0.786 T1 45 J © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 67 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics SOLUTION: • Draw impulse and momentum diagrams of the jumper. • Apply the principle of impulse and momentum to the jumper to determine the force exerted on the foot. The jumper approaches the takeoff line from the left with a horizontal velocity of 10 m/s, remains in contact with the ground for 0.18 s, and takes off at a 50o angle with a velocity of 12 m/s. Determine the average impulsive force exerted by the ground on his foot. Give your answer in terms of the weight W of the athlete. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 68 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving Given: v1 = 10 m/s, v2= 12 m/s at 50º, Δt= 0.18 s Find: Favg in terms of W Draw impulse and momentum diagrams of the jumper mv2 mv1 50º + = W t Favg t y x Use the impulse momentum equation in y to find Favg mv1 (P W)t mv 2 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. t 0.18 s 2 - 69 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving mv2 mv1 + 50º = W t Favg t y x mv1 (Favg W)t mv 2 t 0.18 s Use the impulse momentum equation in x and y to find Favg W W (10) ( Favg x )(0.18) (12)(cos 50) g g 10 (12)(cos 50) Favg x W (9.81)(0.18) Favg 1.295W i 6.21W j © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. W (12)(sin 50) g (12)(sin 50) W W (9.81)(0.18) 0 ( Favg y W )(0.18) Favg y Favg-x is positive, which means we guessed correctly (acts to the left) 2 - 70 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving Car A and B crash into one another. Looking only at the impact, which of the following statements are true? The total mechanical energy is the same before and after the impact True False If car A weighs twice as much as car B, the force A exerts on car B is bigger than the force B exerts on car A. True False The total linear momentum is the same immediately before and after the impact True False © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 71 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics The coefficient of restitution is used to characterize the “bounciness” of different sports equipment. The U.S. Golf Association limits the COR of golf balls at 0.83 Civil engineers use the coefficient of restitution to model rocks falling from hillsides © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 72 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Impact • Impact: Collision between two bodies which occurs during a small time interval and during which the bodies exert large forces on each other. • Line of Impact: Common normal to the surfaces in contact during impact. Direct Central Impact • Central Impact: Impact for which the mass centers of the two bodies lie on the line of impact; otherwise, it is an eccentric impact.. • Direct Impact: Impact for which the velocities of the two bodies are directed along the line of impact. • Oblique Impact: Impact for which one or both of the bodies move along a line other than the line of impact. Oblique Central Impact © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 73 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Direct Central Impact • Bodies moving in the same straight line, vA > vB . • Upon impact the bodies undergo a period of deformation, at the end of which, they are in contact and moving at a common velocity. • A period of restitution follows during which the bodies either regain their original shape or remain permanently deformed. • Wish to determine the final velocities of the two bodies. The total momentum of the two body system is preserved, m Av A mB v B mB vB mB vB • A second relation between the final velocities is required. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 74 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Direct Central Impact e coefficient of restitution • Period of deformation: m Av A Pdt m Au • Period of restitution: Rdt u v A Pdt v A u 0 e 1 m Au Rdt m AvA • A similar analysis of particle B yields v B u e u vB • Combining the relations leads to the desired second relation between the final velocities. vB vA ev A v B • Perfectly plastic impact, e = 0: vB vA v m Av A mB v B m A mB v • Perfectly elastic impact, e = 1: Total energy and total momentum conserved. vB vA v A v B © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 75 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Oblique Central Impact • Final velocities are unknown in magnitude and direction. Four equations are required. • No tangential impulse component; tangential component of momentum for each particle is conserved. • Normal component of total momentum of the two particles is conserved. • Normal components of relative velocities before and after impact are related by the coefficient of restitution. v A t vA t v B t vB t m A v A n mB v B n m A vA n mB vB n vB n vA n ev A n v B n © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 76 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Oblique Central Impact • Block constrained to move along horizontal surface. • Impulses from internal forces F and F along the n axis and from external force Fext exerted by horizontal surface and directed along the vertical to the surface. • Final velocity of ball unknown in direction and magnitude and unknown final block velocity magnitude. Three equations required. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 77 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Oblique Central Impact • Tangential momentum of ball is conserved. v B t vB t • Total horizontal momentum of block and ball is conserved. m A v A mB v B x m A vA mB vB x • Normal component of relative velocities of block and ball are related by coefficient of restitution. vB n vA n ev A n v B n • Note: Validity of last expression does not follow from previous relation for the coefficient of restitution. A similar but separate derivation is required. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 78 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Problems Involving Energy and Momentum • Three methods for the analysis of kinetics problems: - Direct application of Newton’s second law - Method of work and energy - Method of impulse and momentum • Select the method best suited for the problem or part of a problem under consideration. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 79 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.14 SOLUTION: • Resolve ball velocity into components normal and tangential to wall. • Impulse exerted by the wall is normal to the wall. Component of ball momentum tangential to wall is conserved. A ball is thrown against a frictionless, vertical wall. Immediately before the ball strikes the wall, its velocity has a magnitude v and forms angle of 30o with the horizontal. Knowing that e = 0.90, determine the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the ball as it rebounds from the wall. • Assume that the wall has infinite mass so that wall velocity before and after impact is zero. Apply coefficient of restitution relation to find change in normal relative velocity between wall and ball, i.e., the normal ball velocity. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 80 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.14 SOLUTION: • Resolve ball velocity into components parallel and perpendicular to wall. vn v cos 30 0.866v vt v sin 30 0.500v • Component of ball momentum tangential to wall is conserved. vt vt 0.500v t n • Apply coefficient of restitution relation with zero wall velocity. 0 vn evn 0 vn 0.90.866v 0.779v v 0.779v n 0.500v t 0.779 v 0.926v tan 1 32.7 0.500 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 81 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.15 SOLUTION: • Resolve the ball velocities into components normal and tangential to the contact plane. • Tangential component of momentum for each ball is conserved. The magnitude and direction of the velocities of two identical frictionless balls before they strike each other are as shown. Assuming e = 0.9, determine the magnitude and direction of the velocity of each ball after the impact. • Total normal component of the momentum of the two ball system is conserved. • The normal relative velocities of the balls are related by the coefficient of restitution. • Solve the last two equations simultaneously for the normal velocities of the balls after the impact. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 82 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.15 SOLUTION: • Resolve the ball velocities into components normal and tangential to the contact plane. (vA )n = vA cos30° = +7.79 m/s (vA )t = vA sin30° = +4.5 m/s (vB )n = - vB cos60° = - 6 m/s (vB )t = vB sin60° = +10.39 m/s • Tangential component of momentum for each ball is conserved. (v¢A )t = (vA )t = 4.5 m/s (vB¢)t = (vB )t = 10.39 m/s • Total normal component of the momentum of the two ball system is conserved. m A (v A )n + mB (vB )n = m A (v A¢)n + mB (vB¢)n m (7.79) + m (- 6 ) = m (v ¢ ¢)n A )n + m (v B (v¢A )n + (vB¢)n = 1.79 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 83 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.15 • The normal relative velocities of the balls are related by the coefficient of restitution. ( v¢A )n - ( v¢B )n = eéë( vA )n - ( vB )n ùû = 0.90 éë7.79 - ( -6)ùû =12.41 • Solve the last two equations simultaneously for the normal velocities of the balls after the impact. ( v¢B )n = 7.1 m/s ( v¢A )n = -5.31 m/s v¢A = -5.31lt + 4.5ln æ 4.5 ö v¢A = 6.96 m/s tan -1 ç ÷ = 40.3° è 5.31 ø n v¢B = 7.1lt +10.39 ln t -1 æ 10.39 ö v¢B = 12.58 m/s tan ç ÷ = 55.6° è 7.1 ø © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 84 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.16 SOLUTION: • Determine orientation of impact line of action. • The momentum component of ball A tangential to the contact plane is conserved. • The total horizontal momentum of the two ball system is conserved. Ball B is hanging from an inextensible • The relative velocities along the line of cord. An identical ball A is released action before and after the impact are from rest when it is just touching the related by the coefficient of restitution. cord and acquires a velocity v0 before striking ball B. Assuming perfectly • Solve the last two expressions for the elastic impact (e = 1) and no friction, velocity of ball A along the line of action determine the velocity of each ball and the velocity of ball B which is immediately after impact. horizontal. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 85 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.16 r 0.5 2r 30 sin SOLUTION: • Determine orientation of impact line of action. • The momentum component of ball A tangential to the contact plane is conserved. mv A Ft mv A mv0 sin 30 0 mvA t vA t 0.5v0 • The total horizontal (x component) momentum of the two ball system is conserved. mv A Tt mv A mvB 0 mvA t cos 30 mvA n sin 30 mvB 0 0.5v0 cos 30 vA n sin 30 vB 0.5vA n vB 0.433v0 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 86 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.16 • The relative velocities along the line of action before and after the impact are related by the coefficient of restitution. vB n vA n ev A n vB n vB sin 30 vA n v0 cos 30 0 0.5vB vA n 0.866v0 • Solve the last two expressions for the velocity of ball A along the line of action and the velocity of ball B which is horizontal. vA n 0.520v0 vB 0.693v0 v A 0.5v0t 0.520v0n vA 0.721v0 tan 1 0.52 46.1 0.5 46.1 30 16.1 vB 0.693v0 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 87 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.17 SOLUTION: • Apply the principle of conservation of energy to determine the velocity of the block at the instant of impact. • Since the impact is perfectly plastic, the block and pan move together at the same velocity after impact. Determine that velocity from the requirement that the total momentum of the block and pan is conserved. A 30 kg block is dropped from a height of 2 m onto the the 10 kg pan of a • Apply the principle of conservation of spring scale. Assuming the impact to be energy to determine the maximum perfectly plastic, determine the deflection of the spring. maximum deflection of the pan. The constant of the spring is k = 20 kN/m. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 - 88 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.17 SOLUTION: • Apply principle of conservation of energy to determine velocity of the block at instant of impact. T1 0 V1 WA y 30 9.812 588 J T2 12 m A v A 22 12 30 v A 22 V2 0 T1 V1 T2 V2 0 588 J 12 30 v A 22 0 v A 2 6.26 m s • Determine velocity after impact from requirement that total momentum of the block and pan is conserved. mA v A 2 mB vB 2 mA mB v3 306.26 0 30 10v3 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. v3 4.70 m s 13 - 89 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Sample Problem 13.17 • Apply the principle of conservation of energy to determine the maximum deflection of the spring. T3 12 m A mB v32 12 30 10 4.7 2 442 J V3 Vg Ve 0 1 kx 2 2 3 1 2 20 10 4.91 10 3 3 2 0.241 J T4 0 Initial spring deflection due to pan weight: x3 WB 10 9.81 3 4 . 91 10 m 3 k 20 10 V4 Vg Ve WA WB h 12 kx42 392x4 4.91 103 12 20 103 x42 392 x4 x3 12 20 103 x42 T3 V3 T4 V4 442 0.241 0 392 x4 4.91 103 12 20 103 x42 x4 0.230 m h x4 x3 0.230 m 4.91 103 m © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. h 0.225 m 13 - 90 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving SOLUTION: • This is a multiple step problem. Formulate your overall approach. • Use work-energy to find the velocity of the block just before impact A 2-kg block A is pushed up against a spring • Use conservation of compressing it a distance x= 0.1 m. The block is momentum to determine then released from rest and slides down the 20º the speed of ball B after incline until it strikes a 1-kg sphere B, which is the impact suspended from a 1 m inextensible rope. The spring constant k=800 N/m, the coefficient of • Use work energy to find the velocity at friction between A and the ground is 0.2, the distance A slides from the unstretched length of nd the spring d=1.5 m, and the coefficient of • Use Newton’s 2 Law to find tension in the rope restitution between A and B is 0.8. When =40o, find (a) the speed of B (b) the tension in the rope. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 91 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving Given: mA= 2-kg mB= 1-kg, k= 800 N/m, mA =0.2, e= 0.8 Find (a) vB (b) Trope • Use work-energy to find the velocity of the block just before impact Determine the friction force acting on the block A Solve for N Sum forces in the y-direction Fy 0: N mA g cos 0 N m A g cos (2)(9.81) cos 20 18.4368 N F f mk N (0.2)(18.4368) 3.6874 N © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 92 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving Set your datum, use work-energy to determine vA at impact. 1 T1 (V1 )e (V1 ) g U12 T2 (V2 )e (V2 ) g 2 Determine values for each term. T1 0, (V1 )e 1 2 1 k x1 (800)(0.1) 2 4.00 J 2 2 x d Datum (V1 ) g mA gh1 mA g ( x d )sin (2)(9.81)(1.6)sin 20 10.7367 J U12 Ff ( x d ) (3.6874)(1.6) 5.8998 J T2 1 1 mAv A2 (1) (v A2 ) 1.000 v A2 V2 0 2 2 Substitute into the Work-Energy equation and solve for vA T1 V1 U12 T2 V2 : 0 4.00 10.7367 5.8998 1.000 vA2 0 vA2 8.8369 m2 /s2 v A 2.9727 m/s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 93 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving • Use conservation of momentum to determine the speed of ball B after the impact • Draw the impulse diagram Note that the ball is constrained to move only horizontally immediately after the impact. Apply conservation of momentum in the x direction Use the relative velocity/coefficient of restitution equation (vB )n (vA )n e [(vB )n (vA )n ] mA v A cos 0 mA vA cos mB vB (2)(2.9727)cos 20 2vA cos 20 (1.00)vB (1) vB cos vA e[vA 0] vB cos 20 vA (0.8)(2.9727) (2) Solve (1) and (2) simultaneously vA 1.0382 m/s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. vB 3.6356 m/s 2 - 94 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving • Use work energy to find the velocity at Set datum, use Work-Energy to determine vB at = 40o 2 T1 (V1 )e (V1 ) g U12 T2 (V2 )e (V2 ) g Determine values for each term. 1 mB (vB )2 V1 0 2 1 T2 mB v22 V2 mB gh2 mB gl (1 cos ) 2 T1 1 Datum Substitute into the Work-Energy equation and solve for vA 1 1 mB (vB ) 2 0 mB v22 mB g (1 cos ) 2 2 v22 (vB ) 2 2 gl (1 cos ) T1 V1 T2 V2 : (3.6356)2 (2)(9.81)(1 cos 40) 8.6274 m 2 /s 2 v2 2.94 m/s © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 95 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Group Problem Solving • Use Newton’s 2nd Law to find tension in the rope • Draw your free-body and kinetic diagrams en et • Sum forces in the normal direction Fn mB an : T mB g cos mB an T mB (an g cos ) • Determine normal acceleration 1.00 m an v22 8.6274 8.6274 m/s2 1.00 • Substitute and solve T (1.0)(8.6274 9.81cos 40) © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. T 16.14 N 2 - 96 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Concept Question Compare the following statement to the problem you just solved. If the coefficient of restitution is smaller than the 0.8 in the problem, the tension T will be… Smaller Bigger If the rope length is smaller than the 1 m in the problem, the tension T will be… Smaller Bigger If the coefficient of friction is smaller than 0.2 given in the problem, the tension T will be… Smaller If the mass of A is smaller than the 2 kg given in the problem, the tension T will be… Smaller Bigger Bigger © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 - 97 Tenth Edition Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics Summary Approaches to Kinetics Problems Forces and Accelerations Velocities and Displacements Velocities and Time Newton’s Second Law (last chapter) Work-Energy ImpulseMomentum F ma G T1 U12 T2 © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. t2 mv1 F dt mv2 t1 2 - 98