* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Problem Solving Drill - Rapid Learning Center
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
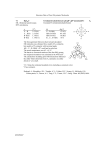
Inorganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 10: Molecular Symmetry and Group Theory Question No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. List all symmetry elements and its point group for CHCl 3. Question (A) E, (B) E, (C) E, (D) E, (E) E, C 3 = C3 2C3, 3σv = C3v 2C3, 3C2, 3σh 2S3, 3σv = D3h C3, σh, S3 = C3h i = Ci A. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Its electronic geometry is distorted tetrahedral. For its molecular geometry, it is pyramidal with 3 H atoms at each of 3 corners, 1 Cl atom at the other and C atom in the centre of a triangular pyramid. Run through the symmetry operations – rotation and plane. B. Correct! Good job! Its electronic geometry is distorted tetrahedral. For its molecular geometry, it is pyramidal with 3 H atoms at each of 3 corners, 1 Cl atom at the other and C atom in the centre of a triangular pyramid. Run through the symmetry operations – rotation and plane. Feedback C. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Its electronic geometry is distorted tetrahedral. For its molecular geometry, it is pyramidal with 3 H atoms at each of 3 corners, 1 Cl atom at the other and C atom in the centre of a triangular pyramid. Run through the symmetry operations – rotation and plane. D. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Its electronic geometry is distorted tetrahedral. For its molecular geometry, it is pyramidal with 3 H atoms at each of 3 corners, 1 Cl atom at the other and C atom in the centre of a triangular pyramid. Run through the symmetry operations – rotation and plane. E. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Its electronic geometry is distorted tetrahedral. For its molecular geometry, it is pyramidal with 3 H atoms at each of 3 corners, 1 Cl atom at the other and C atom in the centre of a triangular pyramid. Run through the symmetry operations – rotation and plane. Correct Answer: B Draw out its 3D structure and run through all the possible symmetry operations. Look up the point group’s character table. Symmetry Elements: E, 2C3, 3σv Point Group: C3v Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 2 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 2. Determine the point group and the polarity of BF4-. Question (A) D4h – Non-polar (B) C4v - Polar (C) C4h – Non-polar (D) Td – Non-polar (E) Ci – Non-polar A. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the highly symmetrical point group with tetrahedron. Check multiple Cn axes with dipole cancellation. B. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the highly symmetrical point group with tetrahedron. Check multiple Cn axes with dipole cancellation. C. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the highly symmetrical point group with tetrahedron. Check multiple Cn axes with dipole cancellation. Feedback D. Correct! Good job. Consider the highly symmetrical point group with tetrahedron. Check multiple Cn axes with dipole cancellation. E. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the highly symmetrical point group with tetrahedron. Check multiple Cn axes with dipole cancellation. Correct Answer: D BF4- has the perfect tetrahedral shape (like CH4) with a point group of Td (E, 8C3, 3C2, 6S4, 6σd). There are multiple high Cn axes (n>1) in Td, all dipoles are cancelled and there is no polarity in BF4-. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 3 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 3. According to VSEPR, Iodine Pentafluoride IF5 has the square pyramidal shape. This one does not follow the Octet rule. IF5 is d2sp3 hybridized and contains 1 lone pair and 5 bonding pairs of valence electrons around the Iodine. Identify the point group and polarity of this molecule. Question (A) D5h, non-polar (B) C4v, polar (C) D4h, non-polar (D) C5v, polar (E) C2v, polar A. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the high C5 rotation and the point group. Remember that only molecules of point groups C1, Cs, Cn, and Cnv can be polar. B. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the high C5 rotation and the point group. Remember that only molecules of point groups C1, Cs, Cn, and Cnv can be polar. C. Correct! Good job! Think about the high C5 rotation and the point group. Remember that only molecules of point groups C1, Cs, Cn, and Cnv can be polar. Feedback D. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the high C5 rotation and the point group. Remember that only molecules of point groups C1, Cs, Cn, and Cnv can be polar. E. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the high C5 rotation and the point group. Remember that only molecules of point groups C1, Cs, Cn, and Cnv can be polar. Correct Answer: C IF5 has the square pyramidal geometry with multiple C5 axes and mirror planes. It has the symmetry elements of E, 2C5 and 5σv, which makes into C5v point group. Recall that only molecules of point groups C1, Cs, Cn, and Cnv can be polar. This is one of them – a polar molecule with C5v point group. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 4 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 4. Determine the symmetry elements of an s-orbital. Question (A) Cn (n=1..∞). (B) Infinite number of mirror planes of symmetry. (C) Center of Inversion i. (D) A and B. (E) A, B and C. A. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: An s-orbital is spherical with the highest symmetry possible. B. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: An s-orbital is spherical with the highest symmetry possible. C. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: An s-orbital is spherical with the highest symmetry possible. Feedback D. Correct! Good job! An s-orbital is spherical with the highest symmetry possible. E. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: An s-orbital is spherical with the highest symmetry possible. Correct Answer: D This sphere shape has every possible symmetry. It contains an infinite number of rotational axes with all possible values of n and mirror planes, plus the center of inversion. This is the point group of a sphere or an atom – the full rotation group, R3. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 5 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 5. A chiral molecule is a molecule that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image. The only chiral point groups are: C1, Cn, Dn, (T, O, and I). The last three are very uncommon, so virtually all chiral molecules fall into the first three types of groups (dissymmetric molecules – no other symmetry but proper rotation Cn). Identify the chirality of these molecules: (1) H2O2; (2) trans-dichloroethene; (3) 2-Butanol. Question (A) (1) (B) (1) (C) (1) (D) (1) (E) (1) Chiral (2) Achiral (3) Chiral. Chiral (2) Chiral (3) Chiral. Achiral (2) Achiral (3) Achiral. Chiral (2) Achiral (3) Achiral. Achiral (2) Achiral (3) Chiral. A. Correct! Good work! Draw out the 3D structures and identify the point groups. If it belongs to one of the three chiral point groups, it is chiral, otherwise it must be achiral. B. Incorrect! Good try! Hint: Draw out the 3D structures and identify the point groups. If it belongs to one of the three chiral point groups, it is chiral, otherwise it must be achiral. C. Incorrect! Good try! Hint: Draw out the 3D structures and identify the point groups. If it belongs to one of the three chiral point groups, it is chiral, otherwise it must be achiral. Feedback D. Incorrect! Good try! Hint: Draw out the 3D structures and identify the point groups. If it belongs to one of the three chiral point groups, it is chiral, otherwise it must be achiral. E. Incorrect! Good try! Hint: Draw out the 3D structures and identify the point groups. If it belongs to one of the three chiral point groups, it is chiral, otherwise it must be achiral. Correct Answer: A (1) HO-OH (C2); (2) trans-CHCl=CHCl (C2h); (3) CH3-CH2-CH(OH)-CH3 (C1) Both H2O2 and 2-Butanol are Cn point groups, therefore they are chiral. transdichloroethene has C2h, hence achiral. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 6 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 6. Irreducible representation is an important concept in group theory. Every symmetric group has a one-dimensional representation called the trivial representation, where every element acts as the one by one identity matrix. Therefore, the trivial representation is _____. Question (A) Reducible. (B) Irreducible. (C) Either reducible or irreducible. (D) Non-primitive. (E) None of the above is correct. A. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the definition of “irreducible representation”. Any onedimensional representation is irreducible, particularly the trivial representation. B. Correct! Good job! Any one-dimensional representation is irreducible, particularly the trivial representation. C. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the definition of “irreducible representation”. Any onedimensional representation is irreducible, particularly the trivial representation. Feedback D. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the definition of “irreducible representation”. Any onedimensional representation is irreducible, particularly the trivial representation. E. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think of the definition of “irreducible representation”. Any onedimensional representation is irreducible, particularly the trivial representation. Correct Answer: B Since the representation is one dimensional then it contains no proper subrepresentation. Therefore it is irreducible. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 7 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 7. A character table is a two-dimensional table whose rows correspond to irreducible group representations, and whose columns correspond to classes of group elements. Such a table contains ______. Question (A) Symmetry classes (elements). (B) Symmetry species. (C) Characters of the group. (D) All of the above. (E) A and B. A. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: Think about the character table’s row and column labels. B. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: Think about the character table’s row and column labels. C. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: Think about the character table’s row and column labels. Feedback D. Correct! Good job! Consider the character table’s row and column labels. E. Incorrect! Good try. Partially correct. Hint: Think about the character table’s row and column labels. Correct Answer: D A character table is a table characters whose rows correspond to irreducible group representation, and whose columns correspond to classes of group elements. The point group is located at the top left-hand corner of the table. The symmetry operations are indicated across the top row of the character table. The symmetry species are indicated on the first column, after the point group. Symmetry labels tell about degeneracies. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 8 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 8. Electronic selection rules for spectroscopic transitions are determined by the transition dipole moment - The criterion for an allowed transition is that the integrand ψ*f z ψi in the Transition-Dipole-Moment Integral have symmetry species A1 and thus be nonzero. NO2 has a bent geometry with an angle of 134. Identify its point group and whether its ground state electronic transition is allowed. Question (A) D2h – allowed. (B) C2 – not allowed. (C) C2v – allowed. (D) C3 – not allowed. (E) C1 – not allowed. A. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Identify each symmetry element and determine the point group. Look up the character table of its point group and see if there is A1 symmetry species. B. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Identify each symmetry element and determine the point group. Look up the character table of its point group and see if there is A1 symmetry species. C. Correct! Good job. Identify each symmetry element and determine the point group. Look up the character table of its point group and see if there is A1 symmetry species. Feedback D. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Identify each symmetry element and determine the point group. Look up the character table of its point group and see if there is A1 symmetry species. E. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Identify each symmetry element and determine the point group. Look up the character table of its point group and see if there is A1 symmetry species. Correct Answer: C NO2 has a trigonal planar electronic pair structure and its geometrical shape is bent, similar to H2O. This molecule contains four symmetry operations: (1) E - the identity operation; (2) C2 - a twofold symmetry axis; (3) σv - the first mirror plane (xz); (4) σv' - the second mirror plane (yz). Hence it is C2v point group with 4 irreducible representations in its character table. Its ground state has A1 symmetry. Therefore the transition is allowed. Solution z, fi e *f z i d Transition Dipole Moment RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 9 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 9. Orbital overlap integrals are encountered in LCAO-MO calculations of molecular electronic wavefunctions Sab = ∫χA* χBdτ . When two atomic orbitals are interacted to form two molecular orbitals, the value of their overlap integral can be an indication of the extent of their interaction. What are the meanings of its value of positive, zero and negative in terms of bonding? Question (A) S > 0: Bonding Interaction; S = 0: Nonbonding; S < 0: Antibonding. (B) S > 0: HOMO; S = 0: Nonbonding; S < 0: LUMO. (C) S > 0: Ionic Bonding; S = 0: Lone Pair; S < 0: Covalent Bonding. (D) S > 0: Ionic Bonding; S = 0: Hydrogen Bonding; S < 0: Nonbonding. (E) None of the above is true. A. Correct! Good Job! Think about meaning of orbital overlap in LCAO-MO, in terms of bonding, antibonding and nonbonding. B. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about meaning of orbital overlap in LCAO-MO, in terms of bonding, antibonding and nonbonding. C. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about meaning of orbital overlap in LCAO-MO, in terms of bonding, antibonding and nonbonding. Feedback D. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about meaning of orbital overlap in LCAO-MO, in terms of bonding, antibonding and nonbonding. E. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about meaning of orbital overlap in LCAO-MO, in terms of bonding, antibonding and nonbonding. Correct Answer: A The Overlap Integral is a measure of the overlap of basis set orbitals to form a molecular orbital. S > 0 indicates a bonding interaction, S < 0 is an antibonding interaction, and S = 0 indicates a nonbonding interaction. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved Question No. 10 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick the answer (4) Go back to review the core concept tutorial as needed. 10. Symmetry-adapted Linear Combinations (SALC) Bases are symmetry-selected linear combinations of atomic orbitals tailored to specific ________. Question (A) Molecules. (B) Atoms. (C) Operations. (D) All of the above are true. (E) None of the above is true. A. Correct! Good work! Symmetry-adapted Linear Combinations (SALC) Bases are symmetryselected linear combinations of atomic orbitals taylored to specific molecules. B. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the molecular shape and bonding. C. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the molecular shape and bonding. Feedback D. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the molecular shape and bonding. E. Incorrect! Good try. Hint: Think about the molecular shape and bonding. Correct Answer: A Symmetry-adapted Linear Combinations (SALC) Bases are symmetry-selected linear combinations of atomic orbitals tailored to specific molecules. SALCs are the linear combinations of basis sets composed of the stretching vectors of the molecule. The SALCs of a molecule can help determine binding schemes and symmetries. The procedure used to determine the SALCs of a molecule is also used to determine the LCAO of a molecule. The LCAO, Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals, uses the basis set of atomic orbitals instead of stretching vectors. The LCAO of a molecule provides a detailed description of the molecular orbitals, including the number of nodes and relative energy levels. Solution RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved