* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congruence - Kids at the Core
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
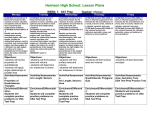
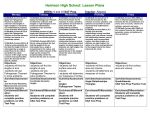
HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Congruence Experiment with transformations in the plane CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.2 Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.3 Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.5 Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using, e.g., graph paper, tracing paper, or geometry software. Specify a sequence of transformations that will carry a given figure onto another. Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.B.6 Use geometric descriptions of rigid motions to transform figures and to predict the effect of a given rigid motion on a given figure; given two figures, use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to decide if they are congruent. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.B.7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent if and only if corresponding pairs of sides and corresponding pairs of angles are congruent. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.B.8 Explain how the criteria for triangle congruence (ASA, SAS, and SSS) follow from the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions. Prove geometric theorems CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.C.9 Prove theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice equidistant from the segment's endpoints. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.C.10 Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.C.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. Make geometric constructions CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.D.12 Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.).Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.D.13 Construct an equilateral triangle, a square, and a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. Congruence Standard Basic: Conceptual “Understand” Standard: Procedural “Doing” Expanded: Application HSG. CO.A.1 Define angle, circle, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments based on the undefined term of a point, a line, the distance along a line and the length of an arc. Ex: How would you determine whether two lines are parallel or perpendicular? HSG. Describe and compare function transformations HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice CO.A.2 on a set of points such as inputs to produce another set of points as outputs, to include translations and horizontal and vertical stretching. HSG. CO.A.3 Describe/Identify the rotations and reflections of a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon that maps each figure onto itself. If the pentagon below is rotated clockwise around its center, the minimum number of degrees it must be rotated to carry the pentagon onto itself is... HSG. CO.A.4 Understand rotations, reflections and translations based on angles, circles, perpendicular lines and line segments. HSG. CO.A.5 Transform a geometric figure given a rotation, reflection or translation using graph paper, tracing paper or geometric software. Create a series of transformations that map a figure onto itself and another geometric figure. HSG. CO.B.6 Understand that rigid transformations preserve size, shape or distance and angle. Generalize, how you could determine if a transformation would maintain congruency from the preimage to the image. Use the definition of rigid motions to determine if figures are congruent. Reflect a given parallelogram with given coordinates over the xaxis. HSG. CO.B.7 Use the definition of congruence, based on rigid motion, to show two triangles are congruent. HSG. CO.B.8 Use the definition of congruence to develop and Andy and Javier are designing triangular explain the triangle criteria: ASA, SSS, SAS. gardens for their yards. Andy and Javier want to determine if their gardens that they build will be congruent by HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice looking at the measures of the boards they will use for the boarders, and the angles measures of the vertices. Andy and Javier use the following combinations to build their gardens. Will these combinations create gardens that enclose the same area? If so, how do you know? a. Each garden has length measures of 12ft, 32ft, and 28ft? b. Both of the gardens have angle measures of 110, 25, and 45 degrees. c. One side of the garden is 20ft another side is 30 ft and the angle between those boards is 40 degrees d. One side of the garden is 20 ft and the angles on each side of that board are 60 degrees and 80 degrees. e. Two sides measure 16ft and 18 ft and the nonincluded angle of the garden measures 30 degrees. HSG. CO.C.9 Prove that when two parallel lines are If line A is parallel to line B find the measure of cut by a transversal the alternate angle C. interior angles are congruent. Write a formal argument to prove two sides are parallel. Apply theorems pertaining to lines and angles (ex: vertical angles are congruent, alternate interior angles are congruent) A carpenter is framing a wall and wants to make sure his edges of his wall are parallel. He is using a crossbrace as shown below. What are several different ways he could verify the edges HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice are parallel. HSG. CO.C.10 Given ΔABC , Prove ≺ BCA is a right angle given the following information... Apply theorems pertaining to triangles (ex: measures of interior angles of a triangle have a sum of 180 degrees, medians of a triangle meet a point, base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent) HSG. CO.C.11 Apply theorems pertaining to parallelograms (ex: opposite sides are congruent Jerry is laying out the foundation for a rectangular outdoor tool shed. He needs to ensure that it is indeed fulfills the definition of a rectangle. The only tools he brought with him are pegs (for nailing in the ground to mark the corners), string and a tape measure. Create a plan for Jerry to follow so that he can be sure his foundation is rectangular. Justify that your plan works. HSG. Describe the process of copying a Bisect an angle ≺ ABC ; Bisect segment AB HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice CO.D.12 congruent segment with a compass and straightedge. Construct perpendicular lines, construct a parallel line to a given line through a point not on the line. HSG. CO.D.13 Describe the process of constructing a regular hexagon inside of a circle using a straightedge and a compass. Construct an equilateral triangle (square, hexagon) so each vertex of the equilateral triangle is on the circle. Donna is building a swing set. She wants to countersink the nuts by drilling a hole that will perfectly circumscribe the hexagonal nuts that she is using. Each side of the regular hexagonal nut is 8mm. Construct a diagram that shows what size drill she should use to countersink the nut. HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Similarity, Right Triangles & Trigonometry Understand similarity in terms of similarity transformations CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.A.1 Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.A.1.A A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.A.1.B The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.A.2 Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.A.3 Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems involving similarity CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.B.4 Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.B.5 Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.C.6 Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.C.7 Explain and use the relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.C.8 HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems.* Apply trigonometry to general triangles CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.D.9 (+) Derive the formula A = 1/2 ab sin(C) for the area of a triangle by drawing an auxiliary line from a vertex perpendicular to the opposite side. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.D.10 (+) Prove the Laws of Sines and Cosines and use them to solve problems. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.SRT.D.11 (+) Understand and apply the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines to find unknown measurements in right and nonright triangles (e.g., surveying problems, resultant forces). Similarity, Right Triangles & Trigonometry Standard Basic: Conceptual “Understand” Standard: Procedural “Doing” Expanded: Application Given a center and a scale factor, verify experimentally, that when dilating a figure in a coordinate plane, a segment of the preimage that does not pass through the center of the dilation is parallel to its image when the dilation is performed. HSG. SRT.A.1 The equation of the line h is 2x+y=1. Line m is the image of line h after a dilation of scale factor 4 with respect to the origin. What is the equation of the line m…. HSG. SRT.A.2 Johnny used a projector to project the below image on the wall in the classroom. He wants to know if the original image is similar to the one on the wall. How can he verify they are similar. How could he determine the scale factor if they are similar? Given two figures, determine whether they are similar and explain their similarity based on the equality of corresponding angles and the proportionality of corresponding sides. HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice HSG. SRT.A.3 Describe a sequence of similarity transformations that shows that Δ ABC is similar to Δ XYZ HSG. SRT.B.4 Prove that ΔABC is similar to ΔXY C (use AA, SAS, SSS) HSG. SRT.B.5 Prove that ΔABC is congruent to ΔXY C (use similarity criteria) HSG. SRT.C.6 Understand the relationships of Explain why cos( x ) =sin(90 x ) for x such that corresponding angles of similar right 0 ≺ x ≺ 90 triangles. (leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles) HSG. SRT.C.7 Explain why cos( x ) =sin(90 x ) for x Explore the sine of an acute angle and the cosine of its complement and determine their such that 0 ≺ x ≺ 90 relationship. Given Triangle ABC with right angle C, show that the Sin(A)=cos(B) HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice HSG. SRT.C.8 Given Triangle ABC with right Angle C and side a=12 and side b=16, find side c, angle A and angle B. A boat is approaching a fort on the coastline of a river. The front of the boat is 2 feet above the water and an observer in the fort is 110 feet above the water. At noon, the observer in the fort measured the angle of depression to the front of the boat to be 6 degrees. Five minutes later, the observer measured the angle of depression to the front of the boat had increased by 49 degrees. Calculate the average speed at which the boat traveled toward the fort. HSG. SRT.D.9 For a triangle that is not a right triangle, draw an auxiliary line from a vertex, perpendicular to the opposite side and derive the formula, A = 1/2ab sin(c) , for the area of a triangle, using the fact that the height of the triangle is h = a sin(c) HSG. SRT.D.10 Using trigonometry and the relationship among Use the laws of sines and cosines to sides and angles of any triangle, such as solve real world problems sin(C) = (h/a) prove the Law of Sines. HSG. SRT.D.11 Understand the law of sines and cosines to can help find unknown measures in right triangles and non right triangles Circles Understand and apply theorems about circles CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.1 Prove that all circles are similar. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.2 HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.3 Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.4 (+) Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle. Find arc lengths and areas of sectors of circles CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.B.5 Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. Circles Standard Basic: Conceptual “Understand” Standard: Procedural “Doing” As shown in the diagram below, circle A has a radius of 3 and circle B has a radius of 5. Using transformations, explain why circles A and B are similar... Expanded: Application HSG. C.A.1 HSG. C.A.2 Understand that inscribed angles on Using definitions, properties, and theorems, a diameter are right angles identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii and chords. Include central, inscribed and circumscribed angles. HSG. C.A.3 Construct an argument to show that Using definitions, properties and theorems, prove Jessica works at a daycare center and opposite angles in a an inscribed properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in she is watching three rambunctious An archaeologist dug up an edge piece of a circular plate. He wants to know what the original diameter of the plate was before it broke. However, the piece of pottery does not display the center of the plate. How could he find the original dimensions? HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice quadrilateral are supplementary. a circle… Construct inscribed circles of a triangle, construct circumscribed circles of a triangle. toddlers. One of the toddlers is in a crib at point A, another toddler is in her high chair at point B and the third toddler is in a playstation at point C. Where can jessica position herself so that she is equidistant from the three children. Create a diagram and construct an argument to prove. HSG. C.A.4 Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle. HSG. C.B.5 Find the arc length of a circle… Using similarity, derive the formula for the area of a sector…. In the diagram below of circle A, find the area of sector ABC in terms of π given the following information…. Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations Translate between the geometric description and the equation for a conic section CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.A.1 Derive the equation of a circle of given center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem; complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle given by an equation. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.A.2 Derive the equation of a parabola given a focus and directrix. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.A.3 (+) Derive the equations of ellipses and hyperbolas given the foci, using the fact that the sum or difference of distances from the foci is constant. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.B.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.B.5 HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.B.6 Find the point on a directed line segment between two given points that partitions the segment in a given ratio. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GPE.B.7 Use coordinates to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., using the distance formula.* Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations Standard HSG. GPE.A.1 Basic: Conceptual “Understand” If the coordinate of point H in the diagram below is (x,y) and the length of segment DH is 4 units, can you write a rule that represents the relationship of the x value and the radius? Why is this relationship true? As point H rotates around the circle, does this relationship stay true? Standard: Procedural “Doing” Expanded: Application Use the Pythagorean Theorem to derive the equation of a circle, given the center and the radius… Given an equation of a circle, complete the square to find the center and radius Given a focus and directrix, derive the equation HSG. Understand that every point on the HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice GPE.A.2 parabola is the same distance from the focus and the directrix... of a parabola... HSG. GPE.A.3 Given the foci derive the equation of the ellipse. HSG. GPE.B.4 Prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle… Prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0,2) Classify the following quadrilateral given the points (0,0), (2,5), (8, 3), and (6, 2). HSG. GPE.B.5 If the product of the slopes of two lines is 1, what does that say about the lines? There is an instance when there is two perpendicular lines but the product of their slope is not 1, explain the situation of when this occurs. Find equations of lines based on certain slope criteria: finding the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point HSG. GPE.B.6 What are the coordinates of the point on the directed line segment frk K(5,4) to L(5,1) that partitions the segment into a ration of 3 to 2? HSG. GPE.B.7 Use coordinate geometry and the distance formula to find the perimeters of polygons and the areas of triangles and rectangles. John was visiting three ciites. THey had coordinate points of (3,0), (3,0) and (0,4). If he visited all cities and came back to original starting point of (0,0), how many miles did he travel? (1 unit = 1mile) HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Geometric Measurement and Dimension Explain volume formulas and use them to solve problems CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GMD.A.1 Give an informal argument for the formulas for the circumference of a circle, area of a circle, volume of a cylinder, pyramid, and cone. Use dissection arguments, Cavalieri's principle, and informal limit arguments. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GMD.A.2 (+) Give an informal argument using Cavalieri's principle for the formulas for the volume of a sphere and other solid figures. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GMD.A.3 Use volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres to solve problems.* Visualize relationships between twodimensional and threedimensional objects CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.GMD.B.4 Identify the shapes of twodimensional crosssections of threedimensional objects, and identify threedimensional objects generated by rotations of twodimensional objects. HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Geometric Measurement and Dimension Standard Basic: Conceptual “Understand” Standard: Procedural “Doing” Expanded: Application HSG. GMD.A.1 Explain the formulas for circumference of a circle and the are of a circle by determining the meaning of each term or factor. HSG. GMD.A.2 Understand Cavalieri's principle Two stacks of 23 quarter each are shown below. One stacks to form a cylinder but the other stack does not. Use Cavalieri's principle to explain why the volumes of these two stacks of quarters are equal. HSG. GMD.A.3 Solve problems using volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones and spheres A cookie factory is making cookies in a pyramid shape with an equilateral triangle as its base. We know that the lateral edge of the cookie is 2 cm long and the base edge of the cookie is 3 cm long. Find the volume of the cookie. Also, if each cookie is wrapped totally in aluminum foil. Prove that the minimum surface of foil necessary to wrap 100 cookies is greater than 960 cm squared. HSG. GMD.B.4 When rotating a square (2D), what 3D figure does it generate? HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice Modeling with Geometry Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder).* CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.MG.A.2 Apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot).* CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.MG.A.3 Apply geometric methods to solve design problems (e.g., designing an object or structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios).* Standard HSG. MG.A.1 Basic: Conceptual “Understand” Standard: Procedural “Doing” Expanded: Application Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects Consider a rectangular swimming pool 30 feet long and 20 ft wide. The shallow end is 3 and half feet deep and extends for 5 feet. Then for 15 feet (horizontally) there is a constant slope downwards to the 10 footdeep end. a. Sketch the pool and indicate all measure on the sketch. b. How much water is neede to the fill the pool to the top? c. One gallon of pool paint covers approximately 75 sq feet of surface. How many gallons of paint are needed to paint the inside walls of the pool? If paint HS Geometry Math Question Stem Bank: Common Core State Standards Standards for Mathematical Practice comes in 5 gallon cans, how many can do you need? d. How many 6 inch square ceramic tiles are needed to tile the top 18 inches of the inside faces of the pool? e. HOw much material is needed to make a rectangular pool cover that extends 2 feet beyond the pool on all sides? ***This covers all three standards*** HSG. MG.A.2 Use the concept of density when referring to situations involving area and volume models, such as persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot. HSG. MG.A.3 Solve design problems by designing an object or structure that satisfies certain constraints such as minimizing cost or working with a grid system.