* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
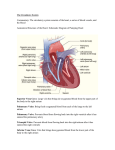
Chapter 1 1. The ability to maintain a constant internal environment in the body is called homeostasis. 2. Cells are considered to be the basic building blocks of the body. 3. The sizes of various cells in humans range from 200nm to several centimeters. 4. The cell material is enclosed by a covering called a semipermeable membrane. 5. There are approximately 75 trillion cells in the human body, of which 1/3 are red blood cells. 6. The process called mitosis is the qualitative reproduction of a cell by division. 7. The body is approximately 56 percent fluid. 8. The musculoskeletal system provides locomotion. 9. Bones and cartilage are the principal types of tissue forming the skeleton. 10. The central nervous system integrates and assimilates data. 11. The sensory nervous system provides information on the external and internal environments. 12. The autonomic nervous system operates mostly at the subconscious level. 13. The endocrine system is a chemical communications and control system within the body. 14. Homeostasis is the process by which the body responds to the environment and regulates levels of sugars, salts, water, acid-base balance, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. 15. A semipermeable membrane selectively permits materials to pass between the inside of a cell and its external environment. 16. The respiratory system takes in oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. 17. The GI system processes food so that it is absorbed into the body. 18. The musculoskeletal system provides locomotion. 19. The musculoskeletal system consists mostly of bones and cartilage. 20. Chemicals called hormones are secreted by eight major glands of the endocrine system. 21. The kidneys act to filter the blood. Chapter 2 1. The upper chambers of the heart are called atria. 2. The lower chambers of the heart are called ventricles. 3. The superior and inferior vena cava return blood to the right atrium. 4. The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. 5. Blood leaves the right ventricle via the pulmonary artery. 6. The mitral valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle. 7. The great artery leaving the left side of the heart is called the aorta. 8. Blood is about 40 % red cells by volume. 9. Very small vessels called capillaries have diameters in the micrometer range. 10. The average human heart weighs about 300g. 11. The sac surrounding the heart is the pericardium. 12. Heart muscle is called myocardium. 13. The SA node is the heart pacemaker. 14. The period of contraction is called systole. 15. An electrical potential is generated across a cell wall because of a difference in ions concentration. 16. The cell wall is a semipermeable membrane. 17. A phenomenon known as the sodium pump keeps sodium ions predominantly outside of the cell wall. 18. Action potentials have amplitude of about 30mV. 19. Resting potentials are about -70mV. 20. The delay line in the heart’s electro-conduction system is called the AV node. 21. The five principal structures of the heart’s electro-conduction system are sinoatrial (SA) node, bundle of His, atrioventricular (AV) node , the bundle of branches, and the Purkinje fibers. 22. Action potentials travel down the conduction system at the rates of 40 cm/s between SA and AV nodes, and at 45 cm/s after the SA node. 23. The AV delay is about 110 ms. 24. The ECG is a recording of the heart’s electrical activity. 25. A heart rate that is too slow is called bradycardia. 26. A heart rate that is too fast is called tachycardia. 27. Atrial fibrillation is an arrhythmia in which the upper chambers of the heart quiver rather than beat. Chapter 6 1. Long-term(more than a few minutes) ECG monitoring is usually done with column electrode. 2. EEG electrodes are used to record bioelectric potentials arising in the brain. 3. A(n) active sensor requires an external ac or dc electrical excitation source. 4. A(n) passive sensor requires no external ac or dc electrical excitation source but generates its own electrical energy. 5. List five different forms of sensor error: insertion , application , characteristic, dynamic, and environmental. 6. Bubbles in a blood pressure transducer line and improper placement of the transducer result in what are called application errors. 7. Departure of a transducer characteristic from the ideal characteristic is the sensitivity error. 8. The resolution of a sensor describes the smallest incremental of an input parameter that can be detected in the output signal.