* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
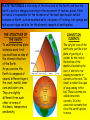
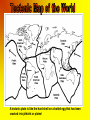
L.O.1: To know the structure of the earth. L.O.2: To understand the theories of continental drift and plate tectonics. Imagine the Earth as a hardboiled egg……………………. The thin brittle shell is the crust that humans live on. The thick jelly like white is the deep hot magma beneath the surface. The yellow yolk is the core of the earth. PLATE TECTONICS is the study of the structure of the Earth, and how the Earth's surface changes according to the movement of tectonic plates. Plate tectonics is responsible for the formation of the most spectacular natural features on Earth, such as mountain belts, volcanoes, rift valleys, hot springs and mid-ocean ridges and also for the dramatic impacts of earthquakes. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH To understand how plate tectonics work, first you must have an idea of the internal structure of the Earth. As you can see, the Earth is composed of several different layers, the crust, mantle, inner core and outer core. They are slightly different from each other in terms of thickness, temperature and density. CONVECTION CURRENTS The very hot core of the earth acts just like a hot plate or gas ring of a cooker. As the rock at the bottom of the mantle is heated by the core, it starts to rise causing movements or currents in the rock. The result is rather like a pan of soup coming to the boil. These currents are called convection currents. It is the convection currents that force the earth’s plates to move. The core The core has two layers: the inner core and the outer core. The inner core is a sphere composed mainly of iron and nickel. Although the inner core is extremely hot (around 6650ºC), the huge pressures in the centre of the Earth mean that the inner core is solid. The inner core is surrounded by the outer core. The outer core has the same composition as the inner core but it exists as a liquid instead of a solid due to slightly lower pressure. Temperatures in the outer core are estimated to be around 4700ºC. It is the heat from the core which generates convection currents on the mantle and drives plate tectonics. The Crust On the very outside of the Earth is the crust. The crust is not a continuous layer, but is made up of a number of continental and oceanic tectonic plates which fit together like pieces of a jigsaw. The Mantle Surrounding the core lies a layer known as the mantle. It reaches temperatures of 3000ºC. The mantle is composed of dense, rocky material which ranges from being virtually solid near the lower boundary with the core, to more soft and squidgy towards the boundary with the overlying layer, the crust . Mantle material is less dense than the core, but still denser than the outer layers of the earth. Maps to Show the Earth’s Tectonic Plates The are two types of tectonic plates forming the earth’s crust continental plates and oceanic plates. Continental crust, is much older and far thicker, forming all of the large land masses. Oceanic crust is much younger and thinner, it underlies all the great ocean basins. The point where two or more plates meet is known as a plate boundary Picture of the San Andreas Fault - the Plate Boundary Between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate Diagram to Show a Cross-Section of the Earth’s Crust Continental Drift In 1912 Alfred Wegener published a theory to explain why the Earth looked like a huge jigsaw. He found evidence in rocks and fossils found all over the world which suggested that the continents of the earth all used to be joined together. He believed that 225 million years ago the continents were once joined forming a supercontinent he called Pangaea. Over 180 million years ago this supercontinent began to "break up" due to the convection (heat) currents underneath the earth’s crust. The broken pieces, which were floating on top of the mantle, began to drift in all directions in a process called continental drift. Diagram to Show Continental Drift Plate Tectonics During the 20th Century, scientists developed Wegener’s ideas and came up with the theory of Plate Tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics suggested that the crust of the Earth is split up into seven large plates (or ‘slabs’ of rock) and a few smaller ones, all of which are able to slowly move around on the Earth's surface. They float on the semi-molten mantle rocks. The plates are forced to move around by convection (heat) currents within the very hot rocks beneath the crust. The crusts may only move a few millimeters a year, but as the earth is about 4000 million years old the effects have been very large!!! A tectonic plate is like the hard shell on a boiled egg that has been cracked into pieces or plates!