* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mischel`s Situational Personality
Survey
Document related concepts
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Relational aggression wikipedia , lookup
Team composition wikipedia , lookup
Zero-acquaintance personality judgments wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
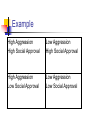
Mischel’s Situational Personality Bryan Hall Kristi Simmons Overview Mini-Bio Personality Aggregation Mischel’s Position on Personality Personality vs. Situation Debate Personality Traits determine how individuals react in everyday occurrences Personality assumes people are characterized by distinctive qualities that are invariant across situations and time Research is counter to this claim Aggregation Acknowledge the importance of situations Aggregate the individual’s behavior over many different situations to give a “true score” Aggregation Example Walter Mischel Biography Born 1930 Vienna, Austria Raised in Brooklyn, New York Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology from Ohio State in 1956 Taught at University of Colorado 1956-1958 Harvard University 1958-1962 Stanford University 1962-1983 Columbia University 1983-Present Another Viewpoint Mischel argues Traits lack internal consistency and crosssituational generality Low agreement in trait structure of individuals described by raters and other methods Low correlations between traits and behaviors Behaviors are predicted better by other methods Situational Personality Mischel proposes a cognitive-affective system theory of personality Situational Personality: Situation Determines Behavior If…Then… People are characterized by stable individual differences in their overall behavior, but also by distinctive and stable patterns of situation-behavior relations For example, Amy does X when A occurs, but Y when B occurs How Behavior Varies Across Situations Summer Camp Examined children’s interactions over the summer Two main features examined: Valence (positive or negative) Type of person involved in interaction (adult counselor or child peer) Situation-Behavior Profiles for Verbal Aggression for Two Children at Two Different Time Samples Results Frequencies of behavior were standardized so that any remaining variance would be attributable to the individual’s distinctive personal qualities Found meaningful stable situation-behavior profiles Indicates there are characteristics intraindividual patterns in how individuals relate to different psychological conditions and that these patterns form a behavioral signature that reflects personality coherence Enduring Characteristics Encodings or construal (of self, others, situations, etc.) Expectancies and beliefs (about outcomes and one’s own efficacy) Competencies (for the construction and generation of social behavior) Subjective values Self-regulatory plans and strategies in the pursuit of goals Personality vs. Situation Debate Personality Determines Behavior OR Situation Determines Behavior Situationist View Small Correlation Between Personality and Behavior (~.30) Richard Nisbett (1980): Revised Personality-behavior Correlation (~.40) Still Small Personality Arguments Small Personality-behavior correlations ≠ Situational Variables Actual Relationship Between Personality and Behavior Higher Than .40 .40 Correlation Not Small Does Not Predict Specific Time in Specific Situation Personality Arguments Choosing Situations Reflects Personality Personality Traits Useful Psychological Tools Improvements in Personality Research Personality View Emotional Personality Traits Affect Behavior Expressions of Behaviors Change Example: Display Different Behaviors in Different Situations Personality: Enduring Genotypes Expressed in Diverse Phenotypes Situationist: Behavior Dependent on Situation Example Aggression (Personality Variable), Social Approval (Personality Variable), and Home vs Party (Situational Variable) Example High Aggression High Social Approval Low Aggression High Social Approval High Aggression Low Social Approval Low Aggression Low Social Approval Alker (1972): Interactionism Interactionist Perspective: Traits and Situations Interact to Influence Behavior Behavior = personality x interpretation of situation Individual Differences in PersonalitySituation Relationship Kenrid et al. (1990): Trait Appears Only in Necessary Situation Alternative View Bem (1972): Trait Like vs. Situational People Are Traits Consistent Across Cultures? Big 5 Found in Other Cultures Culture Specific Traits Exist Expression of Traits Influenced By: Situation Culture Matthews, G., Deary, I., & Whiteman, M. (2003). Personality Traits. 58.