* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Die assesseringsproses
Implicit learning wikipedia , lookup
Problem-based learning wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative learning wikipedia , lookup
Instructional scaffolding wikipedia , lookup
Learning styles wikipedia , lookup
Concept learning wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Differentiated instruction wikipedia , lookup
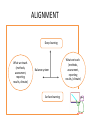
THE PRINCIPLE OF ALIGNMENT EDA 122 ALIGNMENT OUTCOMES PROCESS ALIGNMENT PRODUCT PROCESS OUTCOMES WHAT WHEN WRONG? ALIGNMENT Deep learning What we teach. (methods, assessment, reporting results, climate) Balance system Surface learning What we teach. (methods, assessment, reporting results, (climate) BIGGS MODEL DISTINGUISH BETWEEN DEEP AND SURFACE LEARNING ACHIEVING ALIGNMENT • Setting learning outcomes Make use of active verbs (leads us to design activities to achieve the outcome) Levels of achievement • Selecting learning and teaching activities Learning styles, active participation • Assessing and grading the student Assess the outcome, approach to assessment STUDY THE EXAMPLE IN TERMS OF • THE IMPETUS BEHIND THE LESSON OUTCOMETHE ACTION VERB AND • WHAT IS EXPECTED OF THE LEARNER? • Mastering the skill will enable learners to concentrate on the HOW and not merely WHAT to think. When writing a lesson outcomes an action verb is the impetus to how the outcome should be demonstrated. In the following example the meaning of an action verb is clarified in terms of what is expected of the learners. • THE LEARNERS SHOULD BE ABLE TO PRESENT THEIR FINAL PRODUCT BY MEANS OF MAKING A CREATIVE DRAWING OF THE DIFFERENT PARTS OF A MACHINE. • THE LEARNERS SHOULD BE ABLE TO DRAW A LINE BETWEEN TWO POINTS. • In the first case it indicates the learner’s ability to synthesis previous knowledge into one diagram where as in the second outcome learners should be able to apply their previous knowledge in connecting the two points. When using active verbs identify the context in which the outcome must be demonstrated. Example Identify active verbs Learning outcome Assessment standard : Do investigations and collect data: Investigate the possiblities and the usage of materials and find out how it works. Lesson outcome: Learners will be able to gather data on the increase of temperature over a period of time; and compare the temperature over the different seasons. Activity: Measure the temperature over the different seasons and determine the average of the temperature. Assessment: Learners will be assessed on how they noted the data in the tabels as well as the interpretations that they make in terms of the temperature differences. How do I address: • Learners higher cognitive thoughts? • All three domains of the learner? • The critical Outcomes? THROUGH ASKING THE RIGHT QUESTIONS ON THE RIGHT LEVELS COGNITIVE DOMAIN/ADAPTED VERSION CREATIVE EVALUATION COMPARE 40% SYNTHESIS DESIGN ANALYSE TABULATE APPLICATION APPLY COMPREHENSION INTERPRET KNOWLEDGE RECALL 60% COGNITIVE Knowledge Recognition or recalling of Name list state define ideas Comprehension Requires an understanding of facts Compare discuss match illustrate Application Where the learners can use theory in a new situation Solve predict draw differentiate Analysis The breakdown of content into parts and discovery the relationship between parts Analyzed identify Synthesis Recombination of part into a whole Organise design synthesis Evaluation Judgment about the theory Evaluate assess critise defend PSYCHOMOTOR Imitation Early stages of development of complex skill and involves the repetition of an action Begin come try do Manipulation Continues to repeat a specific skill until it becomes a habit Need gather execute improve Exactness Skill has been acquired and the execution of the skill is fast and occurs smoothly Achieve progress accelerate Articulation Needs a higher level of exactness Adapt change reorganize Spontaneity The response is automatic individual starts to experiment. Inisiates new ideas new motor manipulations Arrange construct create design refine Criteria for the first team. AFFECTIVE Acceptance receiving Acceptance refers to eagerness to accept or give attention Ask follow choose describe recognize Reaction responding Reaction refers to the active involvement of the learner Agree answer follow request Appreciation /value The learner sees the value of the activity theme module the motivation to execute Defend choose accept take Organizing This is about the organization of Compare order values into the system sees the participate relation between the situation and the integration Characterizing Refers to the person being charactererised by his values develops a consistent value system Behave defend advocate demonstrate THEME: POLLUTION 1. List differents types of pollution 2. Distinguish between water- and air pollution 3. Predict what will happen if air pollution is not stopped 4. Analyse the current situation and identfy the most dangerous type of pollution 5. Design a plan on how to improve the current state of the atmosphere 6. Critically evaluate your plan against the criteria set for what the % must be for human to survive in RELATIONSHIP AND PROGRESSION PSYCHOMOTOR Early stages of development Begin come try do of complex skill and involves Try and make a microscopic slide of an the repetition of an action epidermis Continues to repeat a specific skill until it becomes a habit Need gather execute improve Try again and make one with no air bubbles of the epidermis Skill has been acquired and the execution of the skill is fast and occurs smoothly Achieve progress accelerate Make one with no air bubbles and with only a few cells Needs a higher level of exactness Adapt change reorganize Make one with only one layer of cells The response is automatic individual starts to experiment. Inisiates new ideas new motor manipulations Arrange construct create design refine Makes one with only one cell to see all the part very clearly HOLISTIC ASSESSMENT • • • • Domain: cognitive, affective, psychomotor; Different approaches to assessment; Different assessment methods; Learner must be developed in totality, must develop life skills (see critical outcomes).