Minutes 23 11 2010 - the University Sector Framework
... uses it in order to avoid leaners that have entered via an RPL route being “tagged” with this label. ...
... uses it in order to avoid leaners that have entered via an RPL route being “tagged” with this label. ...
Nathan and Sawyer Foundations of Learning Sciences
... Sociocultural scholars draw on the classic theories of the Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky, who argued that social interaction was the primary driver of intellectual development. He argued that thought emerged during development as social interaction gradually became internalized. Through mechanis ...
... Sociocultural scholars draw on the classic theories of the Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky, who argued that social interaction was the primary driver of intellectual development. He argued that thought emerged during development as social interaction gradually became internalized. Through mechanis ...
National Institute of Education
... model that explains the idea of user-friendliness in terms of IT systems operating as an easy-to-access reflective learning tool. Further, that the quality of critical thinking interaction via IT software depends on both humanistic and instructional technology design considerations which affect the ...
... model that explains the idea of user-friendliness in terms of IT systems operating as an easy-to-access reflective learning tool. Further, that the quality of critical thinking interaction via IT software depends on both humanistic and instructional technology design considerations which affect the ...
Diapositiva 1
... Reciprocal listening: The listener is required to take part in the interaction. Nonreciprocal listening: The listener (often to his or her frustration) has no opportunity to answer back , clarify understanding, or check that he or she comprehended correctly. In designing listening tasks, it is impor ...
... Reciprocal listening: The listener is required to take part in the interaction. Nonreciprocal listening: The listener (often to his or her frustration) has no opportunity to answer back , clarify understanding, or check that he or she comprehended correctly. In designing listening tasks, it is impor ...
communities of practice
... relationships that seriously inhibit entry and participation. There is a risk, as Jean Lave and Etienne Wenger acknowledge, of romanticizing communities of practice. However, there has been a tendency in their earlier work of falling into this trap. 'In their eagerness to debunk testing, formal educ ...
... relationships that seriously inhibit entry and participation. There is a risk, as Jean Lave and Etienne Wenger acknowledge, of romanticizing communities of practice. However, there has been a tendency in their earlier work of falling into this trap. 'In their eagerness to debunk testing, formal educ ...
Learning-Centered Learning: Theory Into Practice by Jim Reynolds
... teaching activities. We know that learning can occur without teaching and that teaching does not ensure learning. That is not to say that learning cannot or does not occur from teaching activities. The debate is not over the need or value of teaching activities, but over the need to focus and concen ...
... teaching activities. We know that learning can occur without teaching and that teaching does not ensure learning. That is not to say that learning cannot or does not occur from teaching activities. The debate is not over the need or value of teaching activities, but over the need to focus and concen ...
21st Century Learning: Research, Innovation and Policy
... sweeping and costly reforms. Although there was some real initial progress, these reforms have ultimately come up against a wall, or rather a ceiling, beyond which further progress seems impossible, leading increasing numbers of school administrators and educators to wonder whether schools do not ne ...
... sweeping and costly reforms. Although there was some real initial progress, these reforms have ultimately come up against a wall, or rather a ceiling, beyond which further progress seems impossible, leading increasing numbers of school administrators and educators to wonder whether schools do not ne ...
full text pdf
... Although children are regularly showered with environmental knowledge, this is rarely transformed into concerned action, probably because it is not meaningful for the learner and/or is highlighted at the expense of a personalized process of learning. Research in Education for Sustainable Development ...
... Although children are regularly showered with environmental knowledge, this is rarely transformed into concerned action, probably because it is not meaningful for the learner and/or is highlighted at the expense of a personalized process of learning. Research in Education for Sustainable Development ...
Constructivism Definition Constructivism is a philosophy of learning
... concepts for understanding and responding to physical experiences within his or her environment. Piaget further attested that a child's cognitive structure increases in sophistication with development, moving from a few innate reflexes such as crying and sucking to highly complex mental activities. ...
... concepts for understanding and responding to physical experiences within his or her environment. Piaget further attested that a child's cognitive structure increases in sophistication with development, moving from a few innate reflexes such as crying and sucking to highly complex mental activities. ...
Lifelong learning: overcoming the language barrier at the Vaal
... learners to engage in the process of critical thinking if they can barely construct a sentence or paragraph, or for that matter analyse a text and argue a point in a language which is not their mother tongue (van den Berg, 2000). Language development is thus important, not only in itself but also du ...
... learners to engage in the process of critical thinking if they can barely construct a sentence or paragraph, or for that matter analyse a text and argue a point in a language which is not their mother tongue (van den Berg, 2000). Language development is thus important, not only in itself but also du ...
Final Learning Theorists
... Behaviorism theories define learning as “semi-permanent change in behavior.” In other words, learning has only taken place if a change in behavior is evident (Innovative LearningBehaviorism 2013). The Behaviorist pedagogy aims to promote and modify observable behavior. It considers learning to be a ...
... Behaviorism theories define learning as “semi-permanent change in behavior.” In other words, learning has only taken place if a change in behavior is evident (Innovative LearningBehaviorism 2013). The Behaviorist pedagogy aims to promote and modify observable behavior. It considers learning to be a ...
LearningTaxonomiesElmendorf - the Biology Scholars Program
... First, learning taxonomies can be used to design better assessments. At the most basic level, this means aligning questions on an assignment or exam with a learning taxonomy to ensure that the questions you are asking accurately represent the full range of expected levels of student understanding. ...
... First, learning taxonomies can be used to design better assessments. At the most basic level, this means aligning questions on an assignment or exam with a learning taxonomy to ensure that the questions you are asking accurately represent the full range of expected levels of student understanding. ...
Setting Up Interesting Learning Opportunities
... All of the strategies that we’ve discussed are ways that teachers can use to create interesting learning opportunities for children who might not otherwise be interested in practicing a skill. The purpose or end result of each of these strategies is to draw a child into a learning situation. It’s im ...
... All of the strategies that we’ve discussed are ways that teachers can use to create interesting learning opportunities for children who might not otherwise be interested in practicing a skill. The purpose or end result of each of these strategies is to draw a child into a learning situation. It’s im ...
ppt
... In form-focused ICALL, the interaction workflow proceeds as follows: In response to some prompt or question by the tutor, ...
... In form-focused ICALL, the interaction workflow proceeds as follows: In response to some prompt or question by the tutor, ...
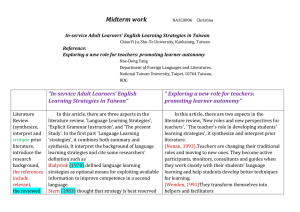
Midterm work
... comprehensible input in the target language. Ellis (1994, 2001) also suggested that the consciousness raising tasks appear to be an effective type of classroom activity. Norris and Orgeta (2000) believed that explicit types of instruction are more effective than implicit types, and the instruction e ...
... comprehensible input in the target language. Ellis (1994, 2001) also suggested that the consciousness raising tasks appear to be an effective type of classroom activity. Norris and Orgeta (2000) believed that explicit types of instruction are more effective than implicit types, and the instruction e ...
Flipped Classroom - "C. Marchesi" – Mascalucia
... Class activities may include: using math manipulatives and emerging mathematical technologies, in-depth laboratory experiments, original document analysis, debate or speech presentation, current event discussions, project-based learning, and skill development or concept practice. ...
... Class activities may include: using math manipulatives and emerging mathematical technologies, in-depth laboratory experiments, original document analysis, debate or speech presentation, current event discussions, project-based learning, and skill development or concept practice. ...
TEL 315 Resiliency Talk
... individuals. Language is absolutely critical for cognitive development. A child’s thought processes are internalized versions of social interactions that are largely verbal in nature. Places greater importance on interactions with adults and other more advanced individuals. ...
... individuals. Language is absolutely critical for cognitive development. A child’s thought processes are internalized versions of social interactions that are largely verbal in nature. Places greater importance on interactions with adults and other more advanced individuals. ...
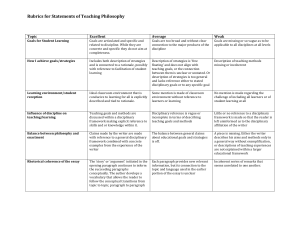
Rubrics for Statements of Teaching Philosophy
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
... Description of strategies is ‘free floating’ and does not align with teaching goals, or the connection between them is unclear or unstated. Or description of strategies is too general and lacks referenc ...
3.1 Presentation
... Encourage learner construction of information and projects Use discovery or guided discovery approaches Have a foundation in situated cognition and its associated notion of ...
... Encourage learner construction of information and projects Use discovery or guided discovery approaches Have a foundation in situated cognition and its associated notion of ...
Hey, Teach! `Lo Learner!
... Addresses pt’s desire or willingness to learn Physical & cognitive abilities, developmental level, physical wellness, thought processes ...
... Addresses pt’s desire or willingness to learn Physical & cognitive abilities, developmental level, physical wellness, thought processes ...
Educating Students with Significant Disabilites
... Strengthening the interactive relationship between the caregiver and the child Beliefs All young children learn through play They need to be encouraged to explore their environment and objects in their environment That all very young children learn by being active, rather than passive recipi ...
... Strengthening the interactive relationship between the caregiver and the child Beliefs All young children learn through play They need to be encouraged to explore their environment and objects in their environment That all very young children learn by being active, rather than passive recipi ...
What is formative assessment?
... (1) current perceptions of the task and the physical, social, and instructional context within which it is embedded; (2) activated domain-specific knowledge and (meta)cognitive strategies related to the task; and (3) motivational beliefs, including domain-specific capacity, interest and effort belie ...
... (1) current perceptions of the task and the physical, social, and instructional context within which it is embedded; (2) activated domain-specific knowledge and (meta)cognitive strategies related to the task; and (3) motivational beliefs, including domain-specific capacity, interest and effort belie ...
Document
... MLH goes on to get several more examples. The kids are apparently having difficulty with Question 1 under READING CRITICALLY. ...
... MLH goes on to get several more examples. The kids are apparently having difficulty with Question 1 under READING CRITICALLY. ...