* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download evolution_natural_selection_2011
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
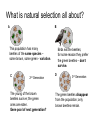
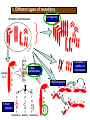
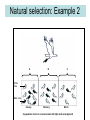
Evolution as “descent with modification” Evolution refers to the changes that life forms have undergone over long periods of time • Evolution means that all present-day forms of life … – – – – have descended from, and are related to, those that lived in the past may look different because they became modified from one generation to another Sometimes the modifications are so great that it is difficult to see the similarities between the modern form and its ancestor http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php www.darwinday.org/englishL/life/beagle.html www.darwinday.org/englishL/life/beagle.ht Used by permission of Darwin Day Celebration (at DarwinDay.org), 2006 I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection. —Charles Darwin from "The Origin of Species" http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. Natural Selection …. • IS a process • IS the simple result of variation, differential reproduction, and heredity - it is mechanistic. • It just selects among whatever variations exist in the population. What is natural selection all about? A B This population has many beetles of the same species – some brown, some green - variation. C 2nd Birds eat the beetles; for some reason they prefer the green beetles – don’t survive. D Generation The young of the brown beetles survive; the green ones are eaten. Gene pool of next generation? 3rd Generation The green beetles disappear from the population; only brown beetles remain. Natural selection Key concepts: • Variation between individuals from the same spesies • Environmental conditions change – shortage of water, nutrition, shelter, etc. • Individuals with favourable/desired (genes) trait/s will survive • Individuals with unfavourabletrait/s became distinct/die • The favourable trait/s are inherited from generation to generation and the composition of the population change – gene pool of population has change • Over time all the members of the population inherited the favourable trait/s Examples of variation for evolution • Phenotypic variation is a result of genetic variation e.g. Finches of Galapagos, Cheetah or the White lion List the sources of variation in populations. • Random assortment/segregation/ recombination of chromosomes during meiosis in the formation of gametes Crossing over • Chance/random fertilisation of gametes/sexual reproduction • Mutation • Outbreeding/Gene flow OR meiosis SOURCES OF GENOTYPIC VARIATION Meiosis Crossing over during phase Prophase Random arrangement of chromosomes during phase Metaphase Reproduction Mutations Outbreeding Fusion of many types of sperm cells and egg cells can produce many different types of offspring Gene mutations Alteration in the sequence of nitrogenous bases on DNA Chromosome mutations • Extra chromosomes added One or more sets of chromosomes are added (a)Lethal: the mutated organism dies and the harmful characteristics are not passed on to the next generation (b) Neutral: has no effect on the structure and functioning of the organism (c) Fixed: advantageous/sometimes the advantageous mutation wipes out all the other alleles controlling the same characteristic within the population 1. Different types of mutations 5. Polyploidy Normal 2n chromosomes A Genes A…F B C D E ... .. C-G A-T T-A G-C A-T T-A ... .. F 1. Point mutation C A T T A T Substitution C A T A T Deletion 4. Deletion or addition of chromosome 1. Gene multiplication C A T G A A T Duplication 4. Rearrangement 3. G H I A B X Y Z W C D E E F X W J G J G H I K Y Z I H K J K Finches of Galapagos Leaves Buds and fruit Insects Larvae/worms Ancestral seedeating species from the mainland Natural selection example 1 Natural selection: Example 2 A B C White mice Black mice January February March A population of mice in an environment with light sand as background Natural selection: Example 3 A B C Roots Offspring Time The structural adaptation of cacti over time Micro-evolution Using examples, explain how variation over a period of time can lead to: micro-evolution (variation within a species) – small changes that occur within a single species • Example : Peppered moths of Manchester • In the early 19th century, both dark-coloured and light-coloured moths lived in Manchester • The light-coloured moths were in greater numbers • Manchester became industrialised and black smoke from the factories collected as soot on the tree trunks