* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objective 3 - Canyon ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
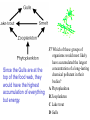
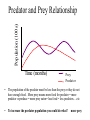
Objective 3 Interdependence of Living Organisms Ecology Ecology – The study of the relationships among living things and their enviroment Biomes Biotic and abiotic factors • Biotic – what kinds of plants and animals live in it. • Abiotic – Nonliving things such as soil type, rainfall amounts, and average temperature cycles. Biotic vs Abiotic Bio -means life These are things that are alive or was alive Abiotic – means not alive These are nonliving objects and never was alive What are they referring to? • Biosphere – The entire area of the planet that supports life. • Biome – An area defined by specific abiotic and biotic factors. • Community – The groups of living things in an area and how they relate. Temperate Desert Forest Name Tundra Grasslands the Biome Tropical Tiaga Rainforest A scientist has hypothesized that the existence of life on Mars is likely because Mars’s atmosphere is 95% carbon dioxide. 36 Which question is valid in testing this hypothesis? F Do most other scientists agree with the hypothesis? G Could abiotic processes account for the carbon dioxide? H What is the percent of argon compared to carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere? J Have the scientist’s other predictions about Mars been validated? Ecology – The study of the relationships among living things Living organisms have many types of relationsips: • 1. Mutualism • 2. Symbiosis • 3. Parasitism • 4. Commensalism • See next slides for examples Mutualism Mutualism- when both are helped Symbiosis • Symbiosis is a close relationship between two living things. Parasitism When one is helped and the other is harmed it is called parasitism Commensulism • Commensulism-when one is helped and there is no effect on the other Commensulism . . . Orchids live high in tree-tops on the branches of large trees. They do not harm the tree, but they are helped by being raised up into the sunshine and receiving water. Mutualism . . . Sharks are cleaned by a little fish known as a Remora. The shark never eats them since they clean bacteria off of the shark. Since both species are helped, this is mutualism. Parasites . . . Parasites harm or kill the host. A good example is a tape worm. It intercepts all of the hosts food, causing the host to starve to death. Parasites of dogs 35 Clown fish are small reef fish that seek protection from predators by sheltering themselves among the stinging tentacles of sea anemones. Clown fish are very territorial and can potentially scare off predators of sea anemones. This relationship is an example of -A neutralism This is not a type of symbiosis Incorrect B mutualism YES=both are helped, it is of mutual benefit C parasitism Neither is harmed so this is incorrect D commensalism Means only one is being helped and the relationship has no effect on the other – also incorrect What is helped? Both the ants and the tree. This is the definition of: All energy on the earth comes from the sun. Photosynthesis and Respiration In plants In animals/people Producer • Plants- they produce energy from sunlightthis energy is passed on to consumers who eat the plants Consumers 3rd Order onsumers animals that eat other animals, they are also known as carnivores 2nd Order Consumers eat only Herbivores and are called carnivores. 1st Order Consumers eat only plants and are also called herbivores. Food Chain – One of many feeding relationships in a community • Arrows the direction of energy flow. • This is not the only feeding relationship for these organisms. • When several or all of the food relationships are shown it’s a . . . Food web Food Webs • Food webs attempt to show all the feeding relationships in a community. • The direction of the arrows shows the direction of energy flow. • At the bottom of every web and every chain is a plant. These are the only things that can turn sunshine into food. Food Web 18 Energy used by producers in a grassland food web is provided byF sunlight This is a process, not an energy source. G photosynthesis H and J are elements which are types of matter, not energy. H oxygen J carbon dioxide So our answer should be: F 39 Wolves and hawks are at the same Trophic trophic level level because they — Means 1st , A both live on land 2nd or 3rd B are both large mammals Order C both eat primary consumers Consumer D have similar hunting patterns Since the Gulls are at the top of the food web, they would have the highest accumulation of everything but energy. 37 Which of these groups of organisms would most likely have accumulated the largest concentration of a long-lasting chemical pollutant in their bodies? A Phytoplankton B Zooplankton C Lake trout D Gulls Energy Diagrams At one end of the diagram are plants. They are called producers since they are capable of turning sunlight into food by photosynthesis. They pass 10% of the energy they absorb to animals that eat them. 10% Energy Rule – Only 10% of the energy moves up to the next tropic level. Decomposers The rest of the energy is used for movement, body functions and keeping warm If we apply the 10% rule, 10% of 43 Approximately how much the 1000 kcal of the plant is of the energy available in the consumed or 100 kcal, and 10% tissues of the producer is of that is 10 kcal which is 1% of eventually incorporated into the original 1000kcal, but only 3 the tissues of a secondary kcal is available to the tissues so consumer? it is A. A Less than 1% B Between 20% and 30% C Approximately 50% D More than 50% Consumer Predator • Eat other animals- hunters Prey • Get eaten by another animal Population (100s) Predator and Prey Relationship Time (months) Prey Predat or • The population of the predator must be less than the prey or they do not have enough food. More prey means more food for predator = more predator reproduce = more prey eaten= less food = less predators….etc • To increase the predator population you could do what? more prey 24 Which of the following is most likely to cause increases in a predator population? Reduces available food – Nope! F Fewer prey G A reduction in competition H More parasites J A period of drought CORRECT Less predators, they would be sick or dying! Less predators and prey, they’d be gone looking for water! Population (100s) Carrying Capacity Time (months) P rey P redat or • This is the maximum number of a specific population that an area can support with enough food and living requirements. It is shown by a line on population graphs for a specific species. Carry capacity • Example- a lot of baby rabbits are born so there is a lot of food for the wolves. The wolves therefore have many cubs survive. The cubs eat most of the rabbits and tn some starve to death. The rabbits then have more survive and breed more babies. The wolves have more food ……etc How it works all together Evolution: The process of change over time. • There are natural variations in all populations. • As climate changes occur, and as pressures in terms of food, space, shelter and predation occur, some variations allow a species to survive. • The members who survive, reproduce causing the change to become a characteristic of the species. Adaptations • Plants and animals change over time in order to adapt to their environment. This change allows them to survive and to reproduce. • The change can be fast, as in a chameleon changing colors, (structural) to hide from predators, or it can be very slow (evolution) Homologous vs. Analogous Structures • Homologous means they • Analogous means they have the same origin, but have the same function but may be different now. come from different origins. • Example, the upper arm bones in dogs, cows, cats • Example, bird wings and and monkeys. wings of bats. Speciation: Separation into new species. • Geographic isolation can cause two different natural variations to become prominent causing 2 separate species. • Reproductive isolation can have the same effect. Speciation of finch What is extinction and what causes it? • A population is extinct when the last of that species is dead. • Example: There are no more dinosaurs. • What happened? Their habitat was destroyed. When they no longer have what they need to live, they die. Fossils • These are imprints or remains of living things. • In undisturbed layers of sedimentary rock, the deeper it is, the older it is. • Give us information about extinct species. 2 Because of this animal’s adaptations, it would be most successful at — F competing with birds G making its own food H hiding from predators J running very rapidly And the answer is? • H hiding from predators. • Its not a plant, so it can’t make food. • It has no wings, so it can not compete with birds. • Although it has long legs, it doesn’t seem balanced for running. Water Cycle • Precipitation (rain and snow) fall on plants and ground. • Plants respire and evaporate water back into clouds. • The ground filters the water run-off into the lakes where it evaporates again. Uses of water 21 The diagram shows physical changes that occur in the water cycle. Which of these shows condensation? A Q Precipitation B R Run Off of ground water C S Evaporation DT Carbon Cycle • Photosynthesis • Glucose that contains carbonC6H12O6 is produced by plants, then eaten by animals. • Cellular Respiration • Animals and plants exhale CO2 which is taken in by plants to make glucose • You are mostly made of Carbon 36 Which question is valid in testing this hypothesis? F Do most other scientists agree with the hypothesis? G Could abiotic processes account for the carbon dioxide? H What is the percent of argon compared to carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere? J Have the scientist’s other predictions about Mars been validated? When testing an hypothesis, there should be only one variable changed at a time. If this is not possible, then all possible reasons for an outcome need to be considered. In this case, carbon dioxide can be produced by chemical reactions other than cellular respiration, which is a biotic process. That is why answer G is the best answer. Nitrogen Cycle • Plants must have Nitrogen • Lightening and bacteria “fix” Nitrogen into a form usable by plants. • It is absorbed by plant • Used to build amino acids for building proteins, enzymes and the nitrogen bases of DNA. Nitrogen Cycle Rock Cycle Pollution • Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes harm to the ecosystem. Man’s Effects on the Environment • More than 90% of fresh water is locked in ice at the polar caps and in glaciers. • Much of the fresh water is polluted by land run-off, dumping of wastes and excess heat directly into lakes, oceans and rivers. Man’s Effects on the Environment • SMOG is air pollution – some causes are fumes from cars and factories. • It can be dangerous to breath the air in some big cities Greenhouse effect Global warming, also called the Greenhouse Effect is caused by excess burning of fossil fuels (gasoline) Destruction of our oxygen producing protist in the oceans, and deforestation on land. Less plants means less oxygen and more CO2. Deforestation • Cutting down the trees in the forest. • Trees are natural filters that clean air and provide oxygen. • Forest provide homes to animals. Many animal species are now extinct because we destroyed there homes. Conservation To protect and preserve the environment Use natural resources wisely Conserve water You need clean air to breath Provide natural homes for animals What is the phrase for ecology? • Reduce Reuse Recycle 54 Which of these activities can help conserve natural resources? F Recycling cardboard boxes G Washing small loads of laundry H Driving large cars J Building wooden fences Yes! Recycle! Not saving water! Wasting fuel! Cutting down trees that give oxygen and clean air! Good job guys! •END