* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download POP Geometric Terms
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Tangent lines to circles wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
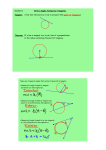
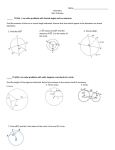
1. Angle Two rays sharing a common endpoint. Angles are typically measured in degrees or radians. Angle 2. Arc of a Circle A connected section of the circumference of a circle. Arcs are measured in two ways: as the measure of the central angle, or as the length of the arc itself. Measurement by central angle (degrees) Measurement by arc length (radians) The red arc (minor arc) measures 120°. The blue arc (major arc) measures 240°. Formula: s = rθ s = arc length r = radius of the circle θ = measure of the central angle in radians Red arc: r = 2 and θ = 2π/3, so s = 4π/3 Blue arc: r = 2 and θ = 4π/3, so s = 8π/3 See also Arc length of a curve SUSME – Workshop Terms for Melissa January 22, 2011 UAB 3. Area of a Circle The formula is below. 4. Central Angle An angle in a circle with vertex at the circle's center. 5. Circumference A complete circular arc. Circumference also means the distance around the the outside of a circle. 6. Chord A line segment on the interior of a circle. A chord has both endpoints on the circle. See also Secant line 7. Perimeter SUSME – Workshop Terms for Melissa January 22, 2011 UAB The distance around the outside of a plane figure. For a polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of the sides. 8. Pi π The ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. Pi is written π and is a transcendental number. π ≈ 3.14159 26535 89793... 9. Polygon A closed plane figure for which all sides are line segments. The name of a polygon describes the number of sides. A polygon which has all sides mutually congruent and all angles mutually congruent is called a regular polygon. Number of sides Polygon name 3 triangle 4 quadrilateral 5 pentagon 6 hexagon 7 heptagon 8 octagon 9 nonagon 10 decagon 11 undecagon 12 dodecagon n n-gon pentagon regular undecagon octagon 10. Radius of a Circle or Sphere A line segment between the center and a point on the circle or sphere. The word radius also refers to the length of this segment. SUSME – Workshop Terms for Melissa January 22, 2011 UAB 11. Ratio The result of dividing one number or expression by another. Sometimes a ratio is written as a proportion, such as 3:2 (three to two). More often, though, ratios are simplified according to the standard rules for simplifying fractions or rational expressions. Note: The word "rational" indicates that a ratio (in the second sense) is involved. The word rate also indicates a ratio is involved, as in instantaneous rate of change or average rate of change. 12. Secant Line A line which passes through at least two points of a curve. Note: If the two points are close together, the secant line is nearly the same as a tangent line. SUSME – Workshop Terms for Melissa January 22, 2011 UAB 13. Tangent Line A line that touches a curve at a point without crossing over. Formally, it is a line which intersects a differentiable curve at a point where the slope of the curve equals the slope of the line. Note: A line tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius to the point of tangency. . Point of Tangency Tangent Line to a Curve SUSME – Workshop Terms for Melissa January 22, 2011 UAB Additional terms if needed: 1. Arm of an Angle Side of an Angle Either of the two rays making up an angle. 2. Circle The locus of all points that are a fixed distance from a given point. 3. Initial Side of an Angle The ray where measurement of an angle starts. Angle, terminal side of an angle, side of a polygon SUSME – Workshop Terms for Melissa January 22, 2011 UAB 4. Line Segment Segment All points between two given points (including the given points themselves). Example: line segment 5. Terminal Side of an Angle The ray where measurement of an angle stops. See also Initial side, coterminal angles, side of a polygon SUSME – Workshop Terms for Melissa January 22, 2011 UAB