* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transmission of HIV
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
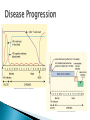
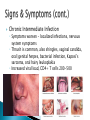
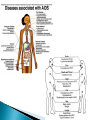
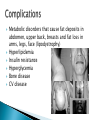
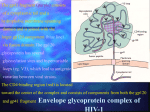
Megan McClintock, MS, RN Fall 2011 “HIV has no cure, continues for life, causes increasing physical disability, contributes to impaired health and ultimately ends in death.” Sexual intercourse Exposure to infected blood ◦ Drug-using equipment ◦ Blood products ◦ Needle stick Perinatal transmission during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding Safe sex – masturbation, insertive sex only if neither person infected or at risk of being infected Barriers – condoms, dental dams, plastic food wrap No alcohol or tobacco Don’t share drug equipment Utilize needle/syringe exchange programs Clean equipment (least effective) If exposed through a needle stick at work, get post-exposure prophylaxis with ART Prevent HIV in women Treat HIV during pregnancy with ART Offer HIV testing to all women Acute Infection ◦ Occurs within 2-4 weeks of infection and lasts 1-2 weeks (often mistaken for the flu) ◦ Mono-like symptoms ◦ Neuro symptoms ◦ High viral load, decreased CD4+ T cells Chronic Early Infection ◦ Generally asymptomatic but spreading the disease b/c they don’t know they are infected ◦ May have night sweats, fatigue, headache, low grade temp, lymphadenopathy ◦ Low viral load, CD4+ T cells fairly normal (>500) Chronic Intermediate Infection ◦ Symptoms worsen – localized infections, nervous system symptoms ◦ Thrush is common, also shingles, vaginal candida, oral/genital herpes, bacterial infection, Kaposi’s sarcoma, oral hairy leukoplakia ◦ Increased viral load, CD4+ T cells 200-500 Late Chronic Infection – AIDS ◦ Can only make this diagnosis when specific criteria is met (pg 245, Table 15-9) ◦ Opportunistic disease (pg 245, Table 15-10), wasting, dementia, malignancies ◦ High viral load ◦ Low CD4+ T cells (<200) HIV antibodies and/or antigens in the blood ◦ May not appear for 2 months after infxn, but can still transmit the virus during this time (window period) ◦ Rapid HIV test (EIA) – looks for antibodies ◦ Western blot test of IFA must be done to confirm diagnosis CD4+ Tcell counts (measure of immune function) – normal 800-1200 Viral load (measure of disease progression) – can be undetectable (but still have the virus and can transmit it) WBC, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, liver function abnormalities, can also test for ART drug resistance, Hep B, Hep C No cure, just decreased disease progression Goals – decrease viral load, increase CD4+ T cell count, delay onset of opportunistic disease Must use at least 3 drugs from 2 different drug classes Critical for the patient to adhere to the drug regimen Drugs interact with many other drugs and herbs Vaccinations are important Assess for risky behaviors ◦ Blood transfusion before 1985 ◦ Sharing drug-using equipment ◦ Any sexual experience (yes, this covers lots of folks) ◦ STDs CDC recommends HIV testing for everyone ages 13-64 Drug therapy ◦ Must take right dose at right time every day ◦ Encourage use of electronic reminders, calendars, timers, group support Promote a healthy immune system ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Good nutrition to keep lean body mass Decrease alcohol/tobacco/drug use Vaccinate for infectious diseases Good rest and exercise Decrease stress Avoid exposure to illnesses Mental health counseling and support groups Metabolic disorders that cause fat deposits in abdomen, upper back, breasts and fat loss in arms, legs, face (lipodystrophy) Hyperlipidemia Insulin resistance Hyperglycemia Bone disease CV disease