* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HIV/AIDS Worldwide 38 million
Survey
Document related concepts
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
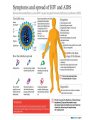
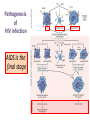
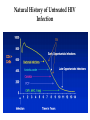
Pongphol Pongthaisong Animal Immunology 6 Feb 2014 • HIV/AIDS Worldwide • General information of AIDS • AIDS and Immunity HIV/AIDS Worldwide • 38 million people live with HIV/AIDS worldwide. • Sub-Saharan Africa is home to 70% of the people living with HIV. • 2.1 million children are infected with HIV/AIDS in the world Top HIV/AIDS-Infected Countries SubSaharan Africa 1. South Africa 9. United States 2. Nigeria 10.Russian Federation 3. Zimbabwe 11.China 4. Tanzania 12.Brazil 5. The Congo 6. Ethiopia 7. Kenya 8. Mozambique 13.Thailand Source: Steinbrook R. The AIDS epidemic in 2004. NEJM. 2004;351:115-117. Acquired - because it's a condition one must acquire or get infected with, not something transmitted through the genes Immune - because it affects the body's immune system, the part of the body which usually works to fight off germs such as bacteria and viruses Deficiency - because it makes the immune system deficient Syndrome - because someone with AIDS may experience a wide range of different diseases and opportunistic infections Pathogenesis of HIV infection AIDS is the final stage CD4 Count in HIV infection • The CD4 cell , also known as "T4" or "helper T cell“ is responsible for signaling other parts of the immune system to respond to an infection. • Initially in HIV infection there is a sharp drop in the CD4 count and then the count levels off to around 500-600 cells/mm (normal 500 1500 ) • CD4 count is a marker of likely disease progression. CD4 percentage tends to decline as HIV disease progresses. • CD4 counts can also be used to predict the risks for particular conditions such as Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, CMV disease or MAI disease. • Treatment decisions are often based on Viral Load and CD4 count. Natural History of Untreated HIV Infection