* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10: Heat Energy
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
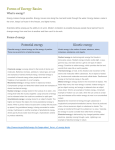
CHAPTER 10: HEAT ENERGY TEMPERATURE AND HEAT HOW IS ENERGY RELATED TO MOTION? • The words hot, warm, cool, and cold are words used to describe the temperature of something. • Temperature is determined by the movement of molecules or atoms. • Any moving object, has energy due to its motion. • This energy is not a fluid that can flow from the moving object, nor is it any kind of matter we can pluck from the moving object. • Energy- the ability to move other material around. Whether it be an object or its atoms. WHAT ARE THE TWO MAIN KINDS OF ENERGY? • Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it only changes form. • There are two main kinds: • Kinetic Energy- The energy of any moving object. • Potential Energy- Energy stored in an object of material. • Moving an object upward is a way to give potential energy. • Chemical binds also are a source of potential energy. • Energy is measured in Joules. • Joule- the amount of kinetic energy gained by a 1kilogram object falling from a height of 10.2 centimeters. WHAT IS TEMPERATURE? • Molecules in a material move about at different speeds. • They have an average speed and most molecules have speeds near the average, while only a few molecules travel at speeds far above or below the average. • The average speed of the molecules in a material determines the molecules’ average kinetic energy. • Temperature- The average kinetic energy of the molecules. • This determines how hot or cold the object is. • Use thermometers to measure temperature. WHAT IS HEAT? • Energy always flow from the hotter object to the cooler one, never the reverse. • Energy will continue to flow until the two object reach the same temperature. • When the objects are both at the same temperature, their molecules will have the same kinetic energy. • Heat- a form of energy. Measured in energy units such as Joules. WHAT IS RADIATION? • Radiation- The transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves. • All objects give off a wide variety of waves. • Types: infrared, visible, and ultraviolet. • Examples: • The Sun • Microwave • Electric Stove • Sometimes you can see the waves give off a color, the higher the temperature of the waves, the more you can see its heat. WHAT IS CONDUCTION? • Conduction- The movement of energy through direct contact. • Example: • The burner on a stove is very hot, which means its atoms are moving very, very, fast. • When these fast moving atoms, hit the pan, the pan’s atoms move faster . • When the pan’s atoms hit the molecules in the sauce, the sauce molecules heat up, making the sauce hotter. WHAT IS CONVECTION? • Convection- The transfer of energy by the flow of a liquid or gas. • Heat is transferred by having hot liquid/gas rise, and then sink when it cools. • Examples: • Lava Lamp • Boiling Liquid • Heating of the atmosphere • The heating of the center of the Earth. DO SOME MATERIALS WARM FASTER THAN OTHERS? • Equal masses of different materials have a different temperature change for the amount of heat absorbed. • The rate that a material heats up is a physical property. • We can use it to tell one substance from another. • Metals are good at heating fast. • Water takes longer to heat. It stays cooler longer, so water is said to be a good coolant. WHAT IS INSULATION? • Insulation- Preventing heat from flowing in or out of a material. • You insulate something by wrapping it securely with a material that is not a good conductor of heat. • There are many instances in our everyday lives where it is important to keep heat from entering or leaving something. • Examples: • Houses are insulated. • Thermoses and coolers are insulated.