* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lower Appendicular Skeleton only
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
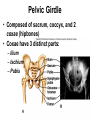
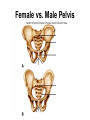
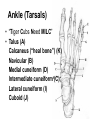
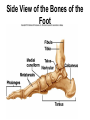
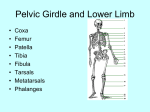
Lower Appendicular Skeleton Pelvic Girdle • Composed of sacrum, coccyx, and 2 coxae (hipbones) • Coxae have 3 distinct parts: – Ilium – Ischium – Pubis Pelvic Girdle, continued….. • Coxae parts fuse together in the acetabulum, a cup-shaped area on the lateral surface of the hip that receives the head of the femur. Ilium • Largest and uppermost portion of the coxa • The upper edge is called the iliac crest • Joins the sacrum at the sacroiliac joint • Anterior superior iliac spine- the bony prominence you feel as your “hipbone” Ischium • Forms the lowest portion of the coxa • Ischial tuberosity – Points posteriorly AND downward – Supports the weight of the body when sitting • Ischial spine – a sharp projection above the ischial tuberosity, near the junction of the ischium and ilium Pubis • Anterior portion of the coxa • Two pubic bones join midline at the symphysis pubis joint • Pubic arch – Angle formed by pubic bones below the symphysis pubis – Arch is wider in females Female vs. Male Pelvis Lower Limb • • • • • • • Femur Patella Tibia Fibula Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges Femur • Longest and strongest bone in the body • Head at top fits into __________of coxa • Greater trochanter – superior, lateral process • Lesser trochanter – inferior, medial process • Distal end: – Two rounded processes posteriorly: Tibia • aka, “shin bone” • Proximal end: – Medial and lateral condyles are concave and articulate with condyles of the femur – Tibial tuberosity just below the condyles; attachment point for patellar ligament • Distal end: medial malleolus forms prominent bony point of inner ankle Fibula • Proximal: head – Articulates with tibia just below the lateral condyle – DOES NOT enter into knee joint or bear any weight • Distal: lateral malleolus forms outer prominent bony part of ankle Ankle (Tarsals) • “Tiger Cubs Need MILC” • Talus (A) Calcaneus (“heal bone”) (K) Navicular (B) Medial cuneiform (D) Intermediate cuneiform (C) Lateral cuneiform (I) Cuboid (J) Side View of the Bones of the Foot Foot • 5 metatarsals – numbered 1-5 starting medially – Heads at distal ends form the ball of the foot • Phalanges – Toes – Each toe has 3 phalanges, except the big toe – What are the phalanges of each toe called? (HINT: Just like the fingers) Joints • AKA “articulations” – functional junctions between bones • Functions: – Bind parts of the skeletal system – Make bone growth possible – Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth – Enable the body to move in response to skeletal muscle contractions