* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download you
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
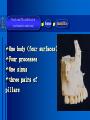
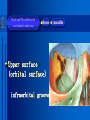
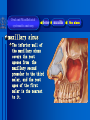
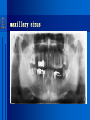
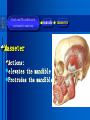
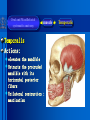
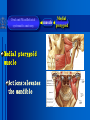
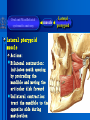
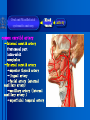
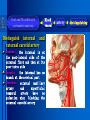
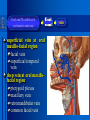
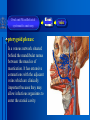
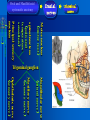
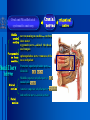
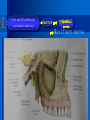
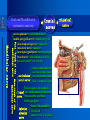
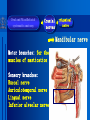
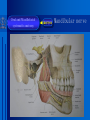
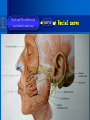
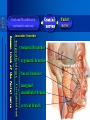
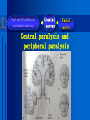
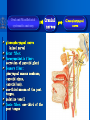
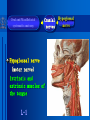
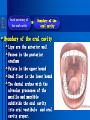
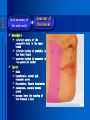
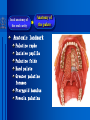
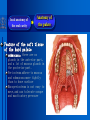
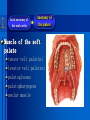
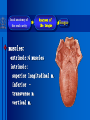
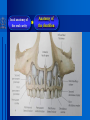
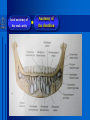
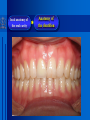
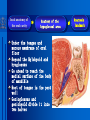
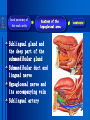
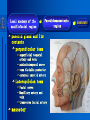
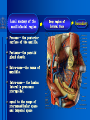
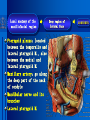
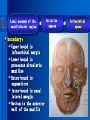
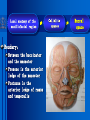
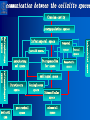
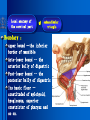
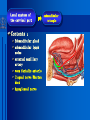
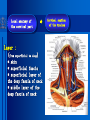
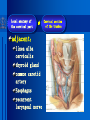
Oral and Maxillofacial Anatomy The First Affiliated Hospital School of Medicine, Zhejiang University Prof. Dr. Gu Xinhua Oral and Maxillofacial Anatomy Oral and Maxillofacial Systematic Anatomy Oral Topographic Anatomy Maxillofacial Topographic Anatomy Oral and Maxillofacial Systematic Anatomy Key points: 1. pillars and processes of maxilla 2. weak regions of mandible 3. composition of the temporomandibular joint 4. muscles of mastication 5. How to distinguish the internal and external carotid artery? 6. pterygoid plexus 7. distribution of trigeminal nerve in oral region 8. branches of facial nerve Oral and Maxillofacial Systematic Anatomy Bones:maxilla and mandible Joints :temporomandibular joint Muscles:muscles of mastication Vessles:carotid artery and jugular vein Nerves:V VII IX XII Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone There’re totally fourteen bones making up the maxillofacial bony framework. Single bone: mandible、 vomer pairing bones: maxilla、 zygomatic bones、palatine bones、inferior nasal concha nasal bones、lacrimal bones Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone Maxilla Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone maxilla One body(four surfaces) Four processes One sinus three pairs of pillars Oral and Maxillofacial 口腔颌面部系统解剖 systematic anatomy bone Anterior surface (facial surface) infraorbital foramen maxilla Oral and Maxillofacial 口腔颌面部系统解剖 systematic anatomy bone Posterior surface Zygomatico-alveolar ridge Maxillary tuberosity maxilla Oral and Maxillofacial 口腔颌面部系统解剖 systematic anatomy bone Upper surface (orbital surface) infraorbital groove maxilla Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone Medial surface (nasal surface) maxilla Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Four processes frontal process zygomatic process palatine process alveolar process bone maxilla Four processes Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone maxillary sinus The inferior wall of the maxillary sinus covers the root apexes from the maxillary second premolar to the third molar, and the root apex of the first molar is the nearest to it. maxilla One sinus maxillary sinus Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone three pairs of pillars Frontonasal pillar (canine pillar) Zygomatic process pillar Pterygoid process pillar maxilla three pairs of pillars Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone Mandible The unique bone which is mobile on the maxillofacial region! Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone Body of mandible Ramus of mandible angle of mandible Mandible Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone Mandible The external surface of the body of mandible Meso-combination mental tubercle external oblique line mental foramen Body of mandible Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone Mandible The internal surface of the body of mandible Mental spines Internal oblique line (mylohyoid line) Sublingual fossa Digastric fossa Submandibular fossa Body of mandible Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone Ramus of mandible coronoid process (muscular process) Condylar process (articular process) simoid notch (mandibular notch) The internal surface of the ramus of mandble mandibular foramen mandibular lingula Mandibular canal Ramus of Mandible mandible Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone angle of mandible Internal surface: pterygoid tuberosity External surface: masseteric tuberosity Mandible angle of mandible Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy bone The weak regions of mandible Meso-combination mental foramen Angle of mandible neck of condyle Mandible Weak region Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Temporomandibular joint Temporomandibular joint Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy condylar process articular fossa articular disk Temporomandibular joint Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Temporomandibular joint articular capsule articular ligaments Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Temporomandibular joint Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy muscle muscles of mastication muscles of mastication Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy muscle Muscles of mastication masseter temporalis medial pterygoid muscle lateral pterygoid muscle muscles of mastication Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy muscle Masseter Actions: elevates the mandible Protrudes the mandible masseter Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy muscle Temporalis Actions: elevates the mandible Retracts the protruded mandible with its horizontal posterior fibers Unilateral contraction : mastication Temporalis Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Medial pterygoid muscle Actions:elevates the mandible muscle Medial pterygoid Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy muscle Lateral pterygoid muscle Actions: Bilateral contraction: initiates mouth opening by protruding the mandible and moving the articular disk forward Unilateral contraction: tract the mandible to the opposite side during mastication Lateral pterygoid Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Blood vessel blood vessel Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Blood vessel artery Internal carotid artery External carotid artery Distinguish the two arteries(location、 branch、pulsation) vein Superficial vein Deep vein Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy common carotid artery →Internal carotid artery frontonasal part intra-orbit encephalon →External carotid artery →superior thyroid artery →lingual artery →facial artery (external maxillary artery) →maxillary artery (internal maxillary artery ) →superficial temporal artery Blood vessel artery Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Blood vessel Distinguish internal and external carotid artery location : the internal is at the post-lateral side of the external first and then at its post-intra side branch : the internal has no branch at the cervical part Pulsation: external maxillary artery and superficial temporal artery have no pulsation when blocking the external carotid artery artery distinguishing Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy superficial vein at oral maxillo-facial region facial vein superficial temporal vein deep vein at oral maxillofacial region pterygoid plexus maxillary vein retromandibular vein common facial vein Blood vessel vein Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy pterygoid plexus: Is a venous network situated behind the mandibular ramus between the muscles of mastication. It has extensive connections with the adjacent veins which are clinically important because they may allow infectious organisms to enter the cranial cavity. Blood vessel vein Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy nerves nerves Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy olfactory nerve optic nerve oculomotor nerve trochlear nerve V.trigeminal nerve-branch 、distribution abducent nerve VII.facial nerve-branch、 distribution vestibulocochlear nerve IX.glossopharyngeal nerve -distribution vagus nerve accessory nerve XII.hypoglossal nerve- distribution Cranial nerves Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy nerves trigeminal nerve Mandibular nerve mixed nerve Maxillary nerve sensory nerve Ophthalmic nerve sensory nerve ) Motor nucleus motoe root spinal nucleus pain and temperature sensation Principal sensory nucleus ( ( ) touch-pressure sensation ) ) ) ) ( ( ( ( Trigeminal ganglion trigeminal nerve Cranial nerves Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy lacrimal gland eyeball Ophthalmic division eyelid skin of forehead nasal mucosa Cranial nerves trigeminal nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves Middle nervus meningeus medius— cerebral cranial section dura mater zygomatic nerve—skin of the cheek and tempus Pterygopalati ne fossa sphenopalatine nerve—mucosa of the nose and palate section Maxillary nerve Orbital section Posterior superior alveolar nerve— distoside Middile superior alveolar nerve— mesial side Anterior superior alveolar nerve— infraorbital nerve—facial section Facial section trigeminal nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy nerves trigeminal nerve Maxillary nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves Fore -trunk of the Meta-trunk of the mandibular nerve mandibular nerve Mandibular nerve nervus spinosus─cerebral dura mater medial pterygoid nerrve─medial pterygoid deep temproal ngerves─temporalis masseteric nerve─masseter lateral pterygoid nerve─lateral pterygoid buccal nerve─skin and mucosa of the posterior tooth’s buccal side auriculotem poral nerve temporomandibular joint external acoustic meatus external acoustic meatus Skin of temporal region Lingual gum of the mandible lingual Twe-thirds mucosa of the fore tongue nerve Mucosa of the oral floor sublingual gland inferior alveolar nerve Gum of the mandible Mylohyoid anterior belly of digastric trigeminal nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves trigeminal nerve Mandibular nerve Motor branches: for the muscles of mastication Sensory branches: Buccal nerve Auriculotemporal nerve Lingual nerve Inferior alveolar nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy nerves Mandibular nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves trigeminal nerve Distribution of n. in oral region anter. Nasopalatine pala.n. n. A m P 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Lingual n. Mental n. Buccal n./ /Inferior alveolar n. Palatal/lingual L-B/teeth Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy nerve Facial nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves Facial nerve Motor fiber:mainly dominate the muscles of facial expression Parasympathetic submaxillary gland, sublingual gland lacrimal gland、mucosal glands of the fiber: nasal cavity and palate Taste fiber: taste bud of the anterior twe-thirds of the tongue Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy nerve Facial nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves Temporal facial trunk Cervicofacial trunk Commen trunk of the facial nerve muscular branches temporal branches zygomatic branches buccal branches marginal mandibular branch cervical branch Facial nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves Facial nerve Central paralysis and peripheral paralysis Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Central paralysis Loss of the upper neurpns, in this case on the left side.presents clinically with paralysis of the contralateral muscles of the facial expression in the lower half of the face , while the contralateral forehead and extraocular muscles remain functional. Thus, the corner of the mouth sags on the right (contralateral) side, but the patient can still wrinkle the forehead and close the eyes on both sides. Speech articulation is impaired. Cranial nerves Facial nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Peripheral paralysis (Loss of the lower neurpns, in this case on the right side).is characterized by complete paralysis of the ipsilateral muscles. The patient cannot wrinkle the forehead, the corner of the mouth sags, articulation is impaired, and the eyelid cannot be fully closed. A Bell phenomenon is present (the eyeball turns upward and outward, exposing the sclera, when the patient attempts to close the eyelids), and the eyelids closure reflex is abolished. Depending on the site of the lesion, additional deficits may be present such as decreased lacrimation and salivation or loss of taste sensation in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. Cranial nerves Facial nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy glossopharyngeal nerve (mixed nerve) Motor fiber: Parasympathetic fiber: secretion of parotid gland Sensory fiber: pharyngeal mucous membrane, carotid sinus, carotid body, one-third mucosa of the post tongue, palatine tonsil Taste fiber: one-third of the post tongue Cranial nerves Glossopharyngeal nerve Oral and Maxillofacial systematic anatomy Cranial nerves Hypoglossal nerve (motor nerve) intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue L-1 Hypoglossal nerve local anatomy of the oral cavity Key points 1. features of the soft tissue of the hard palate 2. papillae and their functions of the tongue 3. lymphatic drainage of the tongue local anatomy of the oral cavity Boundary of the oral cavity Surface marker Anatomy of the lip Anatomy of the cheek Anatomy of the palate Anatomy of the tongue Anatomy of the dentition Anatomy of the hypoglossal area local anatomy of the oral cavity Boundary of the oral cavity Boundary of the oral cavity Lips are the anterior wall Fauces is the posterior erathem Palate is the upper bound Oral floor is the lower bound The dental arches with the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible subdivide the oral cavity into oral vestibule and oral cavity proper. local anatomy of the oral cavity Surface marker oral vestibular groove frenulum of the upper and lower lip buccal frenum opening of the Stensen's duct—Parotid gland retromolar area Pterygonmandibular fold lingual frenulum local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the lips lips local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the lips boundary: basis nasi is the upper bound mentolabial sulcus is the lower bound labial sulccus is the lateral bound anatomic landmark: angle of mouth vermilion vermilion border labial arch labial peak vermilion tubercle nasal columella philtrum、philtrum ridge、 philtrun incisure local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the lips local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the cheeks cheeks local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the cheeks boundary inferior margin of the zygomatic bone is the upper bound inferior border of mandible is the lower bound anterior border of masseter is its posterior border layer skin hypodermis:buccal pad, vascular nerve Buccinator,fascia buccinator submucosa:contain mucous gland mucosa:have thw opening of the Stensen's duct local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the palate palate local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the palate Anatomic landmark Palatine raphe Incisive papilla Palatine folds Hard palate Greater palatine foramen Pterygoid hamulus Foveola palatina local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the palate Feature of the soft tissue of the hard palate submucosa:there are no glands in the anterior part, and a lot of mucous glands in the posterior part. Periosteum adhere to mucosa and submucosa more tightly than to bone surface Mucoperiosteum is not easy to move,and can tolerate scrape and masticatory pressure local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the palate Muscle of the soft palate tensor veli palatini levator veli palatini palatoglossus palatopharyngeus uvular muscle local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the tongue tongue local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the tongue The V-shaped terminal sulcus divides tongue to an anterior twothirds (boby) and a posterior onethird (root) tongue local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the tongue Body of tongue has four kinds of papilla filiform papillasensitive to tactile stimuli fungiform papillamechanical/thermal receptors,taste buds vallate papillaabundant taste buds foliate papilla- taste buds Tongue local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the tongue Root of tongue: no papilla,a lot of nodosity lymphatic tissue called lingual tonsil. Tongue local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the tongue muscles: extrinsic:4 muscles intrinsic: superior longitudinal m. inferior – transverse m. vertical m. Tongue local anatomy of the oral cavity apex of tongue lymphatic vessel Anatomy of the tongue submental lymph nodes nodi lymphaticus juguloomohyoideus ante- lateral tongue Submaxillary L.N lymphonodi cervicales profundi craniales lymphonodi cervicales profundi craniales center of tongue submaxillary L.N part cross to opposite side posterior tongue lymphonodi cervicales profundi craniales Lymphatic drainage local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the tongue lingual frenulum fimbriated fold sublingual caruncle sublingual fold Lingual abdomen local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the dentition dentition local anatomy of the oral cavity Deciduous teeth Anatomy of the dentition Permanent teeth local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the dentition local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the dentition local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the dentition local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the hypoglossal area hypoglossal area local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the hypoglossal area Under the tongue and mucous membrane of oral floor Beyond the Mylohyoid and hyoglossus Go ahead to reach the medial surface of the body of mandible Root of tongue is the post wall Genioglossus and geniohyoid divide it into two halves Anatomic landmark local anatomy of the oral cavity Anatomy of the hypoglossal area Sublingual gland and the deep part of the submandibular gland Submandibular duct and lingual nerve Hypoglossal nerve and its accompanying vein Sublingual artery contents Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Key points 1. features of the soft tissue in the maxillofacial region 2. deep region of lateral face 3. communication between the cellulite spaces Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Surface marker Feature of the soft tissue Parotideomasseteric region Deep layer of the lateral facial region Cellulite spaces Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region nasal columella Base of the nose Nasofacial sulcus Labiofacial sulcus menton infraorbital foramen surface projection of the Stensen's duct the position of the facial nerve efferens stylomastoid foramen Surface marker Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Feature of the soft tissue Skin is thin and soft and has wrinkle whose strike is regular. Subcutaneous tissue is curmbly. Abundant of sebaceous glands, hair follicle and sweat gland Blood vessels are intensive, and blood is plentiful. Expression muscles Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region parotideomasseteric region parotideomasseteric region Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Parotideomasseteric region Prozone-- exterior edge of masseter Postzone-sternocleidomastoid、 mastoid process and exterior edge of the posterior belly of digastric muscle Upper bound -- zygomatic arch and external acoustic meatus Lower bound--inferior border of mandible boundary Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Parotideomasseteric region parotid gland and its contents perpendicular team superficial temporal artery and vein auriculotemporal nerve vena facialis posterior external carotid artery Lateropulsion team Facial nerve Maxillary artery and vein transverse facial artery masseter contents Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Deep region of lateral face Deep region of lateral face Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Prozone-- the posterior surface of the maxilla. Postzone--the parotid gland sheath. Extra-zone--the ramus of mandible. Intra-zone-- the lamina lateralis processus pterygoidei. equal to the range of pteryomandibular space and temporal space Deep region of lateral face boundary Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Pterygoid plexus:located between the temporalis and lateral pterygoid M., also between the medial and lateral pterygoid M. Maxillary artery:go along the deep part of the neck of condyle Mandibular nerve and its branches Lateral pterygoid M. Deep region of lateral face contents Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Cellulite spaces Cellulite spaces Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region boundary: Upper bound is infraorbital margin Lower bound is processus alveolaris maxillae Extra-bound is zygomaticus Intra-bound is nasal lateral margin Bottom is the anterior wall of the maxilla Cellulite spaces Infraorbital space Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Boudary: Between the buccinator and the masseter Prozone is the anterior ledge of the masseter Postzone is the anterior ledge of ramus and temporalis Cellulite spaces Buccal space Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Cellulite spaces Boundary : Between the masseter and ramus Prozone is the mucosa of the retromolar area Postzone is the parotid gland Masseteric space Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Cellulite spaces Pterygomandibular space Boundary : Between the ramus of mandible and the medial pterygoid Prozone is the temporalis and buccinator Postzone is the parotid gland Upper bound is the inferior margin of the lateral pterygoid Lower bound is the point which the medial pterygoid attaches to the ramus Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Cellulite spaces Infratemporal space Boungary : Prozone is the posterior surface of the maxilla Postzone is the styloid process and many muscles which attach to styloid process Intra-bound is lamina lateralis processus pterygoidei Extra-bound is upper part of the ramus and zygomatic arch Upper bound is the infratemporal surface and infratemporal crest of the great wing of sphenoid bone Lower bound is the inferior margin of lateral pterygoid Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Cellulite spaces Temporal space Boundary : Located at the temporal region To have zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest as the boundary to the infratemporal space To be divided into superficial temporal space and deep temporal space Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Cellulite spaces Parapharyngeal space Boundary : Located between the medial pterygoid, deep lobe of the parotid gland and the lateral pharyngeal wall Upper to base of skull Lower bound is the hyoid bone plane Prozone is ligamentum pterygomandibulare Postzone is lateral side of the fascia colli profunda Styloid process and the muscles which attach to it divide the space into anterior parapharyngeal space and posterior parapharyngeal space Local anatomy of the maxillofacial region Cellulite spaces Pterygopalatine space Boundary : Prozone is the maxilla Postzone is the pterygoid process of sphenoid bone Upper bound is the greater wing of sphenoid bone Outside bound is the vertical plate of palatine bone communication between the cellulite spaces Cranium cavity pterygopalatine spaces space parotid spaces parapharyng eal space Pterygomandibu lar space retroesophageal space sublingual space Paraviscera space pretracheal space Genioglossus space temporal Submandibular space submental space buccal space Masseteric space infraorbital space Retropharynge al space mediasti num infratemporal space Local anatomy of the cervical part Submandibular region Cervical section of the trachea Local anatomy of the cervical part Key points: 1. Submandibular region 2. Cervical section of the trachea Local anatomy of the cervical part submandibular triangle submandibular triangle Local anatomy of the cervical part submandibular triangle Boundary : upper bound --the inferior border of mandible Ante-lower bound -- the anterior belly of digastric Post-lower bound -- the posterior belly of digastric Its basic floor -constituded of mylohyoid, hyoglossus, superior constrictor of pharynx and so on. Local anatomy of the cervical part Contents : Submandibular gland submandibular lymph nodes external maxillary artery vena facialis anterio lingual nerve Wharton duct hypoglossal nerve submandibular triangle Local anatomy of the cervical part submandibular triangle Cervical section of the trachea Local anatomy of the cervical part Layer : (from superficial to deep) * skin * superficial fascia * superficial layer of the deep fascia of neck * middle layer of the deep fascia of neck Cervical section of the trachea Local anatomy of the cervical part adjacent: linea alba cervicalis thyroid gland common carotid artery Esophagus recurrent laryngeal nerve Cervical section of the trachea [email protected] Arrangement of Lab. or clinical study Group 1&4 -1st Aff Hospital, Ward of Oral-Maxillofacial Surg, 7th floor Building 3 Chief Tutor: Prof Liu Jianhua 13588890251 Group 2&5 -2nd Aff Hospital, Ward of Oral-Maxillofacial Surg, Ground floor Building 1 Chief Tutor: Dr. Liu Yanming 15967157676 Group3&6-divided into 3a,6a(1st),3b,6b(2nd) Nov.16(Wed),13:15-14:50