* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standards Framework Template
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Tangent lines to circles wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
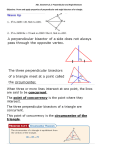
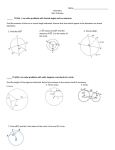
Understand and apply theorems about circles Grade: Common Core/Essential Standard #: G.C.3 Course: Description: Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. Learning Targets: I can define the terms inscribed, circumscribed, angle bisector, and perpendicular bisector. (K) I can construct the inscribed circle whose center is the point of intersection of the angle bisectors (the incenter).(P) I can construct the circumscribed circle whose center is the point of intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of each side of the triangle (the circumcenter)(P) I can apply the Arc Addition Postulate to solve for missing arc measures. (S) I can prove that opposite angles in an inscribed quadrilateral are supplementary. (R) Essential Terminology: Inscribed, circumscribed, angle bisector, perpendicular bisector, construction, compass, straightedge, intersection, incenter, circle, circumcenter, quadrilateral, arc, inscribed angle, Arc Addition Postulate, equation, opposite angles, supplementary Unit: Instructional Days: Recommended Resources: Prentice Hall – Common Core State Standards Phschool.com: Homework Tutorial Videos, Quizzes Prentice Hall Geometry – Chapter 5 Tenmarks.com Online (only links specific to this standard): Phschool.com: Homework Tutorial Videos, Quizzes Tenmarks.com Essential Readings: Prentice Hall Geometry – page 249 – 251, 256 - 259 Enduring Understandings: The properties of polygons, lines, and angles can be used to understand circles; the properties of circles can be used to solve problems involving polygons, lines, and angles. Essential Question: How can the properties of circles, polygons, lines and angles be useful when solving geometric problems? Understand and apply theorems about circles Activating Strategy: Teacher will instruct and model the concepts of the perpendicular and angle bisectors of a triangle. Teacher will teach concurrent lines, medians, and altitudes. The students will learn the points of concurrency for perpendicular bisectors, angle bisectors, altitudes, and medians. Paper Folding Activity in Prentice Hall Geometry – page 256 Suggested Instructional Tasks: Teacher can use construction to show the points of concurrency and how they Literacy Component: Reading Prentice Hall Geometry – page 249 – 251, 256 -259 Writing Explain the four different lines of concurrency and the special points that correlate to the lines. State the special characteristic of the centroid, circumcenter, and incenter. Summarizing Strategy: Support for Differentiation: ELL EC Sample Formative Assessment (aligned to Learning Target): AIG