* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Your Mental and Emotional Health
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
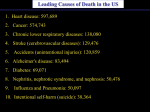
Lesson 1 Cardiovascular Diseases Why should you establish and maintain healthful habits to care for your heart? Lesson 1 Lesson Objectives In this lesson, you’ll learn to: Examine different types of cardiovascular diseases. Recognize the importance of early detection and warning signs that prompt individuals of all ages to seek health care. Identify risk behaviors and risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Develop, analyze, and apply strategies related to the prevention of noncommunicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease. Lesson 1 Cardiovascular Diseases Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases A century ago, communicable diseases were a leading cause of death in the United States. Today, however, major causes of death, such as heart disease and cancer, come from noncommunicable diseases. Lesson 1 Cardiovascular Diseases What Are Cardiovascular Diseases? Your cardiovascular system transports blood to all parts of your body. Without oxygen and other materials that blood carries, your cells would die. Sometimes diseases interfere with the pumping action of the heart or the movement of blood through blood vessels. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are responsible for more than 40 percent of all deaths in the United States, killing almost a million Americans each year. Lesson 1 Cardiovascular Diseases Ways to Avoid Risk of CVD Avoid tobacco. Get plenty of physical activity. Maintain a healthful weight. Follow an eating plan that is low in saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels Hypertension Atherosclerosis Angina Pectoris Arrhythmias Heart Attack Congestive Heart Failure Stroke Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Hypertension Hypertension is a major risk factor for other types of CVDs. Hypertension can occur at any age, but it is more common among people over the age of 35. High blood pressure can be lowered with strategies such as medication, weight management, adequate physical activity, and proper nutrition. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Atherosclerosis At birth, the lining of blood vessels is smooth and elastic. Over time, factors such as tobacco smoke, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels can damage the inner lining of the arteries. Atherosclerosis causes the arteries to thicken and lose their elasticity. It is caused mainly due to food choices—specifically, a high intake of saturated fats and cholesterol. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the Heart Your heart pumps about 100,000 times a day every day to move blood to all parts of your body. Just like every other organ, your heart needs the oxygen from blood to function. When the blood supply to the heart is insufficient to provide enough oxygen, the result can be pain, damage to the heart muscle, or even sudden death. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Diagnostic Tools Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Treatment Options Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Angina Pectoris Angina pectoris, which usually lasts from a few seconds to minutes, is a warning sign that the heart is temporarily not getting enough blood. The most common cause of angina is atherosclerosis. Angina seldom causes permanent heart damage and sometimes can be treated with medication. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Arrhythmias Arrhythmias occur in millions of people who do not have underlying heart disease, and they usually don’t cause problems. In one type of arrhythmia, called ventricular fibrillation, the electrical impulses regulating heart rhythm become rapid or irregular. This is the most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest, in which the heart stops beating without warning. Without immediate emergency help, death follows within minutes. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Heart Attack A heart attack is damage to the heart muscle caused by a reduced or blocked blood supply. Many heart attacks are sudden and cause intense chest pain, but one in four produces no symptoms and is detected only when routine tests are done later. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Congestive Heart Failure A heart attack is an immediate response to stress on the heart. Sometimes, however, the heart gradually weakens to the point that it cannot maintain its regular pumping rate and force. The result is a condition called congestive heart failure. Strategies for managing congestive heart failure include medication and the establishment of healthy lifestyle behaviors, such as a good nutrition and adequate physical activity. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Stroke When arterial blockage interrupts the flow of blood to the brain, a stroke may occur. Stroke can affect different parts of the body, depending on the part of the brain that is deprived of oxygen. It can also occur as a result of a cerebral hemorrhage, a condition in which a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing blood to spread into surrounding brain tissue. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Why Teens Are at Risk The behaviors established during your teen years and early adult life determine, in large part, your risk of developing CVD. Autopsy results of adolescents who died from causes other than CVD have revealed that one in six already had evidence of CVD. Those who had a history of known risk factors, such as smoking or diabetes, were more likely to have blood-vessel damage. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Factors That You Can Control Factors That You Cannot Control Tobacco use Heredity High blood pressure Gender High cholesterol Age Physical inactivity Excess weight Stress Drug and alcohol use Lesson 1 Quick Review Choose the appropriate option. Q. Chest pain that results when the heart doesn’t get enough oxygen is called _______. 1. arrhythmia 2. atherosclerosis 3. hypertension 4. angina pectoris Lesson 1 Quick Review - Answer A. Chest pain that results when the heart doesn’t get enough oxygen is called angina pectoris. Click Next to attempt another question. Lesson 1 Quick Review Provide a short answer to the question given below. Q. What is atherosclerosis? How does it contribute to heart attacks? Click Next to view the answer. Lesson 1 Quick Review - Answer A. Atherosclerosis is the process in which plaques accumulate on artery walls. The clots that form in the plaques can block the arteries leading to the heart, causing a heart attack. Click Next to attempt another question. Lesson 1 Quick Review Provide a short answer to the question given below. Q. Define cardiovascular disease. How does regular physical activity help prevent CVD? Click Next to view the answer. Lesson 1 Quick Review - Answer A. A cardiovascular disease is a disease that affects the heart or blood vessels. Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and helps maintain a healthy weight. Click Next to attempt another question. Lesson 1 Quick Review Provide a suitable analysis. How can practicing healthy lifestyle behaviors now help you avoid cardiovascular disease in the future? Lesson 1 Quick Review - Answer A. Correct! Chest pain that results when the heart doesn’t get enough oxygen is called angina pectoris. Click Next to attempt another question. Lesson 1 Quick Review - Answer You have answered the question incorrectly. Go back to try again, or click Next to view the correct answer. Lesson 1 Cardiovascular Diseases Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases A century ago, communicable diseases were a leading cause of death in the United States. Today, however, major causes of death, such as heart disease and cancer, come from noncommunicable diseases. A noncommunicable disease is a disease that is not transmitted by another person, a vector, or the environment. Lesson 1 Cardiovascular Diseases What Are Cardiovascular Diseases? Your cardiovascular system transports blood to all parts of your A cardiovascular body. disease (CVD) is a Without oxygen other materials that blood carries, your disease thatand affects cells the would die.orSometimes diseases interfere with the pumping heart blood action of the heart or the movement of blood through blood vessels. vessels. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are responsible for more than 40 percent of all deaths in the United States, killing almost a million Americans each year. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Hypertension Hypertension is a major risk factor for other types of CVDs. Hypertension can occur at any age, but it is more common Hypertension among peopleisover age of 35. high the blood pressure. High blood pressure can be lowered with strategies such as medication, weight management, adequate physical activity, and proper nutrition. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis At birth, the lining of blood vessels is smooth and elastic. Over is the process in time, factors such as tobacco smoke, high blood pressure, and which plaques high cholesterol levels can damage the inner lining of the accumulate on artery arteries. walls. Atherosclerosis causes the arteries to thicken and lose their elasticity. It is caused mainly due to food choices—specifically, a high intake of saturated fats and cholesterol. Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Angina Pectoris Angina pectoris, which usually lasts from a few seconds to minutes, is a warning sign that the heart is temporarily not getting enough blood. Angina pectoris is chest cause pain that The most common of angina is atherosclerosis. results when the heart does permanent not get Angina seldom causes heart damage and oxygen.with medication. sometimes enough can be treated Lesson 1 Types of Cardiovascular Disease Arrhythmias Arrhythmias occur in millions of people who do not have underlying heart disease, and they usually don’t cause problems. Arrhythmia change in called ventricular fibrillation, the In one typeisofa arrhythmia, the regular beat heart rhythm become rapid or electrical impulses regulating irregular. of the heart. This is the most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest, in which the heart stops beating without warning. Without immediate emergency help, death follows within minutes.