* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
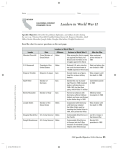
The Rise of Dictators and World War II, 1931–1945 The rise of fascism leads to World War II. The war is won by the allies and has major consequences for the world. British troops advance across the desert during the North Africa campaign of World War II. NEXT The Rise of Dictators and World War II, 1931–1945 SECTION 1 Steps to War SECTION 2 War in Africa and Europe SECTION 3 War in the Pacific SECTION 4 The Home Front SECTION 5 The Legacy of the War NEXT Section 1 Steps to War The rise of dictators in Europe and Asia leads to World War II. NEXT SECTION 1 Steps to War The Rise of Dictators • By mid-1930s, dictators control Italy, Germany, Japan, Soviet Union • Japan, Italy dissatisfied by treaties ending World War I • After WW I Germany treated harshly, loses some territories, all colonies • Forced to disarm, pay war damages, accept war’s responsibility • Great Depression causes mass unemployment, unrest worldwide • Many Europeans turn to new leaders to solve problems NEXT SECTION 1 Mussolini, Hitler, and Stalin • Italy’s Benito Mussolini begins political movement called fascism • Fascism—extreme nationalism, patriotism, linked to racism: - oppress people with different views • Mussolini becomes Italy’s dictator (1925), called IL Duce (the Leader) Image Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 1 continued Mussolini, Hitler, and Stalin • Adolf Hitler leads National Socialist German Worker’s Party (Nazi ) • Nazis preach German racial superiority, revenge of WW I defeat • Win control, government (1933), Hitler called der Führer (the Leader) • In Russia, Joseph Stalin succeeds V.I. Lenin • Imposes strict control, crushes any form of opposition Image NEXT SECTION 1 Dictators Seek to Expand Territory • Japan conquers Manchuria (1931), Italy conquers Ethiopia (1936) • Germany takes over Rhineland, shock French who take no action • Germany, Italy, their allies form alliance known as the Axis • Supported by Hitler and Mussolini, fascist forces take over Spain • Hitler invades Austria (1938), welcomed by many Germans, Austrians Map NEXT SECTION 1 Appeasement at Munich • Hitler wants to take over Sudetenland, Czechoslovakia • France, Russia pledge to support Czechoslovakia if attacked • Britain’s Neville Chamberlain meets with Hitler (1938), agree that: - Germany takes control of Sudetenland - Germany promises not to seek more territory • Agreement is appeasement—meet Germany’s demands to avoid war NEXT SECTION 1 Germany Starts the War • Hitler conquers rest of Czechoslovakia, intends to attack Poland • Germany, Soviet Union sign nonaggression pact, both invade Poland • Germany uses new method of warfare blitzkrieg (lightning war): - stresses speed, surprise in use of tanks, troops, planes • Hitler conquers Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Luxembourg, Netherlands Interactive Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 1 continued Germany Starts the War • British soldiers retreat to Dunkirk, British vessels evacuate them • German troops invade France, reach Paris in two weeks (1940) • Britain’s Royal Air Force fights German Air Force, or Luftwaffe • German planes launch massive bombing attack on London • Battle of Britain frustrates Hitler, British do not surrender Image NEXT SECTION 1 Germany Attacks the Soviet Union • Soviet Union invades Finland, seizes Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania • Despite alliance, Hitler and Stalin distrust each other • Hitler invades Soviet Union, June 1941 • Reinforces armies heading North, South instead of focusing on Moscow • Germans try to capture Leningrad for 3 years, city never falls • Harsh winter halts German advance, Soviets drive Germans back NEXT SECTION 1 The United States Aids the Allies • FDR sets up Lend-Lease Act (1941), allows U.S. to: - lend, lease raw materials, equipment, weapons to the Allies - send $50 billion in war goods to Allies NEXT SECTION 1 Japan Attacks Pearl Harbor • Japan joins alliance with Germany, Italy (1940) • Wants to invade Dutch East Indies, needs to eliminate U.S. Navy • Japanese planes bomb American naval base Pearl Harbor (Dec. 7, 1941) • About 2,400 Americans die in attack, U.S. planes, ships destroyed • U.S. declares war on Japan, Germany; Italy declares war on U.S. Map NEXT Section 2 War in Africa and Europe The Allies defeat the Axis powers in Europe and Africa. NEXT SECTION 2 War in Africa and Europe Mobilizing for War • In U.S., millions volunteer for armed forces, millions more drafted • Selective Service Act—men between ages 18-38 register, military • Mexican, African, Asian and Native Americans enlist • African Americans, some Japanese Americans serve in segregated units • Women serve in armed forces, also join Army, Navy Nurse Corps Image NEXT SECTION 2 Battles in Africa and Italy • Britain fights Axis forces for control of northern Africa, Suez Canal • General Erwin Rommel commands Germany’s troops in Africa • British stop German advance toward the Suez Canal (1942) • U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower, Allied troops land, northern Africa • Defeated by Rommel, regroup, force Axis in northern Africa, surrender • Allies establish base from which to attack southern Europe Image Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 2 continued Battles in Africa and Italy • Allies force Germans out of Sicily (1943), sweep into Italy • Mussolini imprisoned, escapes, Italy surrenders to Allies (Sept. 1943) NEXT SECTION 2 The Allied Advance and D-Day • Germans attack Stalingrad, after harsh winter surrender to Soviets (1943) • D-Day—Allied forces invade Normandy in France (June 6, 1944) • After suffering severe losses, Allies secure Normandy beaches • Allied forces pour into France, liberate Paris • U.S. soldier Audie Murphy kills 50 enemy troops, gets Medal of Honor • Battle of the Bulge—German troops attack Allies, defeated NEXT SECTION 2 Victory in Europe • Allied leaders FDR, Winston Churchill, Joseph Stalin meet in Yalta • Yalta Conference—plans made for end of war, Europe’s future: - Stalin promises to declare war on Japan after Germany surrenders - establish a postwar international peace-keeping organization - discuss types of government to be set up in Eastern Europe Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 2 continued Victory in Europe • FDR dies, vice-president Harry S. Truman succeeds him • Russians reach Berlin, Hitler commits suicide, Germany surrenders • Allies declare May 8, V-E Day (Victory in Europe Day) NEXT SECTION 2 The Horrors of the Holocaust • Allies discover concentration camps where Jews, others murdered • During the Holocaust Nazis kill: - about 6 million Jews - millions of people from other ethnic groups - 11 million people in all • Hitler preaches hatred of Jews, blames Jews for Germany’s problems Chart Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 2 continued The Horrors of the Holocaust • Hitler enforces anti-Semitism, denies Jews their rights, possessions • Starts “The Final Solution”—kill every Jew under German rule • Nazi’s cram Jews into concentration camps • Force able-bodied to work, rest are slaughtered • Kill hundreds at a time in gas chambers, then burn bodies in ovens • In largest concentration camp, Auschwitz, more than 1 million murdered Image NEXT Section 3 War in the Pacific After early losses, the Allies defeat the Japanese in the Pacific. NEXT SECTION 3 War in the Pacific Japan Expands Its Empire • Japan conquers Hong Kong, Thailand, U.S. islands Guam, Wake • Attacks Malaya, Burma, defeats British forces • Invades Philippines, meets stiff resistance from U.S., Filipino troops • In Philippines, U.S. General Douglas MacArthur told to withdraw • U.S. troops on Bataan surrender to Japan, endure Bataan Death March NEXT SECTION 3 The Allies Turn the Tide at Midway • U.S. launches daring air raid on Japanese cities, including Tokyo • U.S. Navy blocks Japanese advance at Battle of the Coral Sea • Defeats Japanese navy at Battle of Midway (June 1942) • Marks turning point in the war NEXT SECTION 3 The Allies Advance • Allies attack Japanese by using method called island hopping: - invade islands not heavily defended by Japanese - use captured islands to stage further attacks Interactive Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 3 continued The Allies Advance • Allies defeat Japanese at Guadalcanal (1942) • Use Navajo language to transmit messages, Navajos as Code Talkers • Allies take over the Philippines, Japanese navy severely damaged • Japanese use kamikazes, suicide pilots fly planes into Allied warships NEXT SECTION 3 Iwo Jima and Okinawa • Allies conquer islands of Iwo Jima, Okinawa (1945) • More than 18,000 U.S. deaths, more than 120,000 Japanese deaths Image NEXT SECTION 3 Atomic Weapons End the War • To avoid heavy U.S. casualties, U.S. uses atomic bomb on Japan • Manhattan Project—top-secret program set up to build atomic bomb • President Truman warns Japanese about destruction • Japan does not surrender, atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima, kills 70,000 • Japan refuses to surrender, 2nd atomic bomb hits Nagasaki, kills 40,000 • Japan surrenders on September 2, 1945 Image NEXT Section 4 The Home Front Americans at home make great contributions to the Allied victory. NEXT SECTION 4 The Home Front Wartime Production • War Production Board (WPB)—guides production of war supplies • WW II ends Great Depression, U.S. unemployment rate falls • Armed forces need for materials makes some items scarce • Rationing—families receive a fixed amount of scarce items • To pay for war, government raises income taxes, sells war bonds Chart NEXT SECTION 4 Opportunities for Women and Minorities • Many men fight overseas, demand for women workers rises sharply • “Rosie the Riveter”—popular image, strong woman works in arms factory • African Americans get many jobs in defense industry • Go to cities offering jobs, influx inflames racial tension Image Continued . . . NEXT SECTION 4 continued Opportunities for Women and Minorities • A. Philip Randolph helps get equal rights for blacks in workplaces • President Roosevelt issues Executive Order 8802, outlaws: - job discrimination in defense industries working for U.S. government • Thousands of Native Americans, Hispanics work in war industries • Bracero program—U.S. government hires Mexicans to do farm labor • Los Angeles, U.S. servicemen attack Mexican Americans in zoot-suit riots NEXT SECTION 4 The Internment of Japanese Americans • After Pearl Harbor, Japanese Americans seen as security threat • President Roosevelt supports JapaneseAmerican internment: - more than 110,000 Japanese Americans moved from homes to camps - kept under guard, live in cramped conditions • U.S. fear of Japanese-American disloyalty is unfounded • Japanese-American military units show courage in battle Map NEXT Section 5 The Legacy of the War World War II has deep and lasting effects on the United States and the world. NEXT SECTION 5 The Legacy of the War The War’s Human Cost • World War II claims more lives than any other war • Soviet Union suffers most severe losses: - 7.5 million military deaths, 5 million wounded • •Civilian casualties number in the millions War creates about 21 million refugees, try to readjust after war NEXT SECTION 5 Economic Winners and Losers • WW II leaves many of world’s economies in ruins • Only U.S. comes out of war with a strong economy • Secretary of State George C. Marshall sets up Marshall Plan (1948): - U.S. gives 13 billion to European countries to help them revive NEXT SECTION 5 Changes in American Society • G.I. Bill of Rights—provides education, economic help to veterans • Returning soldiers cause housing shortage • Many Americans have moved to war-related jobs in cities, California • Includes hundreds of thousands of African-Americans NEXT SECTION 5 The Nuremberg Trials • Nuremberg trials—international court tries Nazi leaders for war crimes • 24 defendants accused of crimes against humanity including: - murder of millions of Jews, others • 19 defendants found guilty, 12 sentenced to death • 185 other Nazi leaders found guilty in later trials Image NEXT SECTION 5 Creation of the United Nations • WW II shows weakness of League of Nations • League is weak largely because U.S. is not a member • 50 nations, including U.S., form peacekeeping body—United Nations NEXT SECTION 5 International Tensions • United Nations helps found Israel, a homeland for Jews in Palestine • Neighboring Arab nations attack Israel • Many colonies around the world fight for independence • Powerful Soviet Union puts Eastern Europe under Communist control • U.S. wants to stop spread of Communism • End of WW II marks beginning of the atomic age NEXT This is the end of the chapter presentation of lecture notes. Click the HOME or EXIT button. NEXT Print Slide Show 1. On the File menu, select Print 2. In the pop-up menu, select Microsoft PowerPoint If the dialog box does not include this pop-up, continue to step 4 3. In the Print what box, choose the presentation format you want to print: slides, notes, handouts, or outline 4. Click the Print button to print the PowerPoint presentation Print Text Version 1. Click the Print Text button below; a text file will open in Adobe Acrobat 2. On the File menu, select Print 3. Click the Print button to print the entire document, or select the pages you want to print Print Text BACK