* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 23/24 - Cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
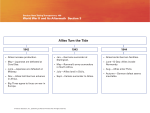
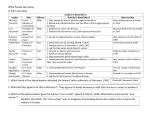
Chapter 23/24 •Coming out of the Depression •The New Deal(s) •Drawn in •Forced In •War in Europe •War in the Pacific •The War’s Effects at Home Coming out of the Depression • Blame placed mostly with Herbert Hoover and policy of “normalcy” • Election of 1932- FDR elected; campaign song “Happy Days are here again” • Help campaigning from wife Eleanor • New Deal promises government help within first “100 days” The New Deal(s) • Closed banks to prevent bank runs and sets up FDIC • Creates new jobs through public works agencies:” Alphabet soup” p. 775 • Codes to prevent business abuses(771) • Help to Homeowners (FHA) • Help to Farmers (AAA) • Rural electrification • Wagner Act- gives workers power • Social Security (776) Drawn in to War • Changing political climate in Europe(map on pg 799) • Rise of Dictators- Stalin, Hitler, Franco , Mussolini. • Germany allies with Soviets; Begin expansion in W. Europe • Invasion of Poland, France, Britain • Genocide of Non-Aryans, especially Jews. Forced In • U- Boat attacks discourage trade, threaten economy. • Germany allies with Italy- Japan soon joins. • This alliance- Axis Powers spread into North Africa and China • Public outcry to help those being killed • Our former allies are being invaded • Japanese attack at Pearl Harbor Dec. 7,1941 • Dec 11, Germany and Italy Declare war War In Europe • Hitler becomes chancellor and president in 1934 and begins to rearm and expand Germany. (violating Versailles treaty.) • Axis powers- Italy and Germany (later Japan) sign treaty- all have a desire to expand holdings. • Blitzkrieg in Poland, sitzkrieg in W. Europe. • German aggression in Norway and Denmark. French retreat and then give up Paris. • London Bltiz by Luftwaffe in 1941. • US joins Fight and signs Atlantic charter- 1st goal is to limit the success of U-boats. • US and Allies regain control of Africa and plan the retaking of Europe at the Casablanca Conference. • Italy was the first to be taken back- Mussolini ousted and Allies gain control. • Axis spread East in face of losses- attempt to gain Russian resources-Germany breaks pact with Stalin. • Germany stopped at Stalingrad. Losses on both sides. • D-day planned as the effort to re-take Western Europe started in 1944. • Paris regained by Allies • Battle of the Bulge in Dec. 1944. 80000 US dead,injured or captured. Germany lost 100000. • Russian Red Army applies pressure from the East. US and British apply from the West. • 1945 - Germany surrenders. Hitler commits suicide. V-E day celebrated but war continued in Asia. • Germany and Berlin split up among Allies at Yalta. War in Asia • Japan needs to expand- population boom in 1920s. • Limited land in Japanese region • Two-party system fails- leaves Japan open for nationalization and military rule. • Manchurian incident- opens up the occupation of China • Japan was part of the Allied powersWW1 • Japan military begins to serve as gov’tneighboring countries see Japan as a threat (see map 815) • Japan becomes part of the Axis Powerscommon enemy with Germany (Russia) • Japanese expansion part of Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere- like lebensraum. • Japan sought possessions throughout Asia as far as India. • Several Allied colonies attacked (pg. 847) • Bataan Peninsula of the Philippines (US and Filipino soldiers surrender) • Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor Dec. 1941 draws US into WWII • Japan’s goal was to take out US aircraft carriers. • Battle at Coral Sea- Japan looking to gain Australia: Stalemate. • Japan expansion continues until battles of Midway (broke code and sunk carriers)and Guadalcanal (US offensive, first jungle battle): turn the tide. • Two largest battles at Iwo Jima and Okinawa • Sudden end of the war brought upon with the use of Atomic bombs (2 dropped) Effects on Societal Groups • • • • • African Americans Native Americans Mexican Americans Japanese Americans Women