* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Europe in Two World Wars
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
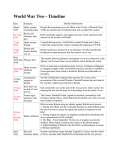
Europe in Two World Wars Causes of world War I • Nationalism – extreme patriotism • Italian nationalists freed Italy from foreign control and unified Italy. • Led by Giuseppe Garibaldi. • Germany also was divided. • Otto von Bismark created a unified Germany. • Both countries sought to find their place among world powers. Militarism • Nationalism and the Industrial Revolution led to Militarism. • Countries built strong militaries to expand their power to build overseas empires. • Carved up much of Africa and Asia. • Powerful countries came in conflict with each other. • Nations glorified war and military power. Alliances • Tension grew, countries formed alliances to aid them in case of war. • Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy formed the Triple Alliance. • France, Britain, Russia formed the Triple Entente. • This created more tension. The Beginning • June 1914 – Archduke Ferdinand of Austria was visiting Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia. • He and his wife were assassinated by a Bosnian nationalists. • Austria accused Serbia of planning this and threatened war. • Germany stood by Austria. • Russia stood by Serbia. The Beginning • August 1, 1914 – Germany declares war on Russia. • France and Britain side with Russia. • Austria and Italy side with Germany. • World War I has begun. WWI • War was fought on many fronts. • Trench warfare – soldiers dug long trenches protected by mines and barbed wire. • One side would shell the other then send its soldiers “over the top”. • Hundreds of thousands of soldiers were lost for very little territory. New Weapons • • • • Both side used new weapons. Machine guns, poison gas. Caused mass casualties. Use of aircraft, first for observation then later for bombing and “dogfights”. • German “U-boats” attacked merchant ships. • April 1917 – U.S. is drawn into the war. The End • Presence of American soldiers boosted the morale of the Allies. • In early 1918 American and Allied forces pushed back a final German offensive. • November 11, 1918 – Allies and Germany signed and armistice agreement ending the war. The Peace • 1919 – Met in Paris to develop a peace settlement. • Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh terms on Germany because it blamed them for starting the war. • Included heavy reparations. • War caused enormous property damage. • Millions killed or wounded. Rise of Dictators • During 1920’s and 1930’s Europe struggled to recover from the WWI. • People faced economic hardships and political unrest. • Turned to powerful leaders who promised a better future. Facist Italy • Italy plagued by bad economy and blmaed government for the problems. • Benito Mussolini founded the Facist Party. • Glorified the state and supported nationalist expansion. • Condemned democracy • Mussolini ruled as a dictator. • Silenced critics, controlled army, created secret police, invaded Ethiopia. Nazi Germany • Experienced extreme turmoil after the war. • Inflation and high reparations weakened the economy. • Adolf Hitler gained control of the National Socialist Party. • Blamed Jews for Germany’s problems. • 1933- Hitler became Chancellor of Germany. • Crushed opposition and became the “Furhrer”. Nazi Germany • Secret Police arrested anyone who opposed the Nazi’s. • Used propaganda to spread their message. • Waged violent campaign against the Jews. • Sent millions of Jews to concentration camps. • 6 million Jews and 5 million others lost their lives in concentration camps. WWII • September 1, 1939 – Germany invades Poland; official beginning of WWII. • Britain and France declare war on Germany (Allies). • Italy and Japan align with Germany(Axis). • Allies will eventually include the Soviet Union, the U.S., and 45 other countries. • The Axis advances across Europe in the early years. • Military strategy was the “blitzkrieg”, “lightning war”. • Planes, tanks, artillery, and mechanized infantry launched a combined attack on a country. • Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France all fall by 1941. • Britain is the next target. • German bombers run nightly bombing raids to weaken England before invading it. • The Battle of Britain was eventually won by courageous British pilots with aid from the U.S. • In June 1941 Hitler invades Russia. Successful until stopped by harsh winter and fierce fighting by Russian soldiers. • December 7, 1941 - Japan launches surprise attack of U.S. Pacific fleet at Pearl Harbor. • U.S. enters the war. • Japan captures the Philippines and other islands in the South Pacific. • U.S. begins sending troops to South Pacific to push back the Japanese. • 1942- the tide begins to turn. • Axis advance in North Africa is stopped and Germans badly defeated at Battle of El Alamein. • Germans defeated at Battle of Stalingrad, 1943. • U.S. Marines push Japanese out of Guadalcanal in February of 1943. • “Island hopping” continues as U.S. gains control of the South Pacific by defeating the Japanese on Tarawa, Iwo Jima, the Solomon Islands, and Okinawa. • June 6, 1944 – D-Day – allies land huge invasion force on the beaches of Normandy on the coast of France. Begin to push Germans back into Germany. • August 25, 1944 – Paris is liberated. • December, 1944 – Battle of the Bulge – major German offensive to try and break the invasion. Eventually fails due to the efforts of U.S. General George S. Patton and his 3rd Armored Division. • Russian troops move into Germany from the east and American and British forces cross into Germany on the west. • April 30, 1945 – Hitler commits suicide in his bunker in Berlin. • May 7, 1945 – Germany officially surrenders and the war in Europe ends. • U.S. prepares for a massive invasion of the Japanese Islands. Estimates of expected casualties are extremely high. • August 6, 1945 – U.S. drops atomic bomb on Japanese city of Hiroshima. • Three days later they drop a second atomic bomb on the city of Nagasaki. • 6 days later, on August 15, 1945, Japan surrenders and WWII comes to an end. • Effects of WWII • 30 million deaths in Europe and possibly 60 million worldwide. • Many cities in Europe and Asia destroyed or heavily devastated. • Millions of homeless people. • 6 million Jews murdered along with another 5 million Gypsies, homosexuals, political prisoners, and mentally and physically handicapped people during the Holocaust. • Two new superpowers emerge – the U.S. and the Soviet Union. • European colonies in Africa and Asia seek independence. (Israel is formed and India gets independence) • United Nations is formed to prevent world wars in the future.