* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operating Systems - Personal Web Server
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
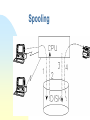
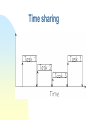
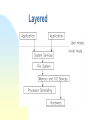
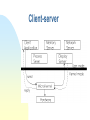
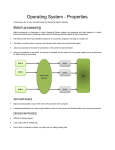
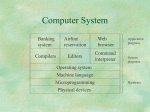
Operating Systems Objective The historic background What the OS means? Characteristics and types of OS General Concept of Computer System A Computer System consists of five components, namely, Hardware provides the basic resources including CPU, Memory, Harddisk, etc. Application programs define the ways in which resources are used to solve the problems of the users Users to OPERATING SYSTEMS (OS) to use the system operate the system Document policy to guide the application How can application programs make use of hardware resources? How to move a program from disk to main memory? How can a character be read in from the keyboard and is displayed on the screen? How to control a printer for printing a file? Operating systems provide a link between application programs and the hardware. What Operating Systems can do? Program modules within a computer system that govern the control of system resources OS is a resource manager which: Keeps track of the resources Enforces policy that determines who get what, when, and how much Allocates resources Reclaims resources Terminology Resource Is a commodity necessary to get work done. This includes the disk drives, CPUs, etc. Process Is a fundamental entity that requires resources to accomplish, basically a program in execution. Command Interpreter It is a special process that reads commands from a terminal.. Thread sometimes called a lightweight process (LWP). It is a basic unit of CPU utilisation Historical Developments Stage one The computer systems at that time were massive, expensive and difficult to use. Stage Two, Operator-driven In an effort to avoid idleness, an operator was hired to perform the repetitive tasks Stage 3 Off-line Much of the operator’s job was mechanical. The next stage was to automate that job Historical Development. Stage Four, Spooling At this stage, disks were introduced as a secondary storage medium. Stage five, Multiprogramming having more than one job by partitioning the main store into several pieces, Stage Six, Time sharing system called multi-tasking and is a logical extension of multiprogramming. Stage Seven, Distributed Systems The more recent development focuses on distributed computing. Spooling Multiprogramming Time sharing Structure of Operating systems There are four different structures as given below: Monolithic system Layered System Virtual Machine Client-server model OS Components Process Management Memory Management Secondary Storage Management I/O System Protection System Command Interpreter System Monolithic Layered Virtual Machine Client-server Future trend Multiprocessing will become much more common. Hardware architectures of the future will distribute control into localized processors. Languages are being developed to exploit concurrency Massive parallelism will become common will be designed to foster (foster means help) the operation of virtual machines Developments in software engineering will result in more maintainable Classification of Operating System Off-line, Batch and Remote batch On -line, Time sharing Personal computing, User progammable Data base, Real time Non-programmable, Multi-user single user, System features Characteristics of OS Have priority over user programs Manage input, output, memory and CPU (Data entry, output to printer) Increase computer system efficiency Sequence and schedule programs Handle hardware errors and pProvide security for user programs Windows 95/98 - Outline Win95 was released in August 1995 Total rewrite and replacement for Windows 3.x Windows-95 “backwards compatible” with software from earlier O/S Major, modern features include Summary Compatibility It means that the ideal operating system is designed to provide execution environments for applications for other operating systems. Portability It means that the operating system can be ported to a variety of different machines Robustness It means that the ideal operating system can provide protection from accidental or deliberate damage by user programme Usability Easy to use, click and drag are more friendly than DOS prompt commands Summary Efficiency The system functions quickly, makes optimum use of the resources Flexibility Adaptability to a specific environment, like Unix can be in Minicomputer or PC Transparency Users are unaware of all details they need not know Security Protecting data from unauthorized access Integrity Protecting itself and users from damage or any other ill effect of other’s error or malice.