* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renaissance
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
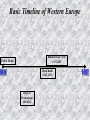
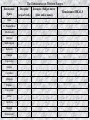
The Renaissance 1300s – 1600s Basic Timeline of Western Europe Hundred Years’ War (1337-1453 Fall of Rome Black Death (1347-1352) Reign of Charlemagne (800-824) Europe is “reborn” • Fall of Rome Dark Ages Black Death… • Death + Destruction + Disease = Bad • But culture & the arts are revived …starting in Italy • Let the Golden Age Begin Political Popes vs. Kings End of feudalism **Turning Point** Age of Transition & Change Economic New middle class More trade and $ Social Renaissance & Reformation Medieval Concerns vs. (Gives way to) Renaissance Faith 1. Reason Authority (acceptance) 2. Questioning Tradition 3.Experiment/Inquire Afterlife 4. Here and now Spiritual 5. Human beings (mind & body) Why Italy? • • • • • Location! Location! Location! Cities survived the Middle Ages Renaissance starts in Florence Ports on the Mediterranean Sea allowed for trade Money from the merchant class spent loads of money supporting the arts – Like the Medicis!! – Lorenzo de Medici aka Lorenzo the Magnificent was a huge patron of the arts • Very powerful family…freakishly powerful! The Renaissance 1. Location of Venice between Western Europe and Middle East and Asian markets 2. Renaissance means REBIRTH 3. People interested in a wide variety of things (secular = worldly, not religious) 4. Humanism = importance of the INDIVIDUAL 1 What Was the Renaissance? • The Renaissance was a time of creativity and change in many areas –political, social, economic, and cultural. Perhaps most important, however, were the changes that took place in the way people viewed themselves and their world. • Renaissance thinkers explored the human experience in the here and now. They emphasized individual achievement. • The Renaissance ideal was the person with talent in many fields. • Leonardo DaVinci IS CONSIDERED BY MANY TO BE THE RENAISSANCE MAN! ______ism • Words that end in “ism” can often be broken down and understood by replacing the “ism” with the following: A belief in (or emphasis on ) ________ (the remaining word) Example = materialism – “a belief in” or emphasis on material objects, comforts and/or considerations. Along with a disinterest or rejection of spiritual, intellectual, or cultural values Global 9 -The RENAISSANCE Consider: What is your “world view”? In other words, how do you see the world today in terms of an “…ism” (a belief in …) Global 9 –Introduction to the RENAISSANCE Write some thoughts down on paper and be prepared to present and defend them! Individualism? Secularism? (a.k.a materialism) Classicism? (“old school” is cool) HUMANISM? An “___ism” can be defined as “a belief in___________: Individualism = belief in the power of the individual mind and body Secularism (a.k.a materialism) = pertaining to worldly or non-religious matters Classicism? (“old school” is cool) = belief or admiration of Greco-Roman culture HUMANISM = philosophical movement during the Renaissance that stressed life on Earth, and the quality of being human. Rejected living only for the afterlife of Christianity (Middle Ages view). 1 Humanism At the heart of the Italian Renaissance was an intellectual movement known as humanism. Humanism was based on the study of classical culture and focused on worldly subjects rather than on religious issues. Humanists studied the humanities, the subjects taught in ancient Greece and Rome. They believed that education should stimulate creativity. Paleolithic art from the cave of Lascaux, France 1 Renaissance Artists and Writers Explored New Themes and Techniques WRITERS PAINTERS Wrote self-help books to help ambitious men and women rise in the Renaissance world Developed realistic style Learned rules of perspective Used shading to make objects look round and real Studied human anatomy Used live models ARCHITECTS Rejected Gothic style Adopted columns, domes, and arches that had been favored by the Greeks and Romans Italy WAS once “Glorious” Roman Empire Italian citystates (Venice) survived the Middle Ages Italian merchants became PATRONS of the arts HUMANISM •Study of classics (Greco-Roman) •Study of WORLDY subjects •Petrarch = Influential writer Golden Age of the Arts •Learned from classical arts •Use of perspective •Artists = Michelangelo, DaVinci, Botticelli •Writers = Dante, Machiavelli Spreads NORTH in Europe •Humanists = More •Artists = Dürer, Breugal •Writers = Chaucer. Shakespeare, Cervantes The Renaissance in Western Europe Renaissance figure Dante Sir Thomas More Machiavelli DaVinci Michelangelo Botticelli Chaucer Copernicus Galileo Cervantes Petrarch Raphael Castiglione Durer Van Eyck Bruegal Shakespeare Discipline (area of work) Examples / Subject matter (titles and/or names) Renaissance IDEALS Classicism The Birth of Venus (c. 1485-86) School of Athens Albrecht Dürer – self-portrait Individualism The Death of Orpheus (son of the God Apollo) Classicism Secularism Individualism & Secularism The Italian Renaissance The Renaissance: Was it a Thing? - Crash Course World History #22