* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP BIO Genetics Guided Notes 1 2016
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
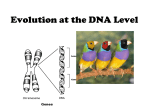
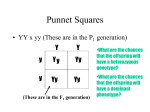
AP Bio Genetics Name_________________________ GENETICS – is Parents send _________________ about TRAITS (__________________ ) to their offspring. We refer to this information as a ____________, which is a segment of DNA that codes for a specific trait. GENES are found on ___________________ and are made up of DNA which we will be talking about in our next unit. Each individual has two copies of a gene, one from each ______________. (One copy from _____ & One from _______) An ALLELE is a – The two copies you have of your genes may or may not have the same ____________________ (or alleles). Example: Both of your parents gave you an ALLELE for the trait of “tongue rolling” A DOMINANT trait – the ______________________ trait (the stronger trait) always represented with a ________ letter Example: A RECESSIVE trait – the weaker trait, can be _________ by a dominant allele, always represented with a _______ letter Example: The ability to roll your tongue is a _______________ trait, and is therefore represented with _______ “T” the choice of letter usually comes from the name of the___________ trait. Not being able to roll you tongue is a ________________ trait, and is therefore represented with a _______________”t” If the ALLELES you got from each parent are the same alleles the individual is said to be _______________________ for the trait. Ex. ________ or ________ *Remember we have talked about these prefixes before “Homo” & “Hetero” Homologous chromosomes are chromosomes with the ______ information, size, & shape. Homo means the _________. If they have different alleles the individual is said to be ___________________ for the trait. Ex. _______ Hetero means the opposite of homo, it means DIFFERENT For the letter combinations (________________________) shown below write Homozygous or Heterozygous AA____________________ Aa________________________ bb ____________________ Tt____________________ pp________________________ Qq ____________________ PHENOTYPE its ______________ appearance. What an organism _________ like. I remember “PH” Phenotype/Physical Examples of Phenotypes: GENOTYPE – the types of _____ or (types of ALLELES) that an organism has for a particular trait (i.e. tongue rolling) Examples of Genotypes: _____, ____, ____ (The combination of the two alleles you have for a trait is your genotype) Homozygous or Heterozygous refer to an organism’s ____________________ (Phenotype or Genotype) 1. If having Acne is dominant to not having Acne write the phenotypes below: AA_____________________ Aa________________________ aa__________________________ 2. If having Big eyes is dominant to having small eyes write the possible GENOTYPES below: Big Eyes_____________ Small Eyes________ 3. We defined the word “Hybrid” for our purposes it means two different parents or traits. If you have a ring that is a gold hybrid, it is made of some different things besides gold. What word that we discussed today would be a synonym (mean the same thing) as the word “Hybrid”? ____________________________ Hybrid = ____________ _________ If “Pure” means being the same throughout, as in pure gold has only gold. What word we discussed today would be a synonym (mean the same thing) as the word “Purebred”? ____________________________ Purebred = ________________________ Introduction to Genetics Problems Name___________________________ New tools in genetics: Punnett Square – Draw one here: Tongue Roller Problem #1 Tongue Rolling is dominant to not being able to roll your tongue (non-roller). Cross a Heterozygous tongue roller with someone who cannot roll their tongue. Legend – Parents – Cross it – 1. We break up the ___________ from each parent simulating ____________, where different chromosomes are separated into different gametes (sex cells). 2. Determine the _____________of the possible ___________ made if each different kind of gamete combined. Genotypic Ratio – Phenotypic Ratio – Legend Parents Cross it Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio Tongue Roller Problem #2 Tongue Rolling is dominant to not being able to roll your tongue (non-roller). Cross a homozygous dominant tongue roller with a Heterozygous tongue roller. Legend Parents Cross it Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio Flower Problem #1: Red petals are dominant to white petals. Cross a Heterozygous Red-petal flower with a white petal flower Legend Parents Cross it Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio What is the probability that these parents would have a child/offspring who would have white petals? To answer these types of questions: Look at the phenotypic ratio – place the number of offspring with white petals ( ), and then count the total number of offspring predicted ( ). The probability of having an offspring with white petals is ___ in ___, or _______% for this couple. Flower Problem #2: Red petals are dominant to white petals. Cross a Heterozygous red flower with a Heterozygous red flower. Legend Parents Cross it Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio What is the probability that these parents would have a child/offspring who would have white petals? Practice Problems. Next you will be working through some practice problems. If you have questions on how to set problems up make sure you ask. Don’t just copy down answers, it will only get more complicated so make sure you understand how to set up the basic problems.