* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
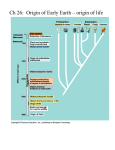
Exam 1 How to start the processes of life Chemistry to biology transition The origin of life – two approaches ! Define life here: Molecular assembly that is alive if it continually regenerates itself, replicates itself, and is capable of evolving ◦ Top-down strategy: " Look at present biology, extrapolate backwards ◦ Bottom-up strategy: " Collection of inanimate elements, molecules and minerals, figure out how they came together to create living organisms " Assemble artificial cells from scratch using non-living organic and inorganic materials Miller-Urey experiments Several variations this experiment have been performed: ! Used different types of energy source ◦ UV light to mimic the sun, as opposed to discharges to mimic lightning ! Used different types of original molecules available ◦ Different types of atmospheric chemistry ! Between all of these experiments: ◦ All of the amino acids used by life produced " including all five bases used in DNA and RNA ◦ Several complex sugar molecules and lipids also produced How to transition from chemistry => biology? ! Life needs a self-replicating molecule ◦ Initially wasn’t DNA " too complex, also require RNA for replication ◦ Discovered that RNA can catalyze biochemical reactions (similar to enzymes) and that they can at least partially catalyze their own replication ◦ RNA is now thought to be the initial selfreplicating molecule Spontaneous chemical reactions produce short RNA strains Free floating RNA bases U G U A G C G U C A A G G C U A G G U C A A G U C C Base pairing rules build a “complementary” strand of RNA A C A G U C A A G U C C A C Base pairing rules build a “complementary” strand of RNA C G A G U C U A The complimentary strand serves as a template for copying the original RNA “gene” • This process explains how RNA can self-replicate. • The self-replicating molecules may then have competed with each other, evolved through some kind of ‘molecular’ natural selection. Question: WHY? • Even though perhaps RNA naturally replicated itself - why would the success of this process matter to nature??? • All this eventually led to complex organisms and intelligence? • Why would it not just continue on at the low level of “curiosity chemistry”? ! The first step in the evolution of cellular life was RNA-based catalysis and information storage. ! RNA is able to store information (similar to DNA) and catalyze reactions (similar to enzymes) ◦ Enzyme is a substance produced by living organism acting as catalyst to bring about specific biochemical reactions. ! May have supported cellular or pre-cellular life. Competitive RNA survival: ! Those RNA/protein molecules that may be concentrated in some form of “bubble”, or “pre-cell” would benefit over others not in isolation. ! Molecular evolution would have been much faster if confined in a closed environment (similar to living cells) ◦ keep the molecules concentrated to increase the rate of reactions ! Isolation from outside would have facilitated natural selection among RNA molecules ◦ Ex: RNA assembles a protein that is able to speed up its replication. ◦ If the enzyme floats freely in the ocean it can speed up the replication of a competitor RNA, but if it is enclosed within a cell it gives the cell RNA an advantage over other cells. Advances in the development of artificial cells. Short RNA (red) is adsorbed to a particle of clay and encapsulated within a fatty acid vesicle (green). The assembly of RNA within the vesicle is coordinated by the clay particle. Rasmussen et al, Science 303 (2004) 963. ! Later on, the RNA world evolved into the DNA and protein world of today. ◦ DNA (due to its greater chemical stability) took over the role of data storage. ◦ Proteins (more flexible in catalysis) became the specialized catalytic molecules. ! How did the RNA world got started? Bottom-up hypothesis ! Experiments show that several types of inorganic minerals can facilitate the selfassembly of complex organic molecules. ! The first molecules of RNA were probably made on the surfaces of clays or other minerals. ! Clays contain layers of molecules to which organic molecules can adhere, ◦ The proximity makes them interact, forming longer chains. ◦ Experiments – produced RNA chains more than 100 bases in length. ! Lipid pre-cells can form on the surface of clay minerals that help assembly RNA molecules, sometimes with RNA inside them. ! RNA world might have been born on early Earth with the catalytic assistance of clay minerals. Membrane formation “Pre-cells” may have been common, can be easily seen in lab experiments: 1. 2. Amino acids in cooling water form enclosed spherical structures Lipids in water form closed “membranes” Membrane formation ! If we cool a warm-water solution of amino acids, they can form bonds among themselves to make an enclosed spherical structure. Not alive, but with lifelike properties: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ! Grow/shrink in size by absorbing/removing short chains of amino acids When they reach an unstable size they split into two daughter shells They allow some molecules to cross in or out, block others Store electrical energy on surface: could help chemical reactions inside The second type of membrane forms when we mix lipids with water. Summary chemistry to biology transition scenario ! Life on Earth formed spontaneously from increasingly complex chemical reactions. ! A combination of atmospheric chemistry, chemistry near deep sea vents, and molecules from space made areas with abundant complex organic molecules ! More complex molecules (short strands RNA) grew with the aid of clay minerals. Some RNA molecules became capable of self-replication ! Membranes formed spontaneously and enclosed some of the complex molecules, facilitating their interactions ! Natural selection changed the pre-cells increasing their complexity becoming living organisms ! DNA became the favoured hereditary molecule