* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECG - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
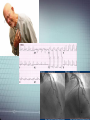
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
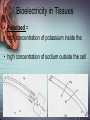
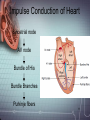
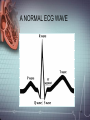
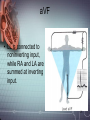
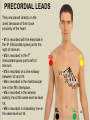
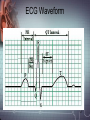
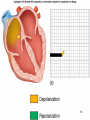
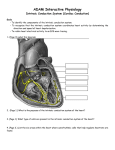
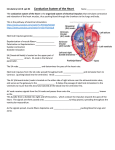
Electrocardiograph 1 2 3 History • 1842- Italian scientist Carlo Matteucci realizes that electricity is associated with the heart beat • 1876- Irish scientist Marey analyzes the electric pattern of frog’s heart • 1895 - William Einthoven , credited for the invention of EKG • 1906 - using the string electrometer EKG, William Einthoven diagnoses some heart problems. 4 Contd.. • 1924 - the noble prize for physiology or medicine is given to William Einthoven for his work on EKG • 1938 -AHA and Cardiac society of great Britan defined and position of chest leads • 1942- Goldberger increased Wilson’s Unipolar lead voltage by 50% and made Augmented leads • 2005- successful reduction in time of onset of chest pain and PTCA by wireless 5 transmission of ECG on his PDA. 6 Modern ECG Instrument 7 Heart Functions • Heart has three functions: • Pumps oxygenated blood to all parts of the body • Has its’ own blood supply – called the coronary arteries • Has an electrical conduction system because cells are electrically charged and produce a wave form 8 Bioelectricity in Tissues • Polarized = • high concentration of potassium inside the cell • high concentration of sodium outside the cell 9 Contd… • Stimulation of cell/Depolarization = sodium rushes in and potassium rushes out • When depolarization is completed, sodium and potassium return to their normal places, bringing the cell back to rest called repolarization. • This process of depolarization and repolarization produces wave forms on the EKG • ECG shows repolarization → polarization 10 with ECG complex. Impulse Conduction of Heart Sinoatrial node AV node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje fibers 11 Biopotential In Heart • SA node = Pacemaker of the heart (initiates the electricity that causes the heart to beat) • Rate=60-100 beats per minute (NSR) • Stimulates the right and left atrium to contract after depolarization of the cells Impulse travels to the: • AV Node= Functions as a delay, keeping the atria and ventricles from contracting at the same time. • Rate is 40-60 beats/minute • Bundle of His= Distal portion of the AV node • Splits into the Right and Left Bundle Branch, stimulating the right and left ventricle 12 Contd… • Purkinje Fibers= Receives the electrical impulse from the Bundle of His • Fibers transmit through the walls of the ventricles • Rate is 20-40/min 13 Definition of ECG • The ECG is a graphical representation of the electrical impulses that the heart generates during the cardiac cycle. • These electrical impulses are conducted to the body's surface, where they are detected by electrodes placed on the patient's limbs and chest. 14 A NORMAL ECG WAVE 15 16 Standard Lead System • The Standard ECG have 12 Leads • 6 Limbs Leads Limbs lead divided into Bipolar and Unipolar Leads 3 Bipolar Limb Leads 3 Unipolar Limb Leads • 6 Precordial Leads 17 Bipolar Limb Leads • They are formed by voltage tracings between the limb electrodes (RA, LA, RLand LL). These are the only bipolar leads. Or • THE EINTHOVEN’S TRIANGLE – LEAD I – LEAD II – LEAD III 18 13-61 LEAD I • LA is connected to amplifier’s noninverting input, while RA is connected to inverting input. 19 LEAD II • The LL is connected to amplifier’s noninverting input, while RA is connected to inverting input. 20 LEAD III • The LL is connected to amplifier’s noninverting input, while LA is connected to inverting input. 21 Unipolar Limb Leads • They are also derived from the limb electrodes, they measure the electric potential at one point with respect to a null point. They are the AUGMENTED LIMB LEADS. – aVR – aVL – aVF aVR aVL aVF 22 aVR • RA is connected to noninverting input, while LA and LL are summed at inverting input. 23 aVL • LA is connected to noninverting input, while RA and LL are summed at inverting input. 24 aVF • LL is connected to noninverting input, while RA and LA are summed at inverting input. 25 PRECORDIAL LEADS They are placed directly on the chest. Because of their close proximity of the heart, • V1 is recorded with the electrode in the 4th intercostals space just to the right of sternum. • V2 is recorded in the 4th intercostals space just to left of sternum. • V3 is recorded on a line midway between V2 and V4. • V4 is recorded in the midclavicular line in the fifth interspace. • V5 is recorded in the anterior axillary line at the same level as lead V4. • V6 is recorded in midaxillary line at the same level as V4 LA RA V1 RL V2 V3 V4V5 V6 LL 26 ECG Waveform 27 ECG • Three distinct wave are produced during cardiac cycle • P wave caused by atrial depolarization • QRS complex caused by ventricular depolarization • T wave results from ventricular repolarization 28 P Wave • P wave represent the atrial depolarization. • P duration: < 3 small squares or 0.08 to 0.1 sec. • P amplitude : < 2.5 small squares or < 2.5 mm 29 PR Interval • Represents the time between the onset of atrial depolarization (P wave) and the onset of ventricular depolarization (QRS Complex). • Normal duration = 0.12-2.0 sec (120-200 ms) (3-5 small squares of ECG paper) 30 QRS Complex • Represent the Ventricular depolarization • Normal duration = 0.08-0.12 seconds 31 ST Segment • Connects the QRS complex and T wave • Duration of 0.08-0.12 sec (80-120 msec) 32 T Wave • It represents the ventricular depolarization and longer in duration than depolarization. 33 QT interval • It represent the time for both ventricular depolarization and repolarization • Measured from beginning of QRS to the end of the T wave • Normal QT is usually about 0.40 sec • QT interval varies based on heart rate. 34 35 Fig. 13.24b 36 Fig. 13.24c 37 Fig. 13.24d 38 39 40 Fig. 13.24g 41 Calibration • Check that your ECG is calibrated correctly • Height – 10mm = 1mV – Look for a reference pulse which should be the rectangular looking wave somewhere near the left of the paper. It should be 10mm (10 small squares) tall. • Paper speed – 25mm/ s – 25 mm (25 small squares / 5 large squares) equals one second 42 ECG Paper 43 44