* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Ms. Bertrand
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
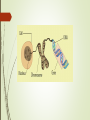
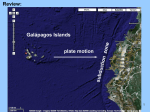
Evidence of Species Change Lesson 11.1 pages 378-383 7th Grade Ms. Bertrand Evolution Evolution is a change over time. The scientific theory of evolution explains how living things descended from earlier organisms. Why does evolution occur? Evolution is a consequence of the interaction of four factors: (1) limits on the potential for a species to increase in number (2) the genetic variation among individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction (3) competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to survive and reproduce (4) the differential production of organisms with different abilities to survive and reproduce in that environment. THEORY=Supporting Evidence in Nature There is evidence that supports the theory of evolution Fossils Similarities in DNA and Protein Structure Similarities in Body Structure Similarities in Early Development Species There are about 5 million different species of organisms living on the Earth today. However, fossil evidence suggests that this is only a small percentage of the number of all the species that have existed on Earth. Genetic Variation A gene is a hereditary unit that can be passed on for many generations. The gene pool consists of the set of genes in a species or population. Different organisms differ in genes. Individuals of the same species should not differ in the number of genes. Extinction A species can go extinct for a variety of reasons: They may have evolved into a new species environmental changes temperature changes changes in rainfall can lead to extinction if the species cannot adapt. The disappearance of a species’ main food source. Extinction will result if the species cannot find a substitute food source. Survival An organism’s survival depends on its inherited traits, which influence its ability to compete for resources, procure mates, and avoid danger to itself and its offspring. Both variation in the genetic information among organisms in a population, and the expression of that variation in genetic information that will lead to differences in performance among individuals are necessary for natural selection to occur. Traits that increase an organism’s chances of survival are more likely to be passed on to future generations; thus, becoming more common in the population. Natural Selection Natural selection is a process by which the gene frequencies in a population change over time because of the differential survival and reproductive success of various genotypes DSQ Answer The Galápagos Islands are very dry, with an average rainfall on some islands of only five inches per year. The amount of rainfall has a large impact on the availability and types of seeds that are available to be eaten by finches. In the process of natural selection, only the finches that are be adapted to the available seed types survive and have offspring Questions Which beak allows the best chance of survival? Which island allows the hairpin beak to survive the best? Which island allows the fork beak to survive the best? Which island allows the clip beak to survive the best? Which island allows the spoon beak to survive the best? Which island allows the tweezer beak to survive the best? Darwin Lab Data Analysis-MEAN Values Island A Beak 1 Beak 2 Beak 3 Beak 4 Beak 5 Beak 1 Beak 2 Beak 3 Beak 4 Beak 5 Beak 1 Beak 2 Beak 3 Beak 4 Beak 5 Beak 1 Beak 2 Beak 3 Beak 4 Beak 5 Beak 1 Beak 2 Beak 3 Beak 4 Beak 5 MEAN Values Island B MEAN Values Island C MEAN Values Island D MEAN Values Island E MEAN Values