* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alcohols and Phenols
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Polythiophene wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
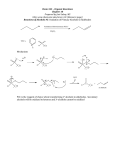
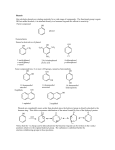
Alcohols and Phenols Chapter 17 Part 3 17.8 Oxidation of Alcohols Can be accomplished by inorganic reagents, such as KMnO4, CrO3, and Na2Cr2O7 or by more selective, expensive reagents Oxidation of Primary Alcohols To aldehyde: pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC, C5H6NCrO3Cl) in dichloromethane Other reagents produce carboxylic acids Converts secondary alcohol to ketone 1 Jones’ Reagent: CrO3 in aqueous sulfuric CH3O CH3OH CH3 PCC CH2Cl2, 25oC O Oxidizes primary alcohols to carboxylic acids: CH3 O Testosterone acid. 4-Androstene-3,17-dione CH3(CH2)8CH2OH 1-Decanol O CrO3 CH3(CH2)8COH H2SO4 Decanoic acid All of the oxidations occur via an E2 mechanism. Mechanism of Chromic Acid Oxidation Alcohol forms a chromate ester followed by elimination with electron transfer to give ketone The mechanism was determined by observing the effects of isotopes on rates Na2Cr2O7 in aqueous acetic acid is an inexpensive oxidizing agent: CH3 OH Na2Cr2O7 acetic acid 4-tert-Methylcyclohexanol What alcohols would give these products on oxidation? O CH3 CH3CHCHO CH3 O 4-tert-Methylcyclohexanone What products would you expect from the oxidation of the following compounds with Jones’ reagent? With PCC? 1 - Hexanol Jones’: PCC: 2 - Hexanol Jones’: PCC: O Hexanal Jones’: PCC: 2 Predict the major organic product: OH Cl 17.9 Protection of Alcohols K2Cr2O7 Hydroxyl groups can easily transfer their proton to a acetic acid This can prevent desired reactions basic reagent Converting the hydroxyl to a (removable) functional group without an acidic proton protects the alcohol OH PCC CH2Cl2 Methods to Protect Alcohols Reaction with chlorotrimethylsilane in the presence of base yields an unreactive trimethylsilyl (TMS) ether The ether can be cleaved with acid or with fluoride ion to regenerate the alcohol Protection - Deprotection 3 17.10 Preparation and Uses of Phenols Industrial process from readily available cumene Forms cumene hydroperoxide with oxygen at high temperature Laboratory Preparation of Phenols 17.11 Reactions of Phenols From aromatic sulfonic acids by melting with NaOH The hydroxyl group is a strongly activating, making at high temperature Limited to the preparation of alkyl-substituted phenols phenols substrates for electrophilic halogenation, nitration, sulfonation, and Friedel–Crafts reactions Reaction of a phenol with strong oxidizing agents yields a quinone Fremy's salt [(KSO3)2NO] works under mild conditions through a radical mechanism 4 Quinones in Nature 17.12 Spectroscopy of Alcohols and Phenols Ubiquinones mediate electron-transfer processes Characteristic O–H stretching absorption at 3300 to involved in energy production through their redox reactions 3600 cm−1 in the infrared Sharp absorption near 3600 cm-1 except if H-bonded: then broad absorption 3300 to 3400 cm−1 range Strong C–O stretching absorption near 1050 cm−1 (See Figure 17.11) Phenol OH absorbs near 3500 cm-1 Butanol (Gas Phase) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 13C NMR: C bonded to OH absorbs at a lower field, δ 50 to 80 1H NMR: electron-withdrawing effect of the nearby oxygen, absorbs at δ 3.5 to 4 (See Figure 17-13) Usually no spin-spin coupling between O–H proton and neighboring protons on C due to exchange reactions with moisture or acids Spin–spin splitting is observed between protons on the oxygen-bearing carbon and other neighbors Phenol O–H protons absorb at δ 3 to 8 5 6