* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - easttechtalk
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
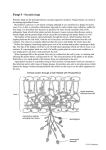
Slide 1 Colonization of Land – Ch 18 18.1 Onto Land 18.1.1 Describe the evolutionary relationship between green algae and land plants. 18.1.2 List the five significant events in the evolution of land plants. 18.1.3 Describe the alternation of generations’ life cycle in plants. 18.2 Diversity of Land Plants 18.2.1 Characterize and give examples of the various groups of land plants. 18.2.2 Describe the life cycles and reproductive strategies used by each group of land plants. 18.2.3 Summarize the economic and ecological significance of plants. 18.3 The Fungi 18.3.1 Describe the general biology of a fungus. 18.3.2 Compare and contrast fungi with animals and plants; explain what makes chytrids unique among fungi. 18.3.3 Explain the life cycles of black bread molds and mushrooms. 18.3.4 Summarize the economic and ecological significance of fungi. 18.3.5 Provide examples of fungal diseases. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 2 ___________________________________ 18.1 Onto Land • Kingdom Plantae – multicellular, photosynthetic eukaryotes which have become adapted to a land existence • • Gametes, zygote, and embryo must be protected from drying out. Most likely land plants evolved from a form of freshwater algae 500 MYA. • • • Share chlorophylls a and b Store excess carbohydrates as starch Have cellulose in cell walls ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 3 ___________________________________ • Land plants most closely related to Charophytes Chara protects its zygotes like plants. Coleochaete has a body composed of long, branched filaments of cells. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 4 • 5 evolutionary events characterize the plants ___________________________________ 1. Embryo protection – all plants protect their embryos Algae do not Mosses – lack vascular tissue but do protect their embryos 2. Vascular tissue - Lycophytes ___________________________________ For water transport, have true roots, stems, and leaves 3. Megaphylls - Ferns Increases amount of photosynthesis and carbohydrates produced 4. Seeds - Gymnosperms ___________________________________ Contains embryo and stored organic nutrients inside a protective coat 5. Flowers - Angiosperms Reproductive structure to attract pollinators and give rise to fruits ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 5 ___________________________________ • Alternation of generations Each type of plant exists in 2 forms Sporophyte • 2n or diploid • Produces haploid spores by meiosis Spore – reproductive cell that develops into new organism without the need to fuse with another reproductive cell ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Gametophyte • n or haploid • Produces gametes by mitosis • Gametes fuse to form diploid sporophyte ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 6 ___________________________________ • Dominant generation Generation that is larger, lasts longer and we recognize Nonvascular plants – gametophyte dominant Vascular plants – sporophyte dominant • Gametophyte becomes smaller and dependent In the history of plants, only the sporophyte generation evolves vascular tissue. • Trend toward sporophyte dominance is an adaptation to life on land. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 7 ___________________________________ 18.2 Diversity of Land Plants • Nonvascular plants Bryophytes Do not have true roots, stems, and leaves ___________________________________ • No vascular tissue Gametophyte dominant generation • Sporophyte dependent on gametophyte Most familiar are liverworts and mosses Flagellated sperm must swim in film of water. Sporophyte produces spores in sporangium. Not every plant named “moss” is a bryophyte. • Irish moss is an alga, Spanish moss is an angiosperm. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 8 ___________________________________ • Vascular plants All other land plants Usually have true roots, stems, and leaves Vascular tissue consists of xylem (conducts water and minerals) and phloem (conducts organic nutrients). • Xylem reinforced by lignin Seedless vascular plants ___________________________________ ___________________________________ • Lycophytes and ferns Seed plants • Gymnosperms and angiosperms ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 9 • Seedless vascular plants Dominant sporophyte, independent gametophyte Lycophytes – club mosses • Among first land plants to have vascular tissue • Small leaves called microphylls ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 10 ___________________________________ • Ferns Have megaphylls or fronds • Large leaves with branched veins Larger surface area for photosynthesis Better able to make food and grow and reproduce Sporangia located in sori on the underside of fronds Small independent gametophyte Flagellated sperm ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 11 • Seed plants Most plentiful land plants today Seed coat and stored food protect sporophyte embryo and allow it to survive until environmental conditions become favorable. Survival advantage of seeds accounts for the dominance of seed plants. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 12 • Seed plants have 2 types of spores… 2 kinds of gametophytes • Pollen grains are drought resistant male gametophytes. • Female gametophyte develops inside ovule. Ovule becomes the seed Embryo inside seed is the sporophyte Gymnosperms – ovule not enclosed by sporophyte tissue at pollination – “naked” seeds Angiosperms – ovule completely enclosed in tissue that will become the fruit No external water need for fertilization ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 13 • Gymnosperms Ovules and seeds are exposed on the surface of a cone scale. “Naked seed” Cycads are ancient gymnosperms that have been around since the Carboniferous period. Conifers have become a dominant plant group today. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 14 ___________________________________ • Conifers Pines, spruces, firs, cedars, hemlocks, redwoods, cypresses, and others Conifer – bears cones containing the reproductive structure of the plant Coastal redwood is tallest living vascular plant • Nearly 100 meters in height ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Bristlecone pine is oldest living tree • One is 4,900 years old ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 15 • Angiosperms or flowering plants Means covered seeds Exceptionally large and successful group of land plants ___________________________________ ___________________________________ • 6 times the number of species of all other plant groups combined First fossils 135 million years old ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 16 ___________________________________ • The flower Most have certain parts despite dissimilar appearances Sepals – collectively called calyx, protect flower bud Petals – collectively called corolla, quite diverse in size, shape, and color Stamen – stalk is filament, pollen produced in anther Carpel – ovary at base contains ovules, style elevates stigma which receives pollen grains ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 17 • Flowering plant life cycle Pollen is transported to stigma where it germinates. Pollen tube carries 2 sperm to ovule. Ovary contains several ovules, each eventually holding an egg-bearing female gametophyte (embryo sac). Double fertilization • 1 sperm unites with egg nucleus forming diploid zygote. • Other sperm unites with 2 other nuclei forming triploid (3n) endosperm - stored food for embryo. Ultimately, ovule becomes a seed containing the sporophyte embryo. In some seeds, endosperm absorbed by cotyledons Fruit derived from ovary and possible other flower parts ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 18 • Adaptations of angiosperms ___________________________________ Successful completion of sexual reproduction requires effective dispersal of pollen and then seeds. Pollination ___________________________________ • Insect and bird pollinated flowers often showy • Night-blooming flowers often white and aromatic to attract mammals or insects • Many flowers attract only specific pollinators ___________________________________ Bee-pollinated flowers have UV shading indicating the location of nectar. Fruit dispersal • Transported by wind, gravity, water or animals • Fleshy fruit to attract animals ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 19 ___________________________________ • Fruits Bananas Coconuts Grains – corn, wheat, rice Pods that contains beans or peas ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 20 ___________________________________ 18.3 The Fungi • Not plants – no, chloroplasts can’t photosynthesize. • Not animals – fungi are chemoheterotrophs like animals. Animals ingest their food, fungi grow into it. Animals are motile, most fungi are not. • Fungal life cycle has windblown spores during both a sexual and asexual life cycle. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 21 • General biology of a fungus Hyphae – thin filaments of cells making up all parts of a typical fungus • Hyphae packed together to make mushroom Main body of fungus is not the mushroom or puffball – these are only temporary reproductive structures. Main body of fungus is mass of hyphae called mycelium. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 22 ___________________________________ • Fungal cells typically have thick cell walls Do not contain cellulose like plants Contain chitin like exoskeleton of crabs and lobsters ___________________________________ • Wall or septa divides the cells of a hyphae in many fungi. • Hyphae give mycelium large surface area for absorption of nutrients. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 23 ___________________________________ • Black bread mold Demonstrates hyphae of a fungus may be specialized for various purposes Horizontal hyphae exist on surface of bread. Others grow into the bread – anchor and carry out digestion. Others form stalks that bear sporangia. Asexual reproduction – spores produced in sporangia Sexual reproduction – 2 different mating types meet, tips of + and – hyphae join, nuclei fuse, and a zygospore results. • Zygospore germinates to produce sporangia. • Sporangia undergo meiosis to produce spores. • Spores give rise to new mycelia. Only zygote is diploid, all other stages are haploid. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 24 ___________________________________ • Mushroom Fruiting body whose function is to produce spores In mushrooms, when + and – hyphae tips fuse, haploid nuclei do not fuse immediately. ___________________________________ • Dikaryotic (2 nuclei) hyphae form a mushroom Mushroom has stalk and cap. • Basidia on gills on underside of cap Fusion of nuclei in basidia followed by meiosis and production of spores ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 25 • Chytrids Unique group of fungi Characterized by their motility Both spores and gametes have flagella. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ • Feature lost in other fungi Some have alternation of generations like plants but uncommon in fungi. Most inhabit soil and water but some are plant or animal parasites. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 26 • Most fungi are saprotrophs Decompose remains of plants, animals and microbes Indispensable role in environment returning inorganic nutrients to photosynthesizers Some fungi eat animals as a nitrogen source. • Oyster fungus has a compound that anesthetizes roundworms so they can be digested. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 27 • Mutualistic relationships 2 different species live together and help each other out. Lichens • Fungus and cyanobacteria or green algae • Fungal partner acquires nutrients and moisture. • Photosynthetic partner makes food. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 28 ___________________________________ Mycorrhizal fungi • From mutualistic relationships with roots of most plants • Help plants grow more successfully in dry or poor soils (especially if deficient in inorganic nutrients) • Hyphae increase surface area for absorption of food and nutrients. • May live on outside of roots, enter between root cells, or penetrate root cells • Fungus and plant exchange nutrients. • Relationship an ancient one – found in fossils • Truffles are fruiting bodies of mycorrhizal fungi. ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 29 • Fungi produce medicines and many types of foods Penicillium the original source of penicillin Yeast fermentation used to make bread, beer, wine Mushroom consumption has steadily increased in the US. Figure 18.28 Commercial importance of fungi ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 30 • Fungi and plant diseases Serious crop losses As much as 1/3 of world rice crop destroyed by rice blast disease ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 31 ___________________________________ • Fungi and animal diseases Ergot fungus grows on grains and can cause hysteria, convulsions and even death. Mycoses – fungal diseases • Cutaneous – only affect epidermis • Subcutaneous – affects deeper layers • Systemic – can spread throughout body Opportunistic fungal infections in AIDS Candida albicans ___________________________________ ___________________________________ • “yeast” infections in women, thrush in the mouth Ringworm • Caused for the most part by fungus Tinea • Fungal colony grows outward in a ring • Athlete’s foot is a form of Tinea ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Slide 32 ___________________________________ • Chytridiomycotis Caused by parasitic chytrid Results in cutaneous infection of frogs worldwide Decimated frog populations • Because fungi are eukaryotes and more closely related to humans than bacteria, it is hard to design an antibiotic against fungi that does not also harm animals. Try to exploit any differences between animals and fungi ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________