* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prepositions - BasicComposition.Com
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Spanish pronouns wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Dutch grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
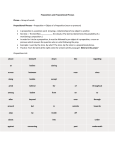
Grammar Prepositions Prepositions begin phrases that m odify other w ord s in the sentence. Often, they d escribe tim e or space relationships, show ing how a noun or pronoun relates to another w ord w ithin a sentence. COMMON PREPOSITION S The m ost frequently used prepositions are at, by, for, from, in, of, on, to, and with. Below is a list of these and other com m on prepositions. (N ote: A preposition m ay be m ore than one w ord .) about aboard above accord ing to across after against along w ith am ong as at because of before behind below beneath besid e betw een but by d ow n d espite d uring except for for from in in ad dition to inside in spite of like near of off on top of out outsid e over past since through throughout till to tow ard und er und erneath until unto up upon w ith w ithin w ithout PREPOSITION AL PHRASES A p reposition is m ost often follow ed by a noun or pronoun that serves as the object of the preposition. The preposition, its object, and all w ord s that m od ify the object m ake up a prepositional phrase. Prepositional Phrase under my old table because of his horrible attitude Preposition und er because of Modifiers m y old his horrible Object table attitud e THE ROLE OF PREPOSITION AL PHRASES Prepositional phrases norm ally function as ad jectives or ad verbs w ithin a senten ce. Adjectival Prepositional Phrases—As ad jectives, prepositional phrases usually follow the noun or pronoun they m od ify and answ er questions like W hich one? or W hat kind? EXAMPLES: The girl from Canada. (Which girl? The girl from Canada. The phrase m od ifies girl.) A d ay like today. (What kind of d ay? A d ay like today. The phrase m odifies day.) Adverbial Prepositional Phrases—As ad verbs, prepositional phrases m od ify verbs, ad jectives, or other ad verbs. They answ er questions such as the follow ing: W hen? W here? How? W hy? To what extent? Under what conditions? EXAMPLES: I slept in the barn. (The phrase m od ifies the verb slept. It answ ers the question W here?) For you, I’ll d o it! (The phrase explains under what conditions you ’ll d o it.) I am tired of this show . (The phrase, of this show, m od ifies the ad jective tired.) ID EN TIFYIN G PREPOSITION S In certain settings, a w ord that is usually a preposition may actually be a conjunction instead . If the w ord introd uces an object of a preposition (noun + w ords that modify the noun), then it is a preposition : P REPOSITION S: Before school (The phrase contains a preposition and a noun , so before is a preposition .) H e w orks as a full-time doctor. (The phrase contains the w ord as, a noun [doctor], and its m od ifiers [a full-time], so as m ust be a preposition. A full-time doctor is its object.) If the w ord introd uces a clause (group of w ord s containing both a noun subject and a verb), then it is not a preposition, but a conjunction. (See Conjunctions hand out.) C ON JUN CTION S: Before you w ent to school (The group of w ord s is a clause because it contains a noun subject [you] and a verb [went]. Therefore, before is a subord inating conjunction .) I w ill w atch as the doctor operates. (The doctor operates is a clause because it has a subject [The doctor] and a verb [operates]. Thus, as m ust be a subord inating conjunction.) Utah Valley University Writing Center Revised 12/15/2008