* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT - Lawless Teaching : Home
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
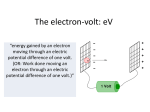
1 The Electron – Learning Outcomes Discuss the properties of the electron and its location in the atom. Discuss the etymology of the electron’s name. Discuss Millikan’s oil drop experiment. Solve energy problems in terms of electron-volts. 2 Properties of the Electron It is a particle that orbits the nucleus of an atom. It has a very small mass (9.1 × 10−31 𝑘𝑔). It is negatively charged (−1.6 × 10−19 𝐶). Instead of the usual q, electron charge is usually represented by e. This is also the smallest amount of charge in nature and all other charges are integer multiples of this (we will later see quarks as the exception to this). Named by an Irish guy, George J. Stoney (cause that’s important). 3 Millikan’s Oil Drop Experiment Millikan found the charge of an electron by suspending charged oil drops in an electric field. The electric force required was equal to the weight of the drops. He determined the charge to be either 1.6 × 10−19 C or some integer multiple of this. He concluded that this was the charge on the electron. 4 Electron-volt For many experiments, it is useful to talk about the energy of individual particles rather than the total energy. Using 𝑊 = 𝑞𝑉 and setting 𝑞 = 1, 1 eV is the energy gained by an electron when accelerated through a potential difference of 1 V. This is equal to 1.6 × 10−19 𝐽. e.g. an x-ray machine is rated at 35 kV. This means the electrons gain 35 keV of energy when accelerated in the machine. 5 Electron-volt e.g. An electron is accelerated from rest through a voltage of 3000 V. Find: i. the electrical potential energy it loses in eV. ii. the kinetic energy it gains in eV. iii. its final velocity. e.g. An electron strikes a phosphorescent screen with a speed of 2 × 107 𝑚 𝑠 −1 . Through what voltage was it passed?