* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Electric Presented by
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Light switch wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
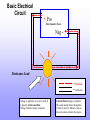
Basic Electricity Basic Electrical Circuit + Pos Electromotive Force Neg - Resistance Load = Electrons = Conductor Voltage is applied to a circuit or load. It is present and does not flow. Voltage transfers along a conductor. Current flows through a conductor. The same amount flows throughout. Current is not lost. Whatever leaves the source must return to the source. Basic Electric Safety Electrical Fire • Do not use water or touch the burning object. Why? ______________________________________ • If possible, disconnect or turn off the power. Use an ABC Fire extinguisher and notify the Fire Department. Call 911. Burns • For a serious burn, seek immediate medical attention. Call 911. 1st degree burn – red inflamed 2nd degree burn - Blistering 3rd degree burn - Charred Lockout Devices Lockout devices are commonly used on circuit breaker panels, switches, and disconnects. They should be brightly colored and easily visible. The following are typical devices: 1. A circuit breaker lockout 2. A padlock 3. A lockout for an electrical cord Types of Circuits • Series circuit: Voltage drops but amperage stays the same. • Parallel circuit: Amperage drops but voltage stays the same. Illustration of Ohm’s Law E I E (Voltage) P R I E = ______________ X ______________ = ______________ X ______________ = ______________ X ______________ = ______________ X ______________ Volts I (Current) Amps R (Resistance) Ohms P (Power) Watts Test Breaker Illustration • How many volts does a single pole breaker 120 supply? _______________________________ It only touches one Bus Bar • Why? _______________________________ • How many volts does a double pole breaker 240 supply? ____________________________ It Touches Two Bus Bars • Why? ______________________________ • What are two ways to test a circuit breaker? Voltage Continuity ___________and ____________ Good • So, continuity means the breaker is _______ • If a double pole breaker has 120 to ground on each leg but when measured together reads Bad zero is the breaker good or bad? ___________ Types of Wires Single • A wire is a _________ conductive strand • Cable contains __________strands of wire Multiple Wire ampacity must be matched to the specific load of its circuit. • Why is it important to use the correct size wire? _____________________________ • Why must aluminum wire only use devices labeled CU/AL or CO/ALR? • As the gauge increases the actual size of Decreases the wire _______________? Wire Size Amp Rating Breaker Size Voltage #6 60 65 240 #8 40 45 240 #10 30 30 240 #12 20 20 120 #14 15 15 120 #16 Light Extension Cord #18-22 T-stats Doorbells Types of Switches • The purpose of a switch is to complete or break a desired path in a circuit. • Most switches used in residential applications are toggle switches. • By far the most common is the single pole switch. It usually breaks an incoming hot wire that is connected to one screw. • The three-way switch has three terminals and is used to control a circuit from two locations. One terminal is marked COM or COMMON and that terminal is attached to the hot wire. • The other two terminals are switch leads. • The double pole switch is typically used with 240 volts. • EVERYTHING you need to know is already on the switch! • UL means underwriters laboratory. • A/C means it will only handle A/C. • CO/ALR for used with aluminum or copper. • 15a-120v it is rated for 15 amps and 120 V.