* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Artifact # 2, The Solar System
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
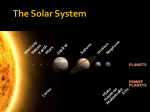
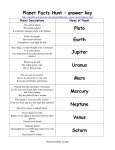
The Solar System What’s out there! Telescopes These are the kind of instruments used to discover our galaxy before satellite imaging was available. The first telescope capable of seeing beyond our moon was built in 1609, by Galileo Galilei. Where today’s pictures come from. Satellites have been able to reach all of the planets except Pluto. Without this technology, we would not have the pictures or facts that we enjoy today, about our solar system. Mercury Closet Planet to the Sun and one of the hardest to observe because it hides in the Sun’s glare. It’s temperature is about 800 degrees Fahrenheit and is the 8th largest planet. Visited by only one space craft, the Mariner 10, in 1974 and 1975. Credit: Astrogeology Team, U.S. Geological Survey Venus Venus is the 3rd brightest object in the sky. Often called the Morning Star. It is slightly smaller than Earth with a thick cloud cover. The clouds rise the temperature to 800 degrees Fahrenheit. Earth The 3rd Planet from the Sun. The 5th Largest planet. It’s 71% covered by water and the only planet believed to have liquid water. It has 1 natural satellite the moon. Our Moon The moon is the only natural satellite of Earth. First visited by Soviet Spacecraft Luna 2 in 1959. It is the second brightest object in our sky besides the Sun. It’s the 4th planet from the sun and the 7th largest. It’s temperature ranges from -67 degrees to 80 degrees Fahrenheit. As of 2004, there are Mars Expedition Rovers gathering data on the surface of the planet. A rocky planet that is cold and lifeless. Mars Jupiter Jupiter is the 5th planet from the Sun and the largest. It’s massive size is more than twice all the planets combined. It has 16 satellites. It is a gaseous planet. This is one of Jupiter’s moons. What makes it interesting is the active volcanoes present. Io is slightly larger than earth. Io, Earth and Venus are the only planets or moons that have active volcanoes. Io It’s the 6th planet from the sun and the 2nd largest. It’s a gaseous planet like Jupiter. Saturn is visibly flattened (oblate) from it’s rapid rotation and fluid state. The rings are composed of water ice and rocky material. It has 18 moons. Saturn Uranus It’s the 7th planet from the Sun and the 3rd largest. It is -300 degrees Fahrenheit. Very cold! It has 15 satellites. It also has rings like the other gaseous planets. The rings are made of large particles and dust. Neptune It’s the 8th planet from the Sun and the 4th largest. It’s a gaseous planet with rings and has a curious twisted structure inside of one. The content of the rings is unknown. It has the fastest winds in our solar system reaching 2000/km/hour. The temperature is -391 Fahrenheit which is as cold as Pluto. Pluto The 9th planet from the sun. We know very little about this planet because it has not been visited by a spacecraft yet. It is smaller than 7 of the solar system’s moons. Some think it could be an asteroid or comet and not a planet. Quiz 1- Which planet is twice the size of all the planets in our solar system combined? 2- Which planet has the highest speed of winds? 7- Which is the closest planet to the Sun? 3- Which planet is covered with clouds that rise the temperature to 800-900 degrees Fahrenheit? 8- Which planet has an oblate shape with very visible rings? 4- Which planet is the 7th and 3rd largest? 9- 5- Which planet is 71% water? 6- Which planet has expedition rovers data on it’s surface? Which planet does people call a comet or asteroid? Student Links Links to more information or activities: Teacher’s Page Note: 1. This Power Point Presentation can be used only as an introduction for your Solar System lesson by using slides 1-14. 2. Or, you can use slides 1-15, which includes a short quiz to determine classroom comprehension. 3. For individual student use, you can have them use all slides and hide the Teacher’s Page. This allows for discovery learning with more sites on the Student Links slide. 4. Remember to hide the Teacher’s Page for classroom viewing. Answers to Quiz: 1-Jupiter, 2-Neptune, 3-Venus, 4Uranus, 5-Earth, 6-Mars, 7-Mercury, 8-Saturn, 9Pluto. Credits Reference Links Bill Arnett :For the use of his sites for educational use which are listed below: www.nineplanets.org www.kids.nineplanets.org www.Bill.nineplanets.org NASA: For the pictures used of the planets included in the above websites. Standards and Indicators II-A: Teachers design developmentally appropriate learning opportunities that apply technology-enhanced instructional strategies to support the diverse needs of learners. Rationale-Allows for group learning and singular learning. II-B: Teachers apply current research on teaching and learning with technology when planning learning environments and experiences. Rationale-Use of curriculum for K-4 knowledge of objects in our ski with the latest information available form NASA, satellites available. This use of technology puts everything together for a visual experience and discovery based experience. IV-A IV-A: Teachers apply technology in assessing student learning of subject matter using a variety of assessment techniques. RationaleThis assignment allows for classroom discussion to evaluate comprehension and the use of a quiz that can be taken and evaluated on individual comprehension of the material presented.