* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapters Four and Twenty
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
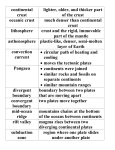
Chapters Four and Twenty-Six Practice Test PT – G – U4C4-26 Name_________________________________________________ Period__________________ Part I: True or False. Identify if each of the following statements is true or false. Write “True” if the answer is true. If the answer is false, write the word that would best replace the underlined word in the statement to make it true. Failure to follow these directions will result in no credit for the statement. (2 points each) _______________________1. At 45° north latitude, there are 16 hours of daylight in the winter and 8 hours of daylight in the summer. _______________________2. Monsoons cause cool air to come from the ocean in winter. _______________________3. Normally, moisture content increases as an air mass rises up to go over a mountain. _______________________4. The greatest amount of precipitation typically occurs around the poles. _______________________5. The way solar energy strikes Earth does influence surface temperature. _______________________6. Water has a higher specific heat than land. _______________________7. If winds consistently blow toward a shore, currents have a weaker effect on air masses. _______________________8. The ocean floor is older than continental rock. _______________________9. Paleomagnetism showed that the polarity of Earth’s magnetic field has changed more than once. _______________________10. Continental drift is the study of the formation of features in Earth’s crust. _______________________11. Earth’s plates move based on conduction currents that warp the asthenosphere and push the lithospheric plates. _______________________12. Rift valleys are formed at convergent plate boundaries. _______________________13. Ocean trenches are formed at convergent plate boundaries. _______________________14. Subduction zones are formed as a result of oceanic crust being more dense that continental crust. _______________________15. The San Andreas fault lies along a convergent plate boundary. _______________________16. Hotter magma is more dense than cooler magma. _______________________17. Each continent is made up of only one lithospheric plate. page 1 – PT – G – U4C4-26 _______________________18. Suspect terranes form primarily along divergent plate boundaries. Part II: Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. No definition will be used more than once. (1.5 points each) _______19. Transform fault boundary _______28. Mid-ocean ridges _______37. Climate _______20. Divergent boundary _______29. Asthenosphere _______38. Convection _______21. Convergent boundary _______30. Convection current _______39. Pangaea _______22. Continental crust _______31. Panthalassa _______40. Lithosphere _______23. Continental drift _______32. Plate tectonics _______41. Island arc _______24. Seafloor spreading _______33. Rift valley _______42. Latitude _______25. Subduction zone _______34. Ocean trench _______43. Monsoon _______26. Temperature range _______35. Oceanic crust _______44. Terrane _______27. Mid-Atlantic ridge _______36. Specific heat A) B) C) D) E) F) G) H) I) J) K) L) M) N) O) P) Q) R) S) T) U) V) W) X) Y) Z) General weather conditions over many years Distance from the equator The giant ocean surrounding Pangaea The single landmass thought to have been the origin of all continents Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius Difference between the highest and lowest temperatures of a particular time period Seasonal wind responsible for heavy rains in summer in Asia Hypothesis stating that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations System of undersea mountain ranges that wind around Earth Undersea mountain range with a steep, narrow valley along its center Material that makes up the ocean floor Material that makes up landmasses Steep, narrow valley formed as lithospheric plates separate Transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid Boundary formed by two lithospheric plates that are moving apart Boundary formed by two lithospheric plates that are moving toward each other Boundary formed by two lithospheric plates that are sliding past each other Movement in a fluid caused by uneven heating in which hotter magma rises and cooler magma sinks Region where one lithospheric plate moves under another Deep valley in the ocean floor that forms along a subduction zone Chain of volcanic islands formed along an ocean trench Zone of mantle beneath the lithosphere that consists of slowly flowing solid rock Outer shell of Earth consisting of the continental and oceanic crusts and the rigid upper mantle Theory that the lithosphere is made up of plates that float on the asthenosphere and that the plates are possibly moved by convection currents Movement of the ocean floor away from either side of a mid-ocean ridge Piece of land with a geologic history distinct from that of the surrounding land page 2 – PT – G – U4C4-26 Part III: Matching. Match the wind with its description. (2 points each) (A) bora (B) chinook (C) foehn (D) mistral _______45. Warm, dry wind that flows down the slopes of the Alps _______46. Warm, dry wind that flows down the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains _______47. Cold, northern wind that flows down from the Alps to the Mediterranean Sea _______48. Cold, northern wind that flows down from the mountains of Greece and the Balkan nations to the Adriatic Sea Part IV: Short Answer. Answer the following questions. 49. Explain how lithospheric plates move. (6 points) 50. Explain the process of mountain formation. (5 points) List at least two specific forms of evidence for continental drift. (3 points each) 51. ____________________________________________________________________________ 52. ____________________________________________________________________________ page 3 – PT – G – U4C4-26