* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practical Activity: Modelling Crossing Over Materials: Method
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
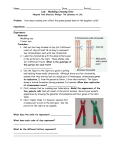
Practical Activity: Modelling Crossing Over Guiding Question: How does crossing over affect the genes on a chromosome, and variation in offspring? Materials: Modeling clay 2 twist ties Method 1. Roll out four long strands of clay about 10 cm long. 2. Join them in pairs to represent two double stranded chromosomes, each with two chromatids, just like in prophase I. Use the diagram to the right as a guide You now have a tetrad formed during prophase I of meiosis. First, assuming that no crossing over takes place. 3. Model the appearance of the four gamete cells that will result at the end of meiosis. Meiosis I will separate the chromosomes and Meiosis II will separate the chromatids, making 4 daughter cells. Record the four gametes’ chromosomes and their genes in the data table. Next, when crossing over takes place between genes B and C so that one pair of non-sister chromatids exchange their copy of gene C. Repeat steps 1-3, however, because crossing over occurs between genes B and A you will need to cut and rejoin two pieces of two non-sister chromatids. See the picture below as an example. Record the four gametes’ chromosomes and their genes in the data table. © David Faure, InThinking www.biology-inthinking.co.uk 1 Practical Activity: Modelling Crossing Over Results No Crossing Over Crossing Over Appearance of Gamete Cells Appearance of Gamete Cells Questions: 1. Define crossing over and state when it occurs. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 2. Compare the number of different allele combinations on the chromosomes in the gamete cells when crossing over occurs and when it does not occur. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 3. Crossing over is responsible for some of the variation seen in offspring produced by sexual reproduction. Explain what this means. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. This activity was adapted from an idea in Glencoe’s Biology: The Dynamics of Life © David Faure, InThinking www.biology-inthinking.co.uk 2