* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
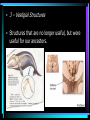
Evolution & Natural Selection First thoughts on the idea… • “Acquired Traits” – If you want it you can make yourself have it • Once a structure is modified it is passed onto offspring Lamark Next to hypothesize….Charles Darwin • “Natural Selection” • Organisms best suited to their environment reproduce more successfully than other organisms, increasing favorable traits. Evolution… • is a gradual change in a species over time that is caused by natural selection. Why change? • Environment causes species to change • Species with traits that help it adapt to its environment have more offspring and pass those traits to them • These species have greater “FITNESS” So what EVIDENCE do we have? • 1 - Homological Structures • Same embryonic structures that have been modified • 2 – Analogous Structures • Structures that look similar and have the same function, but they are not embryologically similar – they are not from a common ancestor • 3 – Vestigial Structures • Structures that are no longer useful, but were useful for our ancestors. • 4 – Similarities in Embryology • Early stages of different vertebrate are VERY SIMILAR! • 5 – Similarities in Macromolecules • Amino acid sequence – the more difference there is between the sequences the longer it has been since there was a common ancestor Co-evolution • The change of two or more species in close association with each other Convergent Evolution • When the environment selects for similar features, even though ancestors are very different Divergent Evolution • Two or more related species become more and more dissimilar, due to changing habitats. • Can eventually result in new species. Artificial Selection Adaptive Radiation • When many different species evolve from one species