* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Communications theory and Buyer Behaviour
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Business model wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Elaboration likelihood model wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Brand ambassador wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Brand awareness wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
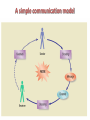
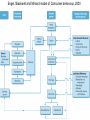
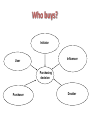
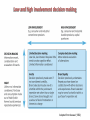
Communications theory and Buyer Behaviour Session 2 Objectives • To understand communications theory • To demonstrate alternative models in marketing communications • To understand key stages in the decision making process Communications Theory • Good communication = good business – helps an organization to thrive – focused and cost effective • Poor communications = bad business – can cost market share, jobs and survival – can damage reputation and image • The communications process – very complex – various theories and models What is communication? • …a transactional process by two or more parties whereby meaning is exchanged through the intentional symbols. Engel, 1994 •Transaction •Intentional •Symbolic A simple communication model The Marketing Communications Process model (P&B) Until 1954 Marlboro was positioned as cigarettes for women, old slogan: “To match your lips and finger-tips” Taken from Pickton and Broderick, 2005 Nivea creams put the life on pause Buyer Behaviour Key first step in developing a marketing strategy is understanding the target market and their buying behaviour • Who is the buyer? • Why do they buy? • How, when and where do they buy? Engel, Blackwell and Miniard model of Consumer behaviour, 2000 Who buys? Initiator Influencer User Purchasing decision Purchaser Decider Behavioural sequence model (BSM) Data inputs 1) WHAT (decision stage) Need arousal Information search Purchase and evaluation Usage 2) WHO (roles) 3) WHERE (location) 4) WHEN (time and timing) 5) HOW (description) Adapted from: Rossiter and Percy, 1997, Advertising communications and promotion management Advertising and promoting to individuals in role: • To initiators – to make them aware of the category need and propose our brand as a possible purchase candidate • To influencers – to communicate the reasons they should communicate our brand • To deciders – to persuade them to select our brand • To purchasers – to “lock in” the selection of our brand • To users – to ensure that they actually use and, perhaps more rapidly use our brand The intervening variables – Perception • means the ways stimuli, such as adverts, commercials, uniforms, are interpreted – Learning – Motivation • defined as the drive to satisfy a need • instinctive versus learned – Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (I954) • • • • • self-actualization esteem social safety physiological The intervening variables – Attitudes • affect buying behaviour • are learnt and tend to stick • can be changed, but not quickly – Group Influence • • • • formal, like committees informal, like friends primary secondary Types of buying situation – Extensive problem solving (EPS) • if the buyer has no previous product experience and the purchase is infrequent, expensive and/or risky – Limited problem solving (LPS) • if the buyer has some knowledge and experience of, and familiarity with, a particular product or service – Routinized response behaviour (RRB) • in the case of strong brand loyalty for a habitually purchased product, eg baked beans – High involvement v low involvement decisions High and Low involvement Decision Process High High involvement decision Spend lots of effort on expensive, personal or emotion-laden products e.g. cars Low involvement decision Acquiring products purchased regularly e.g. milk Low Low and high involvement decision making Adapted from Assael (1992) Hierarchy of Effects models Model Cognitive Affective Conative AIDA Attention Interest, desire Action AIDCA Attention Interest, desire, conviction Action ACCA (or DAGMAR) Awareness, comprehension Conviction Action Lavidge and Steiner Awareness, knowledge Liking, preference, conviction Purchase AIETA Awareness Interest, evaluation Trial, adoption The FCB grid Think Feel High involvement Low involvement Think Feel Do Feel Think Do cars, furniture, loans, appliances Jewellery, perfume, fashion Do Think Feel Do Feel Think Detergents, food, toilet paper Sweets, soft drinks, ice cream Adapted from: Pelsmacker, 2004 Communication strategy High involvement Awareness PR Advertising – broadcast then print – high information content – factual, rational – low frequency Attitude Personal selling - demonstrations - trial Sales Promotion - introductory prices - brochures Behaviour - product quality - price - accessibility Long run behaviour - product quality - corporate PR - guarantees, after sales service Communication strategy Low involvement Awareness PR advertising - Broadcast - Low information context - Emotion - High frequency Attitude - product satisfaction Trial Behaviour - sales promotion - advertising - POS - packaging Long run behaviour - advertising - sales promotion - product quality Reading • Pickton, D. and Broderick, A. (2005) Integrated Marketing Communications Prentice Hal, Chapters 3, 4 • De Pelsmacker, P. Geuens, M., and Van Den Bergh ,J. (2004) Marketing Communications, Prentice Hall, London, Chapter 3 • Fill, C. (2005) Marketing Communications Prentice Hall, London