* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Who is Muhammad?
Imamate (Twelver doctrine) wikipedia , lookup
History of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
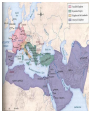
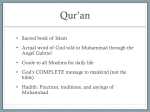
Who is Muhammad? EARLY LIFE • • • • • Born in A.D. 570 at Mecca, Arabia As an orphan, he was raised by his uncle Became a successful merchant and trader Married Khadijah and had kids He was not happy with the life he saw around him The Hills • • • • • • In 610 A.D. he went to the hills to pray There he saw an angel The angel told him to preach Islam Islam means “surrendering to the will of Allah” Allah is the Arabic word for “God” He was the last prophet to be sent by Allah. His Teachings • • • • • • He told people to destroy statues of the false gods Worship only Allah, the one true God All people were created equal Rich should share their goods Wealth was not as important as leading a good life God would reward the good and punish the evil Opposition to Islam • Family members and poor people began believing his message • Wealthy merchants and religious leaders did not like his message • They made his life difficult, beat and tortured followers Hijrah • In 622 A.D., Muhammad and his followers left Mecca • They moved north to Yathrib • This journey became known as the Hijrah • Hijrah means “breaking off relationships” • 622 A.D. became the first year of the Muslim calendar • Yathrib became known as Medina “the city of the prophet” • In 630 A.D., the leaders of Mecca agreed to give Muhammad control of the city • Islam began to spread TEACHINGS OF ISLAM Islam, Judaism, and Christianity have some beliefs in common • All believe in one God • God has all power • Created the universe • Determines right and wrong • Speaks to people through prophets • Holy scriptures THE QURAN • Muslims wrote down the messages that Muhammad said he received from Allah • These writings became the Quran • The Quran is the holy book of Islam (Bible) • Quran is very similar to the Bible • be honest, good, honor parents, give to the poor • no murder, lying, stealing • rules that apply to daily life • no pork, liquor, gambling • family, marriage, divorce, business practices The Five Pillars 1. Belief: Muslims must declare that there is no God but Allah and that Muhammad is his prophet. 2. Prayer: Muslims must pray five times a day, facing Makkah 3. Charity: Muslims must give to the poor 4. Fasting: Muslims must not eat from dawn to dusk during the sacred holiday of Ramadan 5. Pilgrimage: Muslims should visit Makkah once in their lifetime Sunna Customs based on Muhammad’s words and deeds. The Quran and Sunna covers all areas of daily life It applies to daily life, business, and government Quran: your journal Sunna: customs and laws that we live by after reading about your example in your journal Example: •“Today I saw a homeless person on the way to work and gave them my lunch” (Journal) • We should all give to the poor and needy (Book of Customs) THE SPREAD OF ISLAM Arabs spread Islam through teaching, conquest, and trade. Life After Muhammad • After Muhammad’s death, Abu Bakr became the first caliph (KAY-luf), the title that Muslims use for the highest leader of Islam. • Caliphs were not religious leaders, but political and military leaders. • The first four caliphs were called the Rightly Guided Caliphs because they tried to follow in Muhammad’s footsteps. • Each of them had a personal connection to Muhammad. THE RIGHTLY GUIDED CALIPHS Abu Bakr Relationship to Muhammad Umar Father-in-law Friend Uthman Ali Son-in-law First cousin (member and son-inof the law Umayyad Dynasty) Expansion In order to expand their empire, Muslim armies conquered Persia, Syria, Jerusalem, Egypt, and all of southwest Asia. After the First Four Caliphs •The Umayyads, a family of talented military leaders, took control of the empire and ruled from 661 to 750. • They chose the city of Damascus to be their capital, not Makkah. • Muslims began to spread into India and North Africa Why were the Arabs successful? •They also let conquered peoples practice their own religion • Called Christians and Jews “People of the Book” • Non-Muslims were not treated equal, had to pay a special tax