* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of a Plant Labeling Parts of a Flower:
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
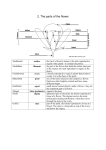
Parts of a Plant Name: ________________________ Read the definitions then label the diagram: flower - Flowers produce the seeds of a plant. leaf - Leaves convert energy from sunlight into food for the plant through a chemical process called photosynthesis. root - Roots take food and water from the soil, store energy, and provides support for the plant. Most roots grow underground. stem - The stem is the main support of the plant. Labeling Parts of a Flower: Important Information The Flower: The flower is the reproductive unit of some plants (angiosperms). Parts of the flower include petals, sepals, one or more carpels (the female reproductive organs), and stamens (the male reproductive organs). The Female Reproductive Organs: The pistil is the collective term for the carpel(s). Each carpel includes an ovary (where the ovules are produced; ovules are the female reproductive cells, the eggs), a style (a tube on top of the ovary), and a stigma (which receives the pollen during fertilization). The Male Reproductive Organs: Stamens are the male reproductive parts of flowers. A stamen consists of an anther (which produces pollen) and a filament. The pollen consists of the male reproductive cells; they fertilize ovules. Fertilization: Pollen must fertilize an ovule to produce a viable seed. This process is called pollination, and is often aided by animals like bees, which fly from flower to flower collecting sweet nectar. As they visit flowers, they spread pollen around, depositing it on some stigmas. After a male's pollen grains have landed on the stigma during fertilization, pollen tubes develop within the style, burrowing down to the ovary, where the sperm fertilizes an ovum (an egg cell), in the ovule. After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed in the ovary. Types of Flowers: Some flowers (called perfect flowers) have both male and female reproductive organs; some flowers (called imperfect flowers) have only male reproductive organs or only female reproductive organs. Some plants have both male and female flowers, while other have males on one plant and females on another Read the definitions then label the diagram: Definitions anther - the anther is the tip of a flower's stamen sepal - the sepals are small leaves located directly under a flower ( the male reproductive organs of the plant) - it they are the outermost part of a flower. contains the pollen. stem (also called the peduncle) - the stem supports the plant. filament - the filament is the part of the flower that holds the anther (and part of the stamen, stigma - the stigma is uppermost part of the pistil, the female the male reproductive organs of the plant). reproductive tissue of a flower. The stigma receives the male pollen grains during fertilization, when they travel through the style to the ovary - the ovary is a female reproductive organ ovary. in plants that produces ovules. It is at the base of the pistil. style - the style is part of the pistil, the female reproductive tissue of a flower. The style is a long tube on top of the ovary, and below the petal - a petal is one of the leafy structures that stigma. comprise a flower. Petals are often brightlycolored and have many different shapes. Plant Adaptations Mini-Project Learning Target: I am able to give examples and explain how characteristic animal behaviors of animals and specialized plant structures increase their odds of reproduction. Knowledge Probe: Plants have specialized in a number of different ways to encourage survival in different environments and successful reproduction. Flowering plants have different adaptations to enable their seeds to be dispersed as far away as possible. Powerpoint Presentation – View the presentation at http://slideplayer.com/slide/4026919/ and write important information below. ___________________________ _________________________ are the way something is built or made. ___________________________ _________________________ are the way something acts naturally or by instinct. Adaptations to get food, water, and nutrients: Behavioral – Structural – Adaptations for reproduction: Behavioral – Structural Adaptations for defense: Behavioral – Structural – Your Task: You and a partner will receive a type of plant. Your task is to research your plant and create a slideshow that answers the following questions or fulfills expected criteria: Where does your plant grow? (Which biome) What is one adaptation it has for gaining food, water, and nutrients? o Label it as structural or behavioral. Explain adaptations for reproduction and pollination o Include a description of the structural or behavioral adaptation and how it benefits the plant’s odds at successful reproduction Explain adaptations for seed dispersal o Include a description of the structural or behavioral adaptation and how it benefits the plant’s odds at successful reproduction Includes pictures or diagrams that aid in understanding Is free of spelling or grammatical errors. Share your slideshow with your teacher prior to the date it is due. Be prepared to share your slideshow with the class. Scoring: Category Correctly lists where the plant grows ( biome) Score _____/1 Lists one adaptation for gaining food, water, and nutrients _____/2 Correctly labeled as structural or behavioral _____/1 Explain adaptations for reproduction and pollination _____/5 Explain adaptations for seed dispersal _____/5 Includes pictures or diagrams that aid in understanding _____/3 Is free of spelling or grammatical errors _____/3 Total Comments: _____/20