* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - howesmath
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
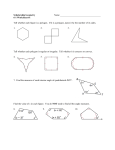
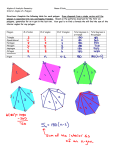
Name _______________________________________ Hour _________ Date _____________ Geometry: Chapter 3 Notes 3.1: Symmetry in Polygons Goal 1: Define a polygon. Goal 2: Define and use reflectional symmetry and rotational symmetry Goal 3: Define regular polygon and central angle of a regular polygon. Polygon: Sides of polygon: Vertices of polygon: Polygons Classified by number of sides Number of sides Name of Polygon Number of sides 3 9 4 10 5 11 6 12 7 13 8 n Equianglular polygon: Equilateral polygon: Regular polygon: Central angle: Reflectional Symmetry: Axis of symmetry: Name of Polygon Triangles Classified by the Number of Congruent Sides Equilateral triangle: Isosceles triangle: Scalene triangle: Rotational Symmetry: Central Angle of a Regular Polygon: Example 1: Find the measure of the central angle of each regular polygon below: a) decagon b) heptagon c) 15-gon 3.2: Properties of Quadrilaterals Goal 1: Define quadrilateral, parallelogram, rhombus, rectangle, square and trapezoid. Goal 2: Identify the properties of quadrilateral and their relationships. Define: 1) Quadrilateral: 2) Trapezoid: 3) Parallelogram: 4) Rhombus: 5) Square: 6) Rectangle: I) Properties of a Parallelogram: a) Opposite sides of a parallelogram are ______________________. b) Opposite angles of a parallelogram are ______________________. c) Diagonals of a parallelogram ____________________________. d) Consecutive angles of a parallelogram are ______________________. II) Properties of a Rhombus: a) A rhombus is a ____________________. b) The diagonals of a rhombus are ______________________. III) Properties of a Rectangle: a) A rectangle is a _____________________. b) The diagonals of a rectangle ________________________. IV) Properties of a Square: a) A square is a _______________________, __________________, and ___________________. b) The diagonals of a square _____________________ each other, are _____________________ and are _________________________ Example 1: In the parallelogram GRAM, find the indicated values. G R 120° 10 in. GR = ___________ MG = __________ mR = _________ M A 15 in. mA = _________ mM = _________ Example 2: In the rhombus ABCD, find the following: Given: AB = 25, AC = 20, mABC = 80° AD = _________ DC = _________ A mBAD = ________ E D B mDCB = ________ AE = _________ C EC = _________ mAEB = ________ 3.3: Parallel Lines and Transversals Goal 1: Define transversal, alternate interior angles, alternate exterior angles, corresponding angles, same-side interior angles. Goal 2: Make and use conjectures, postulates, and theorem about parallel lines. Define: a) Parallel Lines: b) Transversal: Example 1: Identify the following: a) 1 and 8 are _________________________________ b) 7 and 3 are _________________________________ c) 3 and 6 are _________________________________ d) 3 and 5 are _________________________________ e) 6 and 3 are _________________________________ f) 2 and 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 7 are _________________________________ Corresponding Angles Postulate: If two lines cut by a transversal are parallel, then ____________________________________ are _________________________. Alternate Interior Angle Theorem If two lines cut by a transversal are parallel, then ____________________________________ are _________________________. Alternate Exterior Angle Theorem If two lines cut by a transversal are parallel, then ____________________________________ are _________________________. Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem If two lines cut by a transversal are parallel, then ____________________________________ are _________________________. Example 2: Find the measure of each angle. a c 1 ║ 2 . b d 1 e 110° f g Example 3: Find the measure of each angle. 1 2 48° 2 1 ║ 2 . 3.4: Proving that Lines are Parallel Goal 1: Identify and use the converse of the corresponding angle postulate. Goal 2: prove that lines are parallel by postulates and theorems. I) Converse of Corresponding angles Theorem ______________________________________________________________________________________________ II) Converse of Alternate Interior Angle Theorem ______________________________________________________________________________________________ III) Converse of Alternate Exterior Angle Theorem ______________________________________________________________________________________________ IV) Converse of Same- Side Interior Angle Theorem ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Example 1: Indicate which lines are parallel and give a reason. A) If t 1 m 4 5 n 8 7 6 2 3 3.4: The Triangle Sum Theorem Goal 1: Identify and use the parallel postulate and triangle sum theorem. Parallel Postulate: Given a line and a point not on the line, there is ______________________________ Line that contains the given point and is _____________________ to the given line. Triangle Sum Theorem: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle equals _________________. Example 1: Find the measure of each missing angle. B A A) C 30° B) A 70° 30° C B M C) D) R 5x + 40 L Q 60° 60° S 3x 2x N Exterior Angle Theorem: The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the _____________________________________________. Example 2: Find the measure of the indicated angle. B A) 80° 63° A B D B B) 3x 2x A x B D 3.6: Angles in Polygons Goal 1: Develop and use formulas for the sums of the measures of interior and exterior angles of a polygon. Define: Convex Polygon: Concave polygon: Examples of Convex Polygons Polygon Examples of Concave Polygons Number of Sides Number of Triangles Sum of interior angles triangle quadrilateral pentagon hexagon n-gon Sum of the Interior Angles of a Polygon: The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is __________________________________ Regular Polygon Number of Sides Sum of interior angles Measure of one interior angle triangle quadrilateral pentagon hexagon n-gon Measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon with n sides is ________________________________________. Example 1: Use a straight edge to construct a convex polygon. Then use a protractor to measure each exterior angle. Sum of the Exterior Angles of a Polygon: The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon is __________________________________________. Example 2: find the indicated measures. Show work. F A) E E B) D 110° A D C B A C) C B 8x B D) C 6x – 4 3x + 3 7x 2x + 20 A 5x + 1 4x D 3.7 Midsegments of Triangles and Trapezoids Goal 1: Define midsegments of triangles and trapezoids. Goal 2: Develop and use formulas based on the properties of triangles and trapezoids. Midsegment of a Triangle: Midsegment of a Trapezoid: Activity 1: 1. Draw triangle ABC. Find the midpoints, M and N, of sides AB and AC . Then draw MN , the midsegment. 2. Measure MN and BC . What is the relationship between their lengths? 3. Use a protractor to find the measure of each angle. What do your measurements suggest about BC and MN ? Triangle Midsegment Conjecture: A midsegment of a triangle is _______________________ to a side of the triangle and has a measure equal to ________________ of that side. A Example 1: XY is a midsegment of triangle ABC. If BC = 15, What is the length of XY ? X Activity 2: 1. Draw trapezoid ABCD. Find the midpoints, M and N, of the nonparallel sides. Draw MN , the midsegment. 2. Measure the lengths of the bases AB and DC and the midsegment MN . What is the relationship between their lengths? (Hint: Find AB + DC). 3. Use a protractor to find the measure of each angle. What do your measurements suggest about the relationship between MN and the bases of the trapezoid? Y B C 15 Trapezoid Midsegment Conjecture: A midsegment of a trapezoid is ________________________ to the bases of the trapezoid and has a measure equal to ______________________________. Example 2: XY is the midsegment of trapezoid ABCD, if BC = 15 and AD = 26, find XY. B 15 C X Y A D 26 Example 3: Find the indicated value. Show work. A A) B) L 50 M Q X N Y 40 P B 60 C AB = ____________ QN = _______________ A C) X B 2x + 1 Y 6x – 10 x = ________ AB = _________ HK = __________ C O 3.8: Analyzing Polygons with Coordinates Goal 1: Develop and use theorems about equal slopes and slopes of perpendicular lines. Goal 2: Solve problems involving perpendicular and parallel lines. Define: Slope: Example 1: Find the slope of AB with endpoints A(5, -3) and B(2, 3). Example 2: Find the slope of MN with endpoints M(-1, 6) and N(-4, 0). Parallel Theorem: Two nonvertical lines are parallel if and only if ___________________________________ Vertical lines are ______________________________. Perpendicular Theorem: Two nonvertical lines are perpendicular if and only if the ______________________ of their slopes is _________________. Any vertical line is ____________________________ to a horizontal line. Example 3: Plot the following points for quadrilateral QUAD. Q(1, 4), U(7, 8), A(9, 5), D(3, 1). Find the slope of each side. What type of quadrilateral is QUAD? Slope QU = _________ Slope DA = __________ Slope QD = _________ Slope UA = __________ Midpoint Formula: Example 4: Find the midpoint of AB with endpoints A(-4, 2) and B(6, 4). Example 5: Plot the triangle ABC with A(2, 6), B(0, 0), and C(4, 0). a) find the midpoint of AB b) find the midpoint of c) find the slope of the midsegment. d) find the slope of e) Is the midsegment parallel to AC BC BC ?