* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
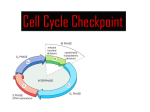
CHAPTER 18 CELL-CYCLE CONTROL AND CELL DEATH 2004 Garland Science Publishing Overview of the Cell Cycle 18-1 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Each word or phrase may be used more than once. The four phases of the cell cycle, in order, are G1, _______ S _________, ______ M _________, and __________________. A cell contains the most DNA after __________________ phase of the cell cycle. A cell is smallest in size after __________________ phase of the cell cycle. Growth occurs in __________________, __________________, and __________________ phases of the cell cycle. A cell does not enter mitosis until it has completed __________________ synthesis. DNA G1 G2 M nucleotide organelle protein S The Cell-Cycle Control System 18-7 Levels of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) activity change during the cell cycle as a result of (a) the Cdks phosphorylating each other. (b) the Cdks activating the cyclins. (c) the level of production of Cdks changing throughout the cell cycle. (d) the Cdks binding different cyclins to become active. (e) changing levels of cyclin phosphorylation. 18-9 Which of the following statements about the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) is FALSE? (a) It promotes degradation of proteins that regulate M phase. (b) It inhibits M-Cdk activity. (c) It is active throughout the cell cycle. (d) M-Cdk stimulates its activity. (e) It can attach multiple ubiquitin molecules to a single substrate. 18-14 When mammalian cells are irradiated, they stop dividing and arrest at a G1 checkpoint. Place the following events in the order in which they occur. A. Production of p21 B. DNA damage C. Inactivation of cyclin-Cdk complex D. Activation of p53 303 18-16 Cells in the G0 state (a) cannot reenter the cell cycle. (b) can remain in that state for a lifetime. (c) have entered from G1 or G2 checkpoints. (d) do not divide. (e) have duplicated their DNA. Programmed Cell Death (Apoptosis) 18-18 Programmed cell death occurs (a) rarely and selectively where survival factors are not present. (b) to eliminate unneeded cells. (c) only in unhealthy or abnormal cells. (d) only during embryonic development. (e) by means of an intracellular suicide program. 18-19 Apoptosis differs from necrosis in that necrosis (a) happens more frequently. (b) causes DNA to fragment. (c) causes cells to swell and burst while apoptotic cells shrink and condense. (d) uses a caspase cascade. (e) contributes to cancer when deregulated. Extracellular Control of Cell Numbers and Cell Size 18-22 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase should be used only once. The survival, __________________, and size of each cell in a multicellular organism are controlled by extracellular signals secreted by neighboring and distant cells. Many of these extracellular signals are ligands that bind to a cell-surface __________________, thereby triggering an intracellular __________________ pathway. One class of ligands, called __________________, stimulates cell division by releasing the molecular brakes that keep cells in the __________________ or __________________ phase of the cell cycle. Members of a second class of ligands are called __________________ because they stimulate biosynthesis that leads cells to increase in mass. The third class of stimulatory ligands, called __________________, inhibit the cell death program (also known as __________________) by regulating members of the __________________ family of proteins. In addition to the stimulatory factors discussed above, some natural extracellular factors like __________________ act negatively on other cells. anaphase differentiation 304 nourishment annihilation apoptosis arrestase Bcl-2 biosynthetic cascades caspase Cdk cyclin G0 G1 G2 growth factors interphase ligand M mitogens myostatin 305 nutrition phosphatases proliferation receptor S signaling survival factors transcription