* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matter and Chemical Change Quick Summary
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
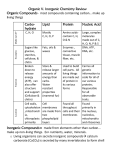
Matter and Chemical Change Quick Summary - - - - - - Matter has mass and occupies space. It is generally grouped into pure substances (elements and compounds) and mixtures (solutions, mechanical mixtures, colloids, suspensions, emulsions) All forms of matter have physical and chemical differences. Water, for example, is a pure compound that is distinguished by its clear color, 100 degrees Celsius boiling point and its violent reaction with sodium metal. Safety becomes an issue when working with chemicals. Proper handling and storage of chemical substances must follow WHMIS and product safety guidelines. An atom, the basis of all matter, is the smallest part of matter that can exist by itself. Three subatomic particles, electrons, protons and neutrons give an atom its properties. Protons and neutrons remain stationary within the nucleus of an atom while electrons revolve around the nucleus. o Example: The element aluminum has an atomic number of 13 and an atomic mass of 27. This means that the aluminum atom has 13 protons, 13 electrons and 14 neutrons. All naturally occurring and man-made elements are grouped together in the Periodic Table. Mendeleev determined the groupings according to similarities in properties and placed the elements in family and periodic groupings. Metals are placed on the left side, non-metals toward the right side, metalloids between the metals and non-metals and the inert gases appear on the extreme right. Electrons are the basis of all chemical reactions and are responsible for forming new compounds. Electrons are transferred or shared to make ionic and molecular compounds. o Example: The sodium atom releases an outer ring electron to the chlorine atom to make the ionic compound sodium chloride. Metal atoms combine with non-metal atoms t produce ionic compounds. Often 2 non-metallic atoms share electrons. o Example: Sulfur and oxygen share electrons to form the molecular compound sulfur dioxide. Chemical compounds react with each other to form new substances. The mass of the starting materials (reactants) is always equal to the material formed (products). This is referred to as the Law of Conservation of Mass. Chemical reactions are written in word and symbol equations: o Example: The reaction of hydrogen gas with oxygen gas to form water can be written as: Hydrogen gas + Oxygen gas Water 2H2 + O2 2H2O Some reactions occur very slowly, while others occur rapidly. The rate of reaction is affected by: surface area, concentration and temperature Some reactions release energy in the form of heat and light (exothermic) while other reactions require energy to get started (endothermic). All oxidation reactions require oxygen. Corrosion, respiration and combustion are examples of oxidation reactions. Environmental Chemistry Quick Summary -The environment is made up of biotic and abiotic factors that rely on chemicals to sustain life. Living things require both organic and inorganic compounds for survival. Living organisms are composed mainly of organic compounds, made from the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They require nutrients that contain traces of inorganic elements, magnesium, phosphorous and calcium. -Many of the nutrient materials come from the soil and are recycled back to the soil. Nitrogen gas is converted by lightning and nitrogen-fixing bacteria into useable nitrogen compounds. Nitrogen compounds are eventually converted back into free nitrogen by decomposers. Carbon and carbon compounds are also cycled. -The release of industrial chemical compounds into the air and the leaching of agricultural products into the soil may interfere with natural carbon and nitrogen cycles. The combustion of fossil fuels is the leading cause of acid rain. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine with water vapor in the air to produce rain that is acidic in nature. Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticide by farmers also has an effect on the normal balance of living things. Fertilizers may cause an overgrowth of plants while pesticides end up destroying helpful plants and animals. -Chemical substances are classified as acids, bases or neutral substances. Acids have a high hydrogen ion (H+) concentration while bases have a high hydroxyl (OH-) concentration. On a pH scale, acids fall in range from 0 to 6, while bases are in range 8 to 14. A substance with pH of 7 is neutral. - Acids are neutralized when mixed with a base. The neutralization process produces a salt and water. The neutralization reaction can be represented as a word equation. - Acid + Base Salt + Water -All living things require nutrients for growth and reproduction. Elements such as nitrogen, phosphorous, magnesium and calcium are required in large quantities and referred to as macronutrients. Micronutrients, such as selenium are needed in small or trace amounts. -Nutrients are absorbed by plants passively or actively. During diffusion, nutrients particles move into the plant’s cells from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. During osmosis, particles pass from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. No energy is required for diffusion and osmosis. In active transport, plants use energy to move nutrient molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. -Animals require organic compounds. Animals require carbohydrates for energy, lipids for energy, proteins for repairing and nucleic acids for controlling heredity and cell activities. -Monitoring the chemical dispersion in water and air is important. Water is monitored for dissolved oxygen, acidity, heavy metals, pesticides, salts and excessive plant nutrients. The chemical concentration must fall within government guidelines in parts per million. A concentration of 4ppm means 4 parts of chemical in 1,000,000 parts of chemical water solution. -Toxins or poisons are measured with a scale called LD50. LD stands for “lethal dose” and 50 stands for 50%. LD50 refers to the amount of substance that will cause 50% of a test sample of organisms to die if given a specified dose. - Air is monitored for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, carbon dioxide and ground level ozone emissions. Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, released mainly from vehicles are the leading causes of acid rain. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas; it is the leading cause of global warming. The use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) is depleting the upper atmosphere ozone layer. - Air and water quality monitoring is carried out using chemical analysis and biological indicators. Chemical analysis includes the use of chemical reagents to test for pH, iron, chlorine, phosphorous and heavy metal. Biological testing uses invertebrate organisms. Organisms such as caddisfly larva require high oxygen concentrations. Leeches need very little oxygen. The higher the oxygen concentration the greater the biodiversity. - Potentially harmful chemicals are dispersed in the air by wind and air currents. Chemicals are leached into soil by water and transported with the ground water. Certain bacteria remove chlorine from certain chemicals. Certain plants use their root systems to breakdown chemical pollutants into useable forms. This method is called phytoremediation. When sunlight decomposes plastic material the process is called photolysis. - If chemicals are left to build up, their accumulation leads to biomagnifications. Mercury, for example, builds up in food chain to a point where the animal at the top of the chain accumulates the highest concentration. - It is important to store, dispose, and transport chemical wastes properly. Proper transportation and collection of hazardous chemical must be closely monitored. It is the responsibility of every individual to properly handle, store and dispose of chemicals. Space Summary Notes -Aristotle studied the sun and its planets and proposed the geocentric model of the solar system. He said that the Earth was the center and all other planets revolved around it. -In the 1500’s Copernicus concluded that the sun was the center of the solar system. His heliocentric model is what we sue today. -The telescope used for space study today includes: -Optical reflecting: uses mirrors to reflect light - Optical refracting: uses lenses to bend light - Radio: uses radio wave frequencies to detect distant objects - Unlike optical telescopes, the radio telescope is not affected by weather and can be used during day and night. - Telescopes are often arranged in groups called arrays to produce high-resolution images. This technique is called interferometry. -The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990 as an orbiting telescope has sent back thousands of images about comets, Jupiter’s moons, Saturn’s rings and other objects in our solar system. -Scientists us the astronomical unit (AU) to measure distances within our solar system One AU is the distance from Earth to the sun. Pluto is 39.5 AU away. Greater distances, such as the distance to stars, are measured in light years. The nearest star is approximately 4.2 light years away. -Found within space are stars, asteroids, comets, galaxies and planets -Stars begin as a nebula, and then go through stages ranging from red giants, white dwarfs, supernovas and end as black holes or neutron stars. - Asteroids are found within a belt that lies between Mars and Jupiter. Occasionally small fragments leave the belt as meteoroids. Meteoroids enter Earth’s atmosphere as meteors or “shooting stars”. Meteors that fall on Earth before burning up are called meteorites. -Comets are balls of dust and ice that travel in an elliptical pattern around the sun. The heat from the sun causes some of the ice to vaporize producing a huge tail. The most frequent visible comet is Halley’s. It appears every 76 years. - A galaxy is groupings of billions of stars. We live in the galaxy called the “Milky Way” It is one of millions of galaxies that exist today. - A planet is defined as a celestial body that revolves around the sun. -Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are solid in structure and are referred to as terrestrial planets. Because Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are gaseous in nature they are called Jovian planets. Venus has the highest surface temperature of all planets. Jupiter has the most satellites or moons of a planet. -The sun produces heat and light through the process of fission. The fission reaction releases a tremendous quantity of energy when hydrogen is converted into helium. Some of this released energy appears as solar flare. -Astronomers use different techniques to gather information about objects in space. -The position of a star can be determined using an astrolabe. The astrolabe provides information on the azimuth (compass direction) and the altitude (height readings) - Triangulation and parallax are used to determine the distance of objects in space. Triangulation uses an imaginary triangle between the observer and an object whose distance is being estimated. - Parallax is an apparent shift in position of an object against a certain background when viewed from two different positions. Parallax is a form of triangulation. -The technique of spectroscopy uses the light spectrum to determine the composition of space objects and to determine whether they are moving toward or away from Earth. Most stars produce spectra lines similar to these of the elements hydrogen and helium. A shift to the red end of the spectrum indicates the star is moving away from the observer. A shift to the blue end means the star is moving toward the observer. - Artificial satellites and probes play an important role in space exploration. Satellites help us communicate, forecast weather and find locations in space. -A GPS (Global Positioning System) uses a series of satellites orbiting in a geosynchronous pattern to pinpoint a location. Signals from a minimum of three satellites are picked up and transferred to a computer. A digital display of the exact position is calculated. -A satellite in a geosynchronous orbit is always above the same position on Earth because it is travelling at the same speed as Earth. -Probes are remote controlled devices that carry out remote sensing objects in space. The “Opportunity” and “Spirit” probes landed on Mars in 2004 and have relayed important information about the Red Planet. -Rockets are the major transporters of satellites and probes into space. A rocket gets its energy from the chemical fuel it sues. Experimentation today is being done with ionic drive rockets and solar sails as alternative forms of propulsion devices. -The International Space Station is a joint effort of 16 nations working together to explore the possibilities of living in space.