* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pyramid Practice
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
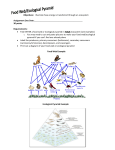
Name___________________________ Date_____________ Pyramid Practice ANSWER QUESTIONS ON NOTEBOOK PAPER!!! Label each step of the pyramid with the appropriate trophic level. Assume the sun transmits 5,000,000 Kcal of energy to this area. Calculate the amount of energy that is passed to the next trophic level if producers are 1% efficient, herbivores (primary consumers) are 15% efficient and all other consumers are 10%. Questions: 1. Why are there more herbivores in an ecosystem then carnivores? (usually) 2. Why could an ecosystem support an omnivore more easily than a carnivore? 3. What units would a pyramid of biomass use? __________________ 4. Explain what happens to the energy “lost” at each trophic level. What process is involved that explains this “loss”? 5. What types of pyramids (from which ecosystems) would not be “pyramidal” in shape? 6. Explain why humans should eat “low on the food chain” if they are an environmentally concerned person. Include both ecological footprints/resource use as well as energy flow. Graph the data from the two examples below 1. Create a pyramid of energy 2. Create a pyramid of biomass FOOD CHAINS, FOOD WEBS AND ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS 1. Give three examples of food chains that exist in nature. 2. In an ecological pyramid, what happens to energy, biomass and # of species as you move up? Why? 3. What is biomass? 4. In an ecosystem, can there be more carnivores than herbivores? Explain why or why not? 5. What is the 10% rule? What is its significance? Why is energy lost? 6. Brainstorm to create a list of 4 human activities that interfere with ecosystems, food chains and food webs. For each explain how it happens, why we do it, and mention short and long-term effects. 7. Label the ecological pyramid below with the following words: producers, tertiary consumer, secondary consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, primary consumer, decomposers, hawk, grass, chicken, grasshopper. Also label and explain what happens to energy, biomass and number of organism. 8. Discuss what trophic level humans occupy on an ecological pyramid, and explain what happens to contaminants and environmental pollution (such as mercury) as you move down and up the ecological pyramid (what is this called?). 9. Look at the food web below. Who does the Bald Eagle depend on for survival? 10. Using the same food web, which organism may not increase in population if all the bivalves were removed from this ecosystem? 11. Using the same food web, which organisms would be affected if the phytoplankton were to overproduce? 12. Using the same food web, who eats the small plankivorous fish? 13. Show one food chain within this food web.