* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AddPlannerCA2
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical model wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
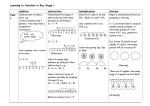
Transition: Counting from One on Materials to by Imaging Achievement Mathematical Processes: Level One Problem Solving: Objectives Use equipment appropriately when exploring mathematical ideas. Logic and Reasoning: Classify objects. Communicating Mathematical Ideas: Devise and follow a set of instructions to carry out a mathematical activity. Record and talk about the results of mathematical exploration. Domain:Addition and Subtraction E Number and Algebra: Level One Make up, tell, and record number stories, up to 9, about given objects and sequence pictures. Form a set of up to 20 objects. Read and write any two-digit whole number. Rote count to at least 50. Make sensible estimates and check the reasonableness of answers. Model and explain addition calculations with a sum of up to 20. Using up to 20 objects, model and explain subtraction calculations. Problem progression References Knowledge being developed Resources Solve one step result addition (joining) problems, with answers up to 20, by counting all the objects in their head (by imaging).. 4 + 3 = , 5 + 2 = , 6 + 1 = , 8 + 4 = , 2 + 6 = , 3 + 7 = , 8 + 5 = , 16 + 2 = . Teaching Addition, Subtraction, and Place Value (Book 5) Using one hand (12) Using tens frames (13) Both hands (13) Imaging with tens frames (14) Imaging many hands (15) Crossing the five barrier (16) Identify numbers in the range 0–20, at least. BSM 2-1-5, 6-1-7, 6-1-9, 6-3-2, 6-33, 6-3-4, 6-3-5, 6-3-6, 6-3-7, 6-3-22, 6-3-43, 6-3-44, 6-3-45, 6-3-46, 6-3-49, 6-3-50, 6-3-81, 6-3-83, 7-1-1, 7-1-2, 7-1-41, 7-1-42, 7-1-43, 7-3-4, 7-3-9, 7-3-45, 7-4-46, 8-1-4, 8-1-43, 8-1-44, 8-1-53, 11-1-6, 11-1-47, 11-1-82 © 2006 Crown Copyright Numeracy Development Projects AC EA AA AM Strategies being developed BSM 6-1-9, 6-1-46, 6-1-47, 6-1-81, 6-1-82, 6-3-7, 6-3-8, 6-3-49, 6-3-82, 6-3-84, 7-16, 7-1-52, 7-1-53, 7-1-84, 7-1-85, 7-3-4, 7-3-7, 7-3-50, 7-3-51, 7-352, 7-3-82, 8-1-5, 8-1-9, 8-1-51, 8-1-52, 8-1-83, 8-1-84, 8-3-7, 8-3-9, 8-3-50, 8-3-51, 10-1-3, 10-1-42, 10-1-82, 11-1-10, 11-111, 11-1-54, 11-1-55, 11-1-56, 11-1-85 CA AP 1 Strategies being developed Problem progression References Knowledge being developed Solve one-step subtraction (take away) problems, with the starting numbers up to 20, by counting all the objects in their head (by imaging).. 5 - 3 = , 6 - 2 = , 8 - 4 = , 10 - 3 = , 12 - 5 = , 15 - 3 = , 18 - 4 = , 13 - 4 = . Teaching Addition, Subtraction, and Place Value (Book 5) Using one hand (12) Using tens frames (13) Both hands (13) Imaging with tens frames (14) What’s hidden (15) Imaging many hands (15) Crossing the five barrier (16) Say the forwards and backwards number word sequences in the range 0–20, at least. Resources E CA AC EA AA BSM 8-1-10, 8-1-53, 8-1-85, 8-3-8, 8-3-9, 9-1-14, 9-1-15, 9-1-16, 9-1-55, 9-1-56, 10-1-2, 10-1-41, 10-1-81 Solve addition and subtraction problems with decade numbers by counting tens in their heads. 2 + 2 = so 20 + 20 = , 5 + 5 = so 50 + 50 = , 3 + 4 = so 30 + 40 = , 5 – 3 = so 50 – 30 = , 10 – 5 = so 100 – 50 = , 8 – 4 = so 80 – 40 = Teaching Addition, Subtraction, and Place Value (Book 5) Ten sweets per packet (17) AM Order numbers in the range 0–20, at least. BSM 7-1-4, 7-1-5, 7-1-46, 7-1-48, 7-1-81, 7-1-82, 7-3-3, 7-3-44, 8-1-6, 8-3-3, 8-3-4, 8-3-5, 8-344, 8-3-45, 8-3-46 Instantly recognise patterns to ten (doubles and five based), including finger and tens frame patterns. BSM 7-1-49, 7-1-50, 7-1-51, 7-1-83, 8-1-5, 8-1-7, 8-1-46, 8-1-47, 8-1-48, 8-1-49, 8-1-82, 9-1-6, 9-1-12, 9-1-13, 9-1-43, 9-1-44, 9-1-50, 9-1-51, 9-1-52, 9-1-53, 9-1-54, 9-1-85, 9-1-86 Recall facts within five and doubles to ten. © 2006 Crown Copyright Numeracy Development Projects 2 AP