* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CARDIAC ARREST
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
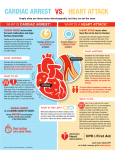
CARDIAC ARREST 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. RESUSCITATION-Cardiac arrest is the sudden failure of the heart to supply adequate blood The most common causes of cardiac arrest are Myocardial infarction Anesthesia over dosage Electrolyte imbalance Drowning Electrocution shock THE OA MUST KNOW 1. 2. 3. 4. To diagnose cardiac arrest Summon the emergency team Initiate resuscitation effectively Where to find the necessary equipment SIGNS OF CARDIAC ARREST UNCONSCIOUS PATIENT Pulse rate high Low or unrecordable blood pressure Absent respiratory movements Cyanosis Cessation of heart beat Dilated pupils MANAGEMENT Upon discovering a collapsed patient The OA must act quickly and calmly Must get the resuscitation trolley,ECG machine and defibrillator The OA should diagnose cardiac arrest quickly ABC-airway ,breathing and circulation Airway is secured by the combined maneuver of head tilt and chin lift Mouth to mouth breathing must be commenced by the OA if the patient is not breathing Carotid pulse must be palpated for checking circulation Pulse must be palpated for at least 5secs to find if circulation has stopped The ribs are depressed forcefully and rhythmically by about 3-5cm , 60 to 80 times per minute in an adult The compression to ventilation ratio is 15:2 If the pressure is applied on the xiphoid process it may cause internal injury ON ARRIVAL OF MEDICAL HELP The OA must be familiar with the location and use of equipment and drugs on the emergency trolley If the patient is in ventricular fibrillation it can be stabilized by electrical defibrillation The doctor applies electrode jelly to the paddles to prevent skin burns The current will pass across the chest to the cardiac muscle The doctor has to give administer IV adrenaline 1mg followed by IV atropine 2mg POST RESUSCITATION CARE 1. 2. The patient’s airway, breathing and circulation and blood pressure are checked Notes about emergency drugs Adrenaline-this increases the heart rate and increases the force of cardiac contraction. It is supplied in 1ml ampules of 1:10000 Isoprenaline – This primarily increases heart rate but also increases the force of contraction.It is supplied in 2ml ampules of 50mg per ml Atropine- increases heart rate. It is supplied in 1ml ampules of 600mg per ml Calcium chloride- Temporarily increases the force of cardiac contraction and reduces the effect of dangerously high blood potassium .10ml ampules of 10% calcium chloride Lignocaine- Local anesthetic that acts on the heart to reduce electrical excitability and is supplied as 10ml ampules of 10mg per ml Aminophylline- This causes bronchodiation and therefore relieves bronchospasm Hydrocortisone- this is a steroid used in anaphylactic shock.It suppresses tissue edema and is supplied in 1ml ampules of 100mg Naloxone- this reverses the depressant and analgesic effect of opiate narcotics. 1ml ampules of 400mg VERY IMPORTANT ALWAYS READ THE LABEL AND MAKE SURE IT IS THE DRUG THAT HAS BEEN ASKED