* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Subclassification
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
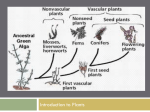
Plant Subclassification Plants probably evolved from charophycean algae, sharing rosette cellulose-making complexes that make cell walls, peroxisomes that limit photorespiration food loss, flagellated sperm cells, and cell division details; Plant derived features include apical meristem, alternation of generations, protected embryos, sporopollenin spore and pollen walls, and gametangia which make gametes. Division Class Groups sphagnum, Polytrichium (small, to 2", erect plants) Mosses Bryophytes (no vascular tissue) Liverworts (all bryophytes lack true roots, stems, leaves, lignin) Tracheophytes (seedless vascular plants) Pterophyta (seedless vascular plants) Tracheophytes (seed plants) sporophyte dominant and gametophyte reduced to a few cells Gymnosperms (naked-seed plants) club mosses, spike mosses, quillworts, Isoetes short plants on the forest floor with short needle-like leaves; produce strobili which release spores that grow gametophytes whisk ferns (Psilotum) small branching stems with tiny/no leaves and no true roots horsetails (Equisetum) short needle-like leaves on rigid stems to 1 meter high ferns the familiar fern; flat leaves that grow from underground stems (rhizomes) in most species to one meter high Cycadophyta cycads thick palm-like pinnate leaves that grow from a thick stem Ginkgophyta Ginkgo flat leaves on large upright stems; grows as a tree in many yards Gnetophyta Welwitschia (desert plant with long strap-like leaves); Gnetum (tropical shrubs, lianas, and small trees); Ephedra (small plant that grows as stems only) have vessels similar to angiosperms but molecular data indicates close gymnosperm relationship (sporophyte is dominant gametophyte is temporary) (sporophyte is dominant gametophyte is temporary) Amborella sporophyte dominant and gametophyte reduced to a few cells Marchantia (plant consists of flat leafgametophyte is dominant; have like structures that grow on the small umbrella-like sporophytes ground) gametophyte is dominant; have spike-like sporophytes Coniferophyta Tracheophytes (seed plants) features gametophyte is dominant, sporophyte consists of small brown stalks and caps only Anthoceros (plant consists of flat leaf-like structures that grow on the ground) Hornworts Lycophyta Examples mostly needle leaves coated in wax; some grow to giant size and extreme age; many are used as wood for lumber Amborella trichopoda; small are the oldest lineage of shrubs/trees that grow only in New angiosperms and lack vessels Caledonia (special xylem cells) Sequoia, Redwood, Pine, Spruce, Cedar, Yew, Fir, Hemlock, Juniper, Cypress, etc. (evergreens) Magnoliids Magnolias; small trees that produce large and showy flowers flower structure indicates they are an old lineage of angiosperms Monocots iris, grasses, orchids, lilies, palms, (very few trees); about 25% of all angiosperms flower parts in 3's, parallelveined leaves; single cotyledon embryos, fibrous root systems, and scattered stem vascular bundles Eudicots most broad-leaf trees (that are not coniferous or ginkgo); most broadleaf shrubs and herbs; about 67% of all angiosperm species branch veined leaves; flower parts in 4's or 5's; double cotyledon embryos, fibrous or tap root systems; vascular bundles in rings Angiosperms (flowering plants)