* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drugs used for Congestive Heart Failure
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
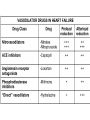
Drugs used for Congestive Heart Failure Drug List Inotropic Drugs Digoxin Dobutamine Dopamine Milrinone Drugs affecting the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Captopril Enalaprilat Losartan Spironolactone Diuretics Furosemide Thiazides More drugs have been mentioned in the following slides Beta-blockers Metoprolol Carvedilol Vasodilators Nitrates Hydralazine Nesiritide • Vasodilators: Nitrates that act to directly relax vascular muscle tone and cause decrease in blood pressure with pooling of blood in the veins. The preload and afterload will be decreased • ACE inhibitors: are agents that block the conversion of angiotensin 1 to angiotensin 2. These drugs causes vasodilatation and decreased blood volume. The afterload will be decreased. • Diuretics: are employed to decrease the blood volume, which decreased the venous return and blood pressure. The results are decreased preload and decreased afterload. • Beta agonists: will stimulate the beta receptors in the heart, increasing the myocardial contraction – called positive inotropic effect • Cardio-tonic drugs: These agents effect the intracellular Ca++ levels in the heart muscle cells leading to increased contractility. The result is increased cardiac output, increased renal blood flow, increased perfusion and increased urine formation. Cardiotonic drugs are: • Cardiac Glycosides • Phosphodiesterase inhibitors Cardiac glycosides - Digoxin • They increase the level of calcium inside the cardiac myocyte by inhibiting the Na+/K+ pump. • More Ca++ accumulates in the cytoplasm during depolarization and the myocardium will contract forcefully. This is known as positive inotropic effect • Increased cardiac output • Increased blood flow to the body organs like the kidney and liver Effects of Cardiac Glycosides • Negative chronotropic effect: The heart rate is slowed due to decreased rate of cellular repolarization • Decreased conduction velocity through AV node Contraindications and Precautions • • • • • • • Allergy Ventricular dysrhythmias Heart block Sick sinus syndrome Acute myocardial infarction Aortic stenosis Electrolyte imbalances: Hypokalemia, Hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia • Renal failure may cause accumulation of drug Adverse effects of digoxin • Headache, weakness, seizures and drowsiness • Arrhythmias • Signs of digitalis toxicity: anorexia, nausea and vomiting, visual changes – yellow halo around objects, palpitations or slow heart rate