* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Med Drugs 8 Keynote
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
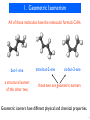
Discovery and development of tubulin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
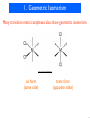
DNA-encoded chemical library wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
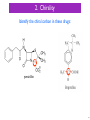
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
http://www.compadre.org/Informal/index.cfm?Issue=122 Medicines and Drugs 8 Drug Action 1 Assessment Statements D.8.1 Describe the importance of geometrical isomerism in drug action. D.8.2 Discuss the importance of chirality in drug action. D.8.3 Explain the importance of the beta-lactam ring action of penicillin. D.8.4 Explain the increased potency of diamorphine (heroin) compared to morphine. 2 Fitting Molecules into Other Molecules Here are FOUR important concepts related to how the SHAPE of a drug (or part of a drug) that will affect the ACTION of the drug: 1. geometric isomerism 2. chirality ! 3. polarity 4. ring strain 3 Review - Isomers Isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. structural isomers stereo isomers atoms/groups are in different positions in the molecule bonding pattern is the same, BUT the position in SPACE is different e.g. propan-1-ol vs propan-2-ol geometric isomers e.g. but-1-ene vs but-2-ene optical isomers (cis trans isomers) (need chiral carbons) 4 1. Geometric Isomerism All of these molecules have the molecular formula C4H8. ! ! but-1-ene a structural isomer of the other two ! trans-but-2-ene cis-but-2-ene these two are geometric isomers Geometric isomers have different physical and chemical properties. 5 1. Geometric Isomerism Many transition metal complexes also show geometric isomerism. http://cnx.org/content/m34480/latest/ cis form (same side) trans form (opposite sides) 6 1. Geometric Isomerism and Cisplatin Cisplatin is an anti-cancer drug used to treat ovarian and testicular cancers. ! Cisplatin is a geometric isomer of a complex ion of platinum diaminedichloroplatinum (II). The molecular formula of this compound is Pt(NH3)2(Cl)2 http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cisplatin-3D-balls.png 7 1. Geometric Isomerism and Cisplatin There are two geometric isomers of this compound: The shape of these molecules is square planar. Both drugs are neutral overall and can pass through cell membranes. 8 1. Geometric Isomerism and Cisplatin Only the cis isomer has a therapeutic effect. Once inside the cell, the Cl- ions are exchanged for water molecules. H2O + In the nucleus, the cis forms bonds with two Guanosine molecules on DNA. This blocks the replication of DNA and the virus dies. 9 1. Geometric Isomerism and Cisplatin The trans form is inactive. NH3 Cl Pt Cl NH3 The trans form does not have the correct orientation to bind to two adjacent Guanosine molecules on DNA. 10 2. Chirality Recall: Chiral molecules are non superimposable mirror images of each other. The two “mirror image” molecules are called enantiomers. They occur whenever there are four different groups bonded to a carbon atom (the “chiral carbon atom”). 11 2. Chirality Identify the chiral carbon in these drugs: 12 2. Chirality Enantiomers have different chemical properties ONLY when they interact with other optically active materials. Biological molecules are usually optically active. Many drugs are optically active (i.e. are optical isomers with a chiral carbon). The two enantiomers have different chemical properties. Only ONE enantiomer is therapeutic. 13 2. Chirality Taxol is an anti-cancer drug used to treat ovarian cancer. Plants that produce useful chiral drugs naturally will only produce ONE enantiomer. http://www.elucidationimages.com/Portfollio/Portfollio%20Pages/yew.html Consider: How does the natural production of a medically useful substance in nature compare with the synthetic production of the same compound in the laboratory? 14 2. Chirality When drugs are synthesized in the laboratory, BOTH enantiomers are produced. This gives a RACEMIC MIXTURE, where there are equimolar amounts of both enantiomers. RECALL: Different enantiomers of chiral compounds have different chemical properties. 15 2. Chirality Thalidomide anti-nausea agent limb malformations The synthetic production of thalidomide yields BOTH enantiomers. Why is this a problem? What are the implications for the drug development process? 16 2. Chirality Ibuprofen Identify the chiral carbon. What are the implications? 17 3. Ring Strain 18 3. Ring Strain Penicillin Where is the beta lactam ring? What is the hybridization of each atom in the beta lactam ring and the expected bond angle? sp3 = 109.5º sp2 = 120º What are the actual bond angles? 90º This puts a strain on the bonds, and makes them weaker. 19 3. Ring Strain Penicillin The amide group is very reactive due to ring strain. The amide group reacts with (and deactivates) the bacterial enzyme transpeptidase that is needed to make bacterial cell walls. This reaction is not reversible and bacterial cell growth stops. 20 4. Polarity Drug polarity is important in terms of: 1. ability to be transported through the blood and body tissues • polar molecules are transported more easily 2. ability to pass through the blood brain barrier (for CNS active drugs) • nonpolar molecules pass through the blood brain barrier 21 4. Polarity The ester groups make diamorphine less polar so it penetrates the blood-brain barrier more effectively and rapidly. As a result, diamorphine is much more potent. 22